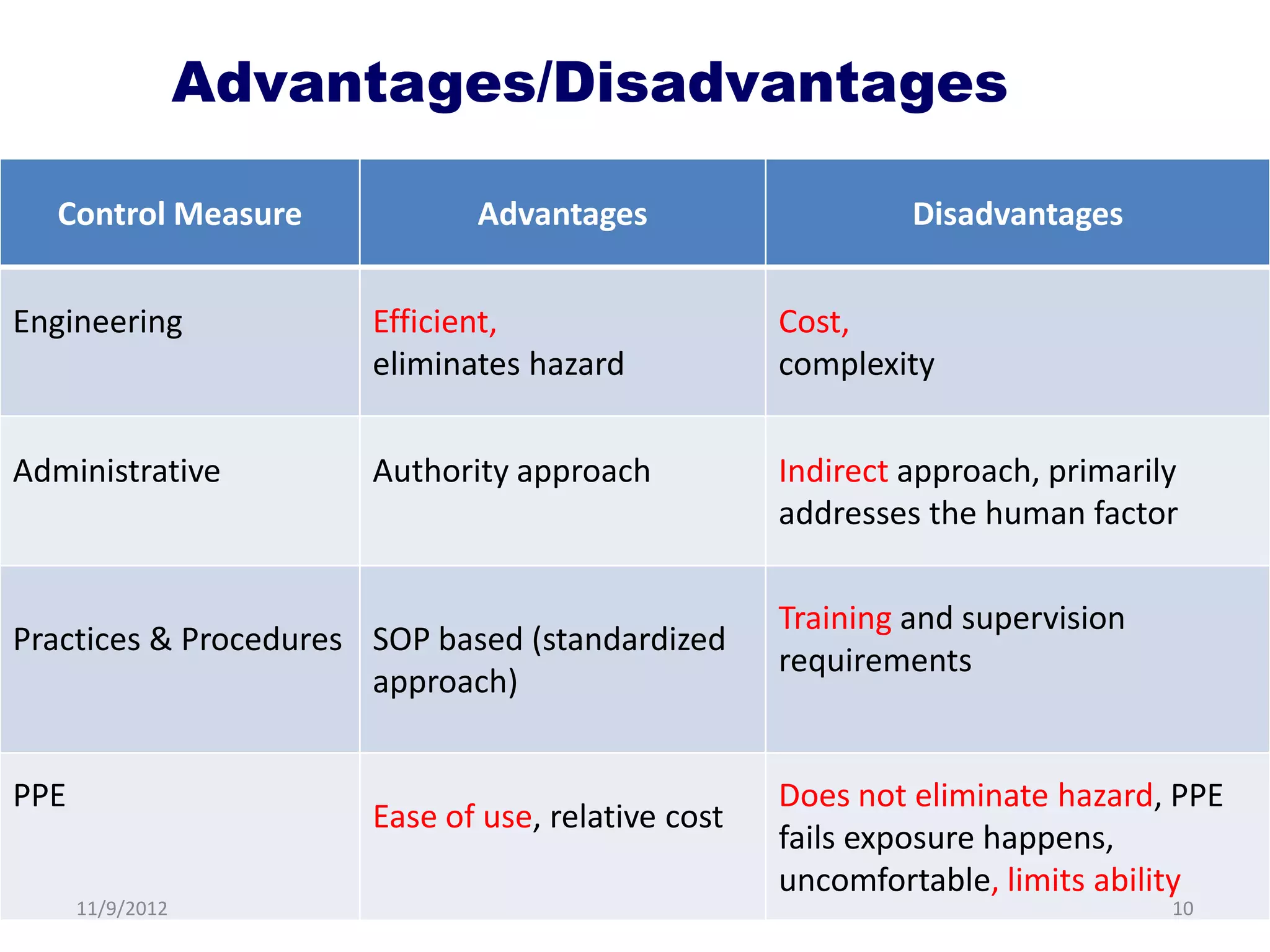
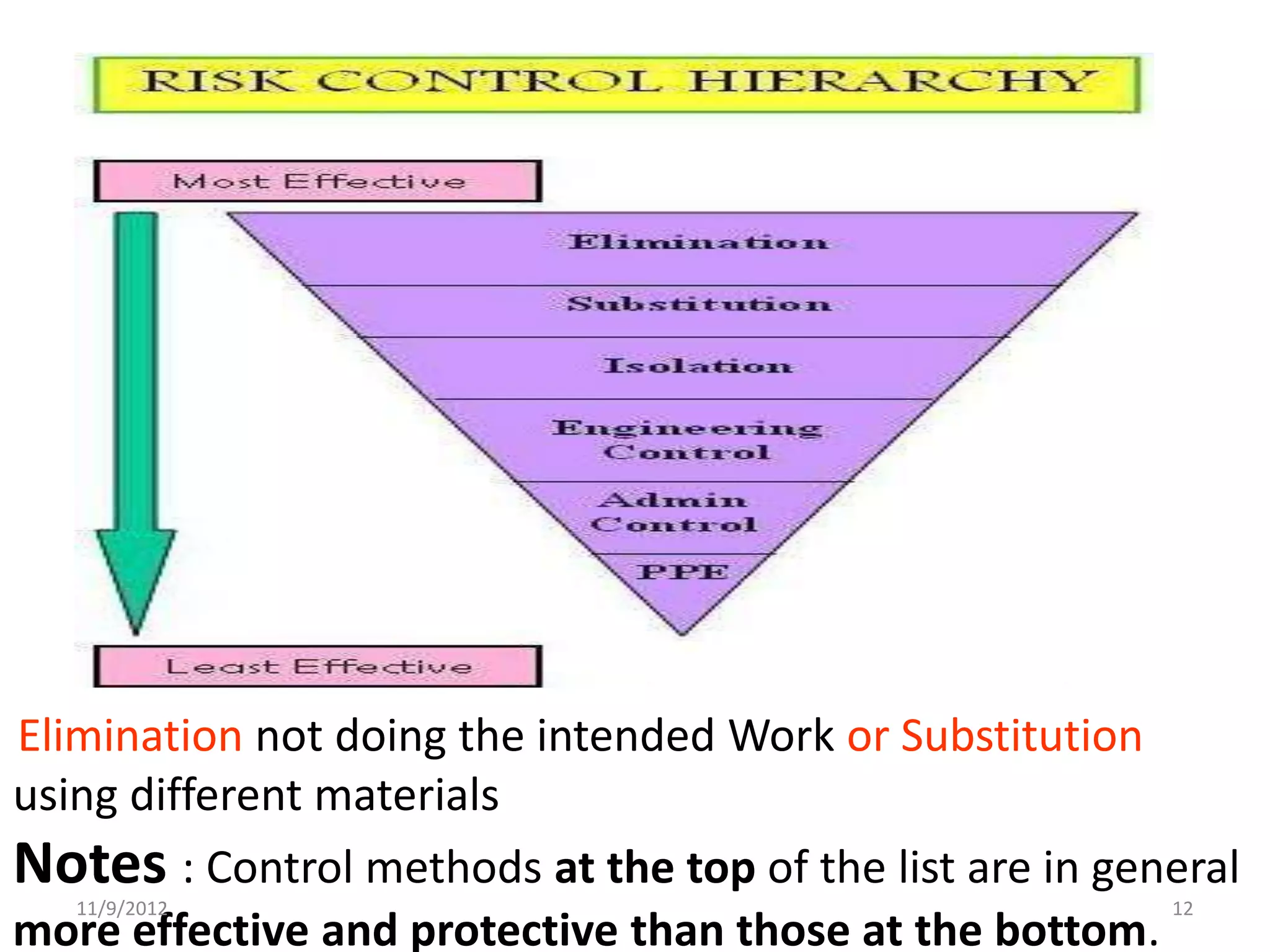
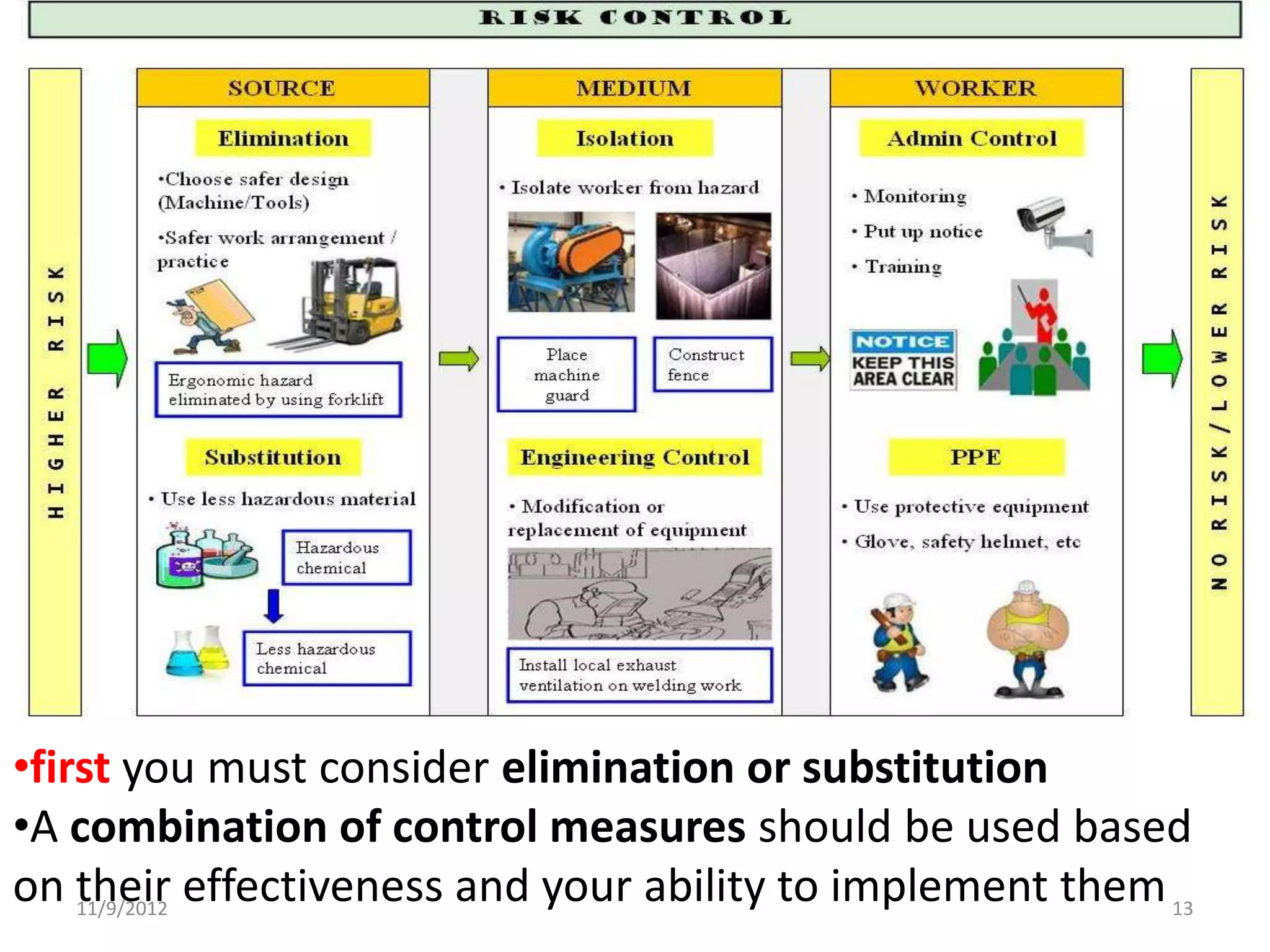
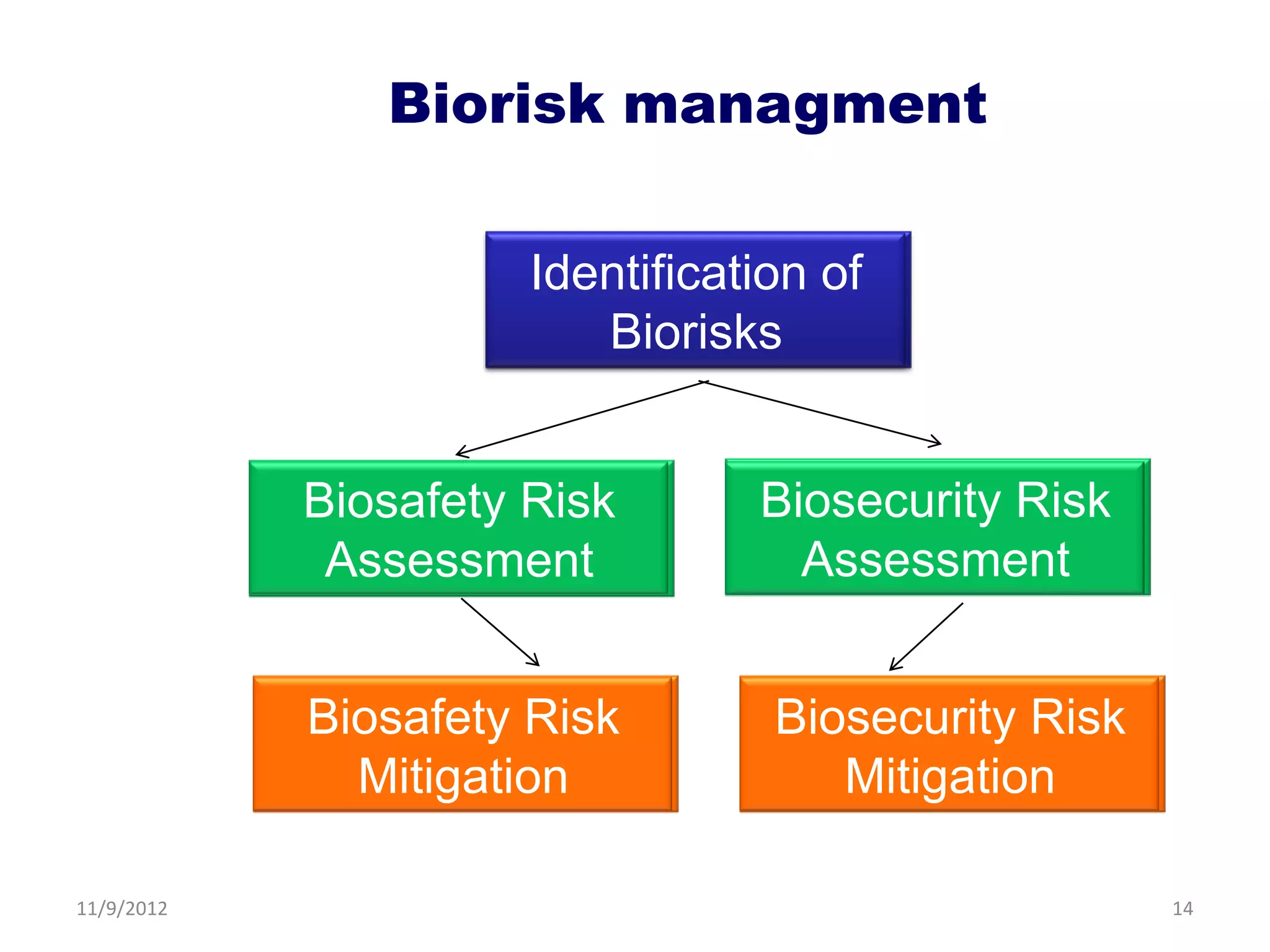
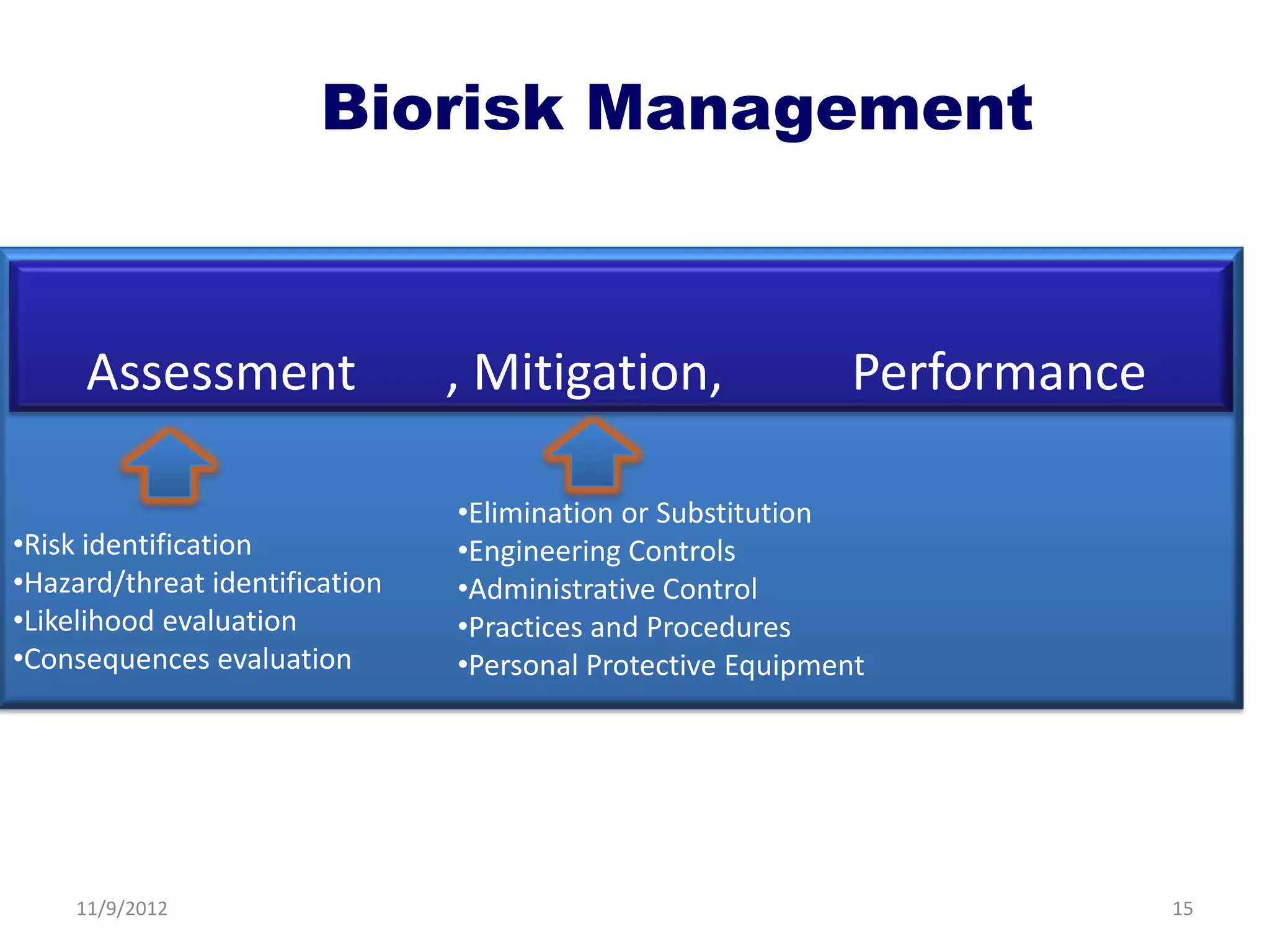
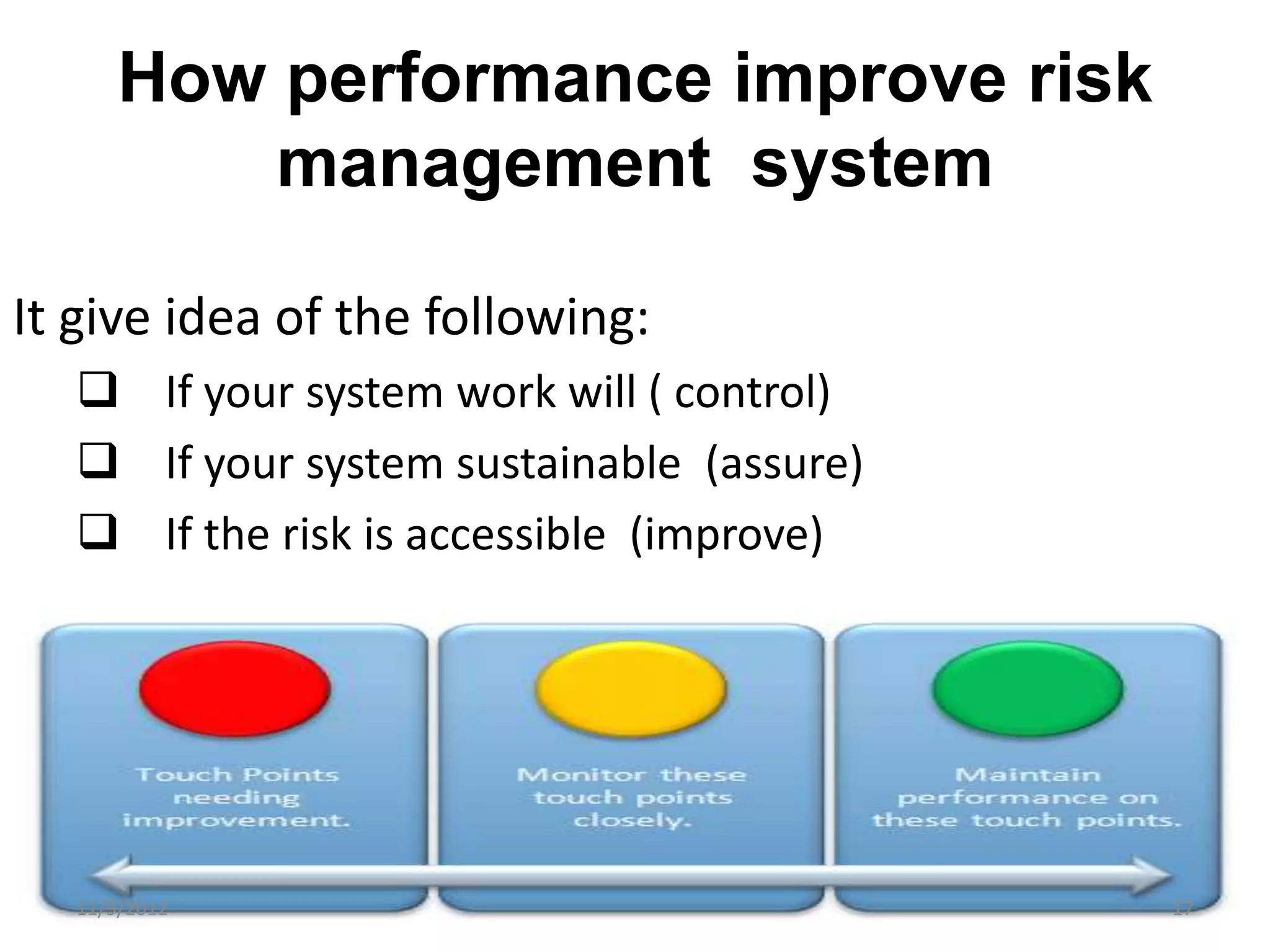
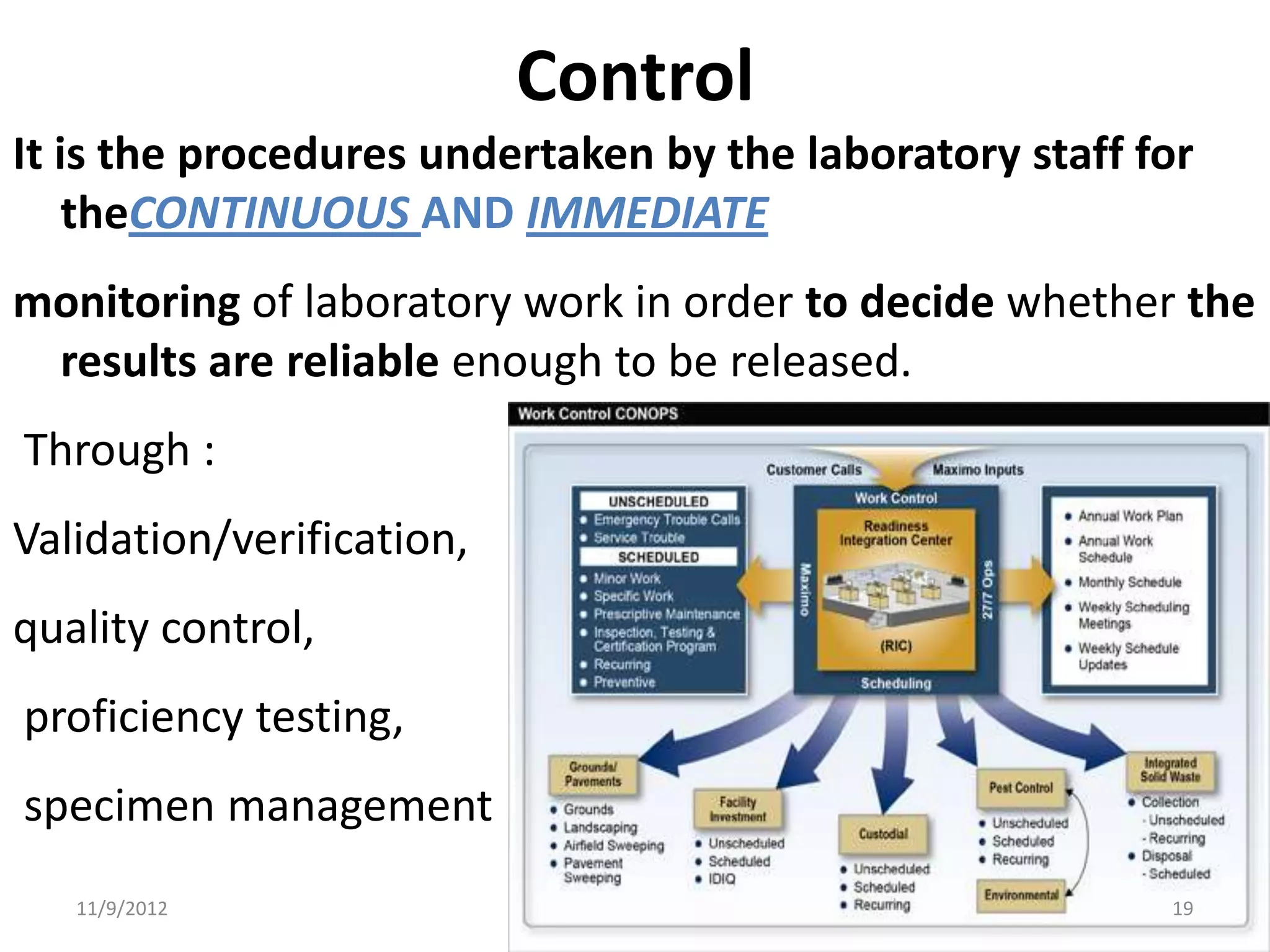
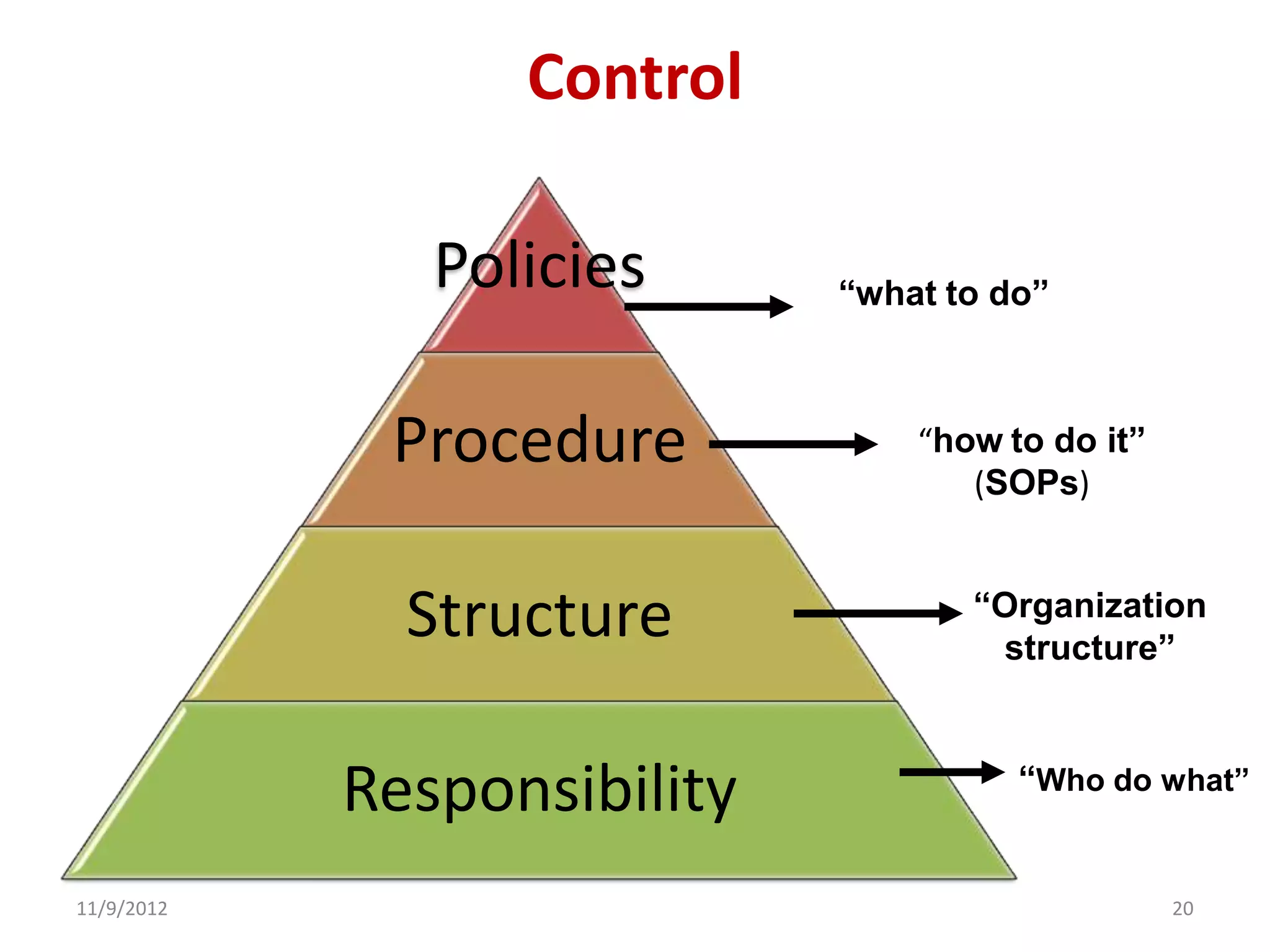
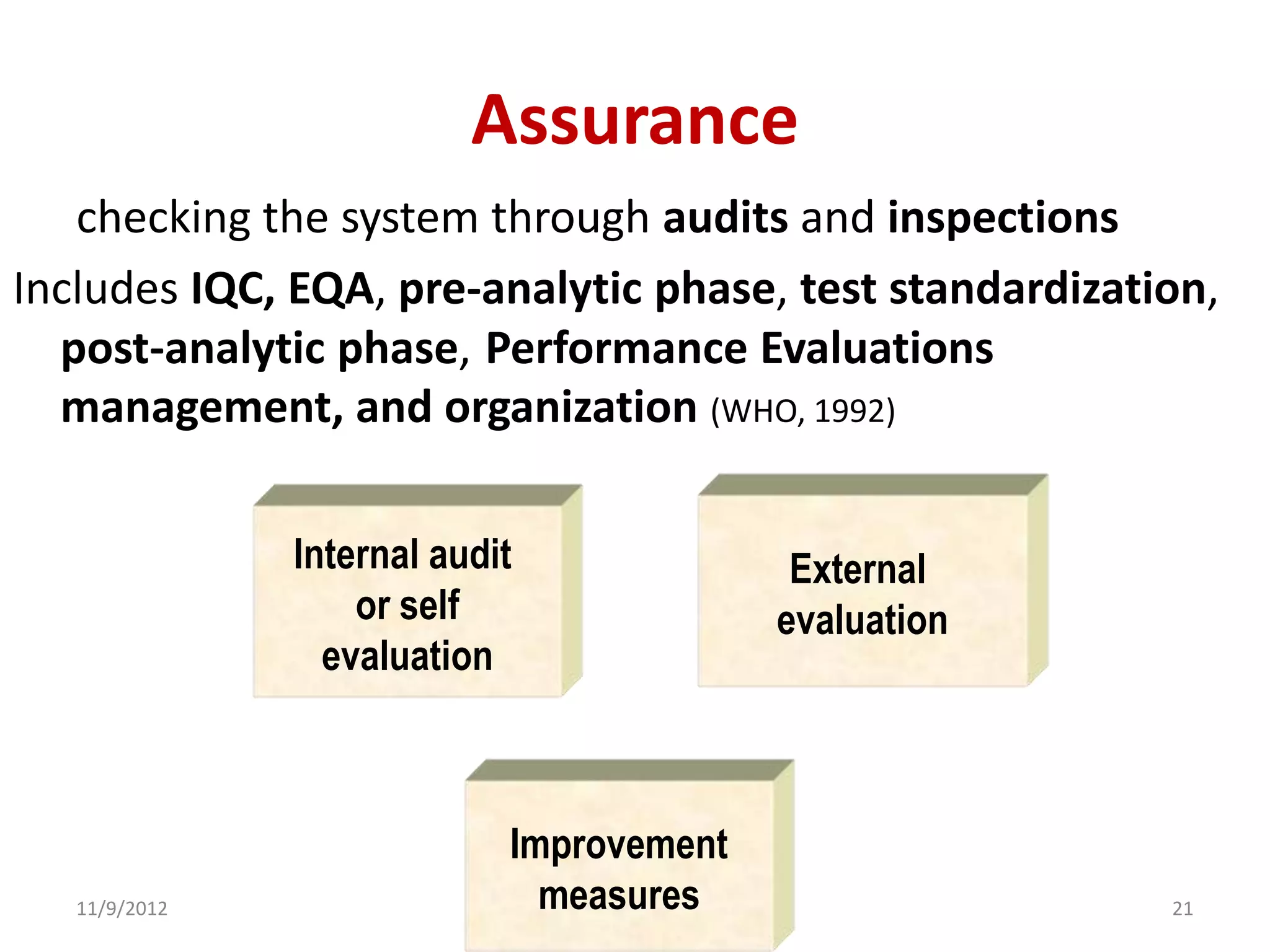
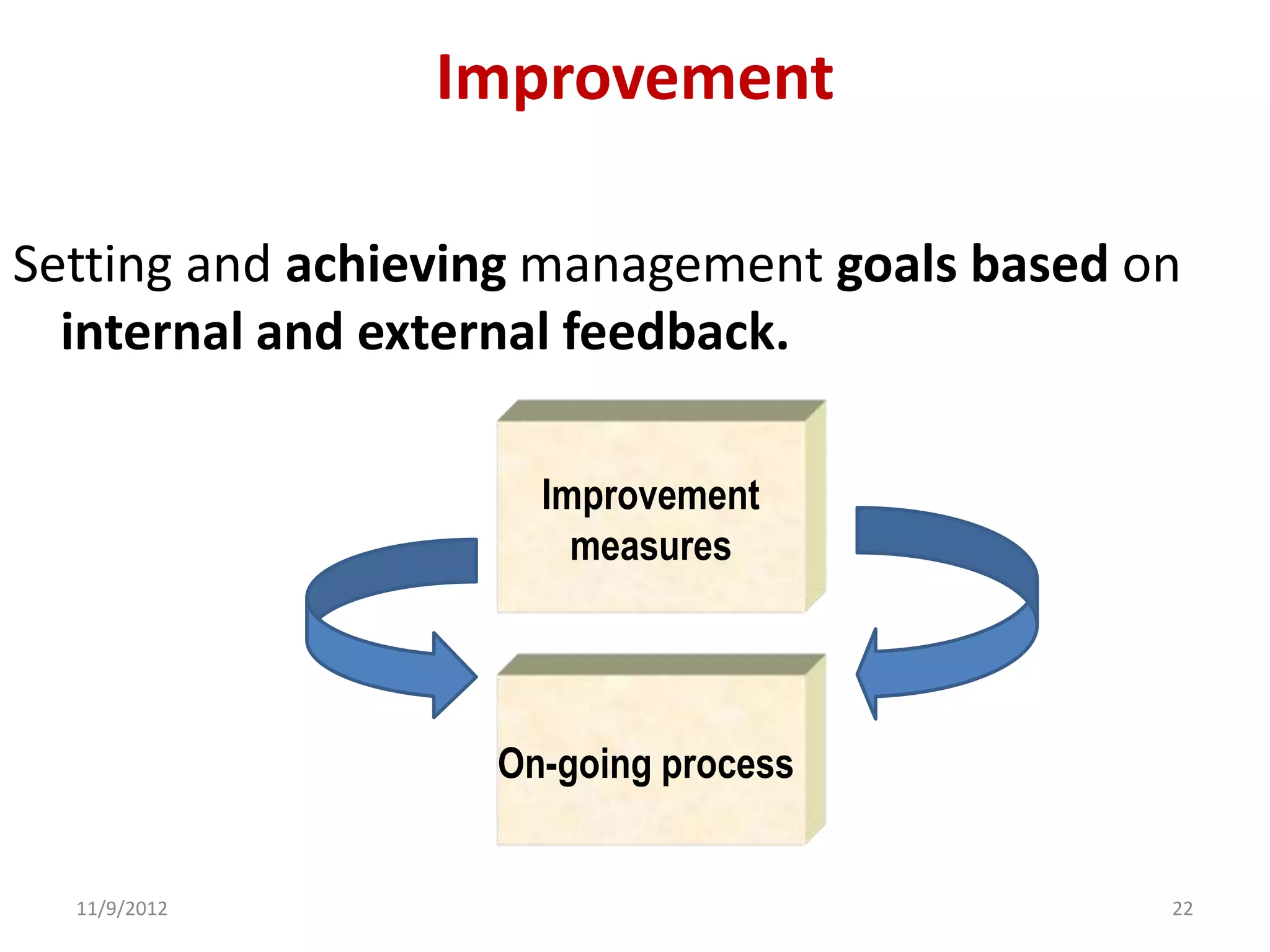
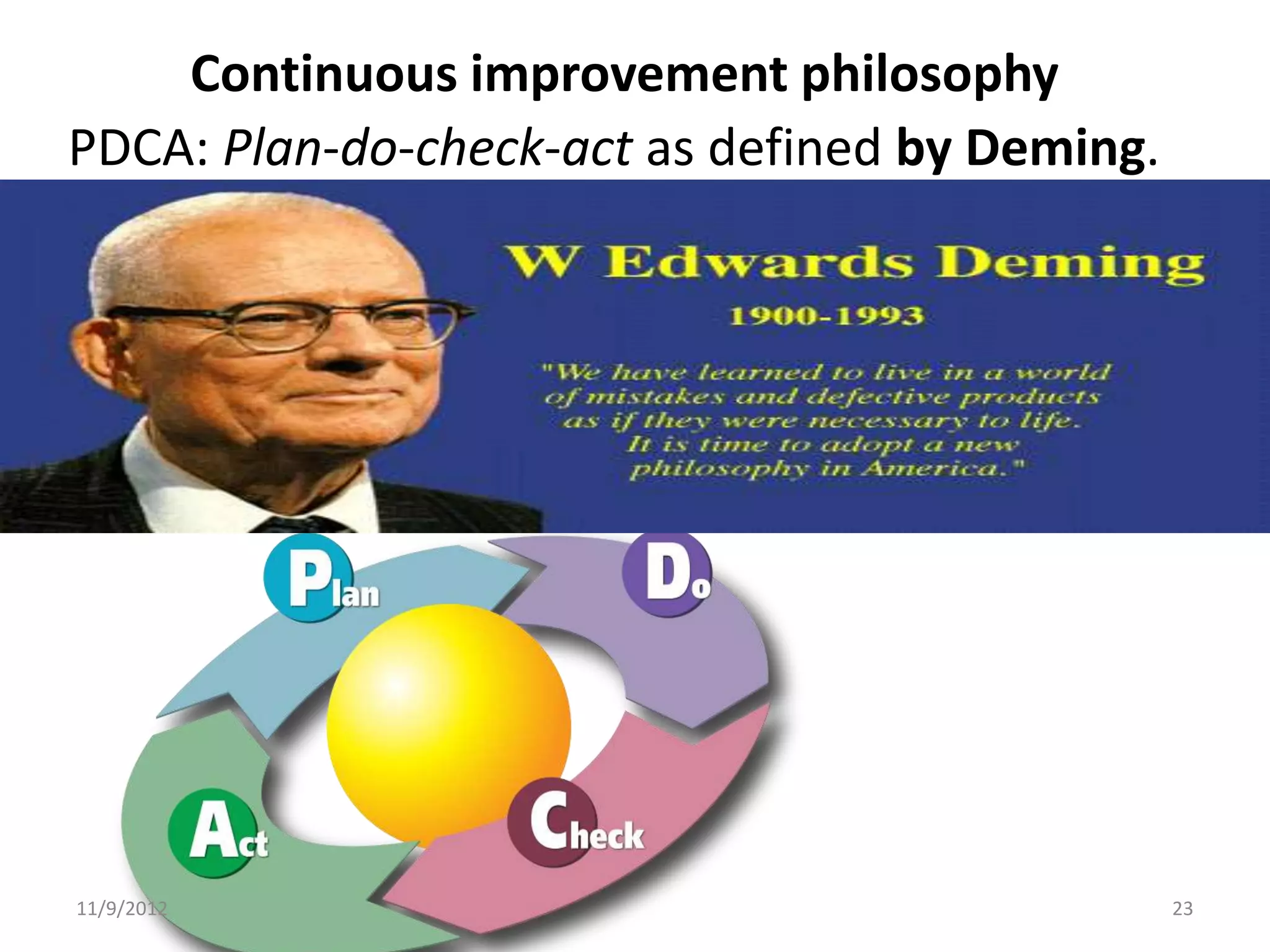
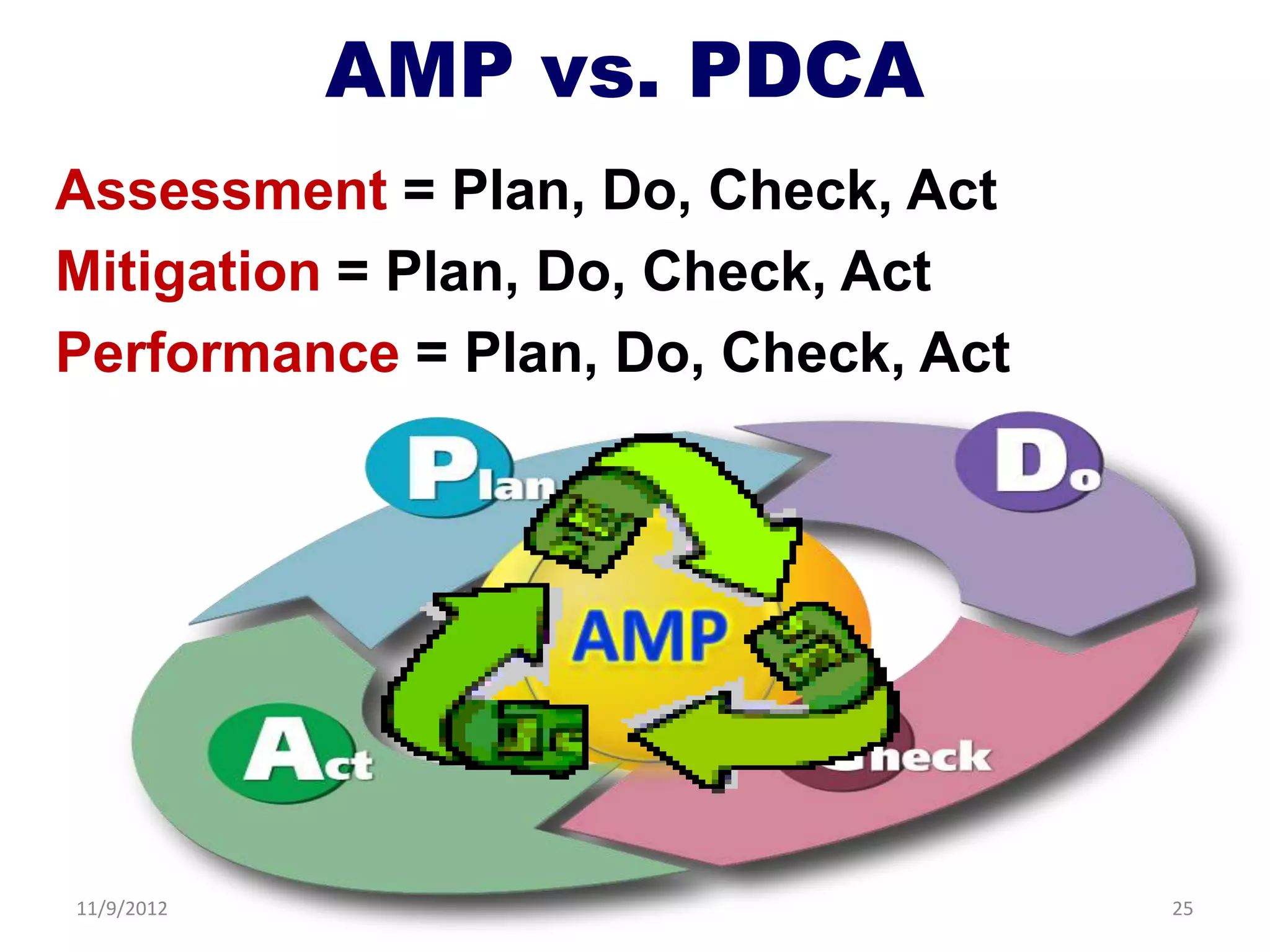
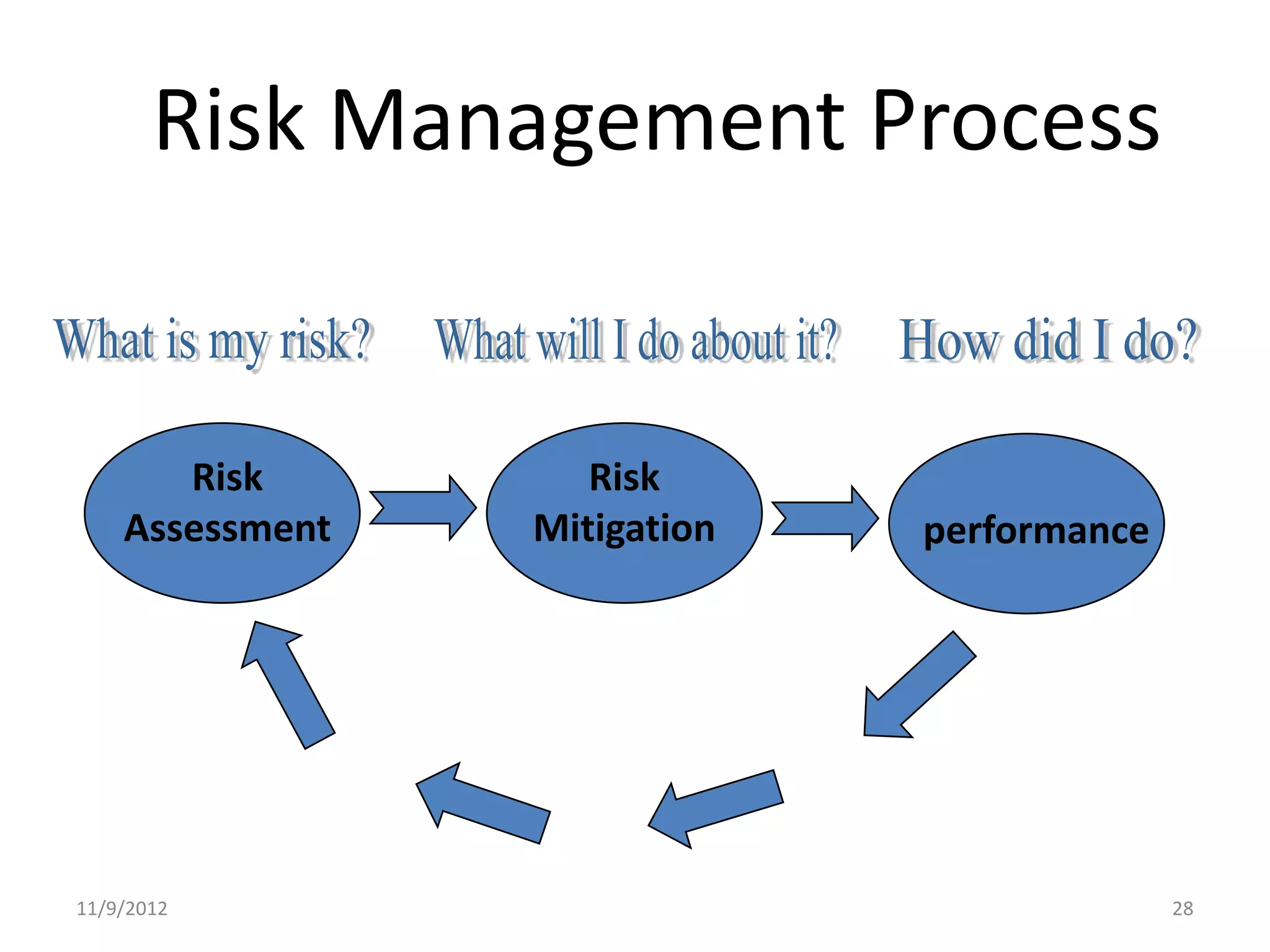
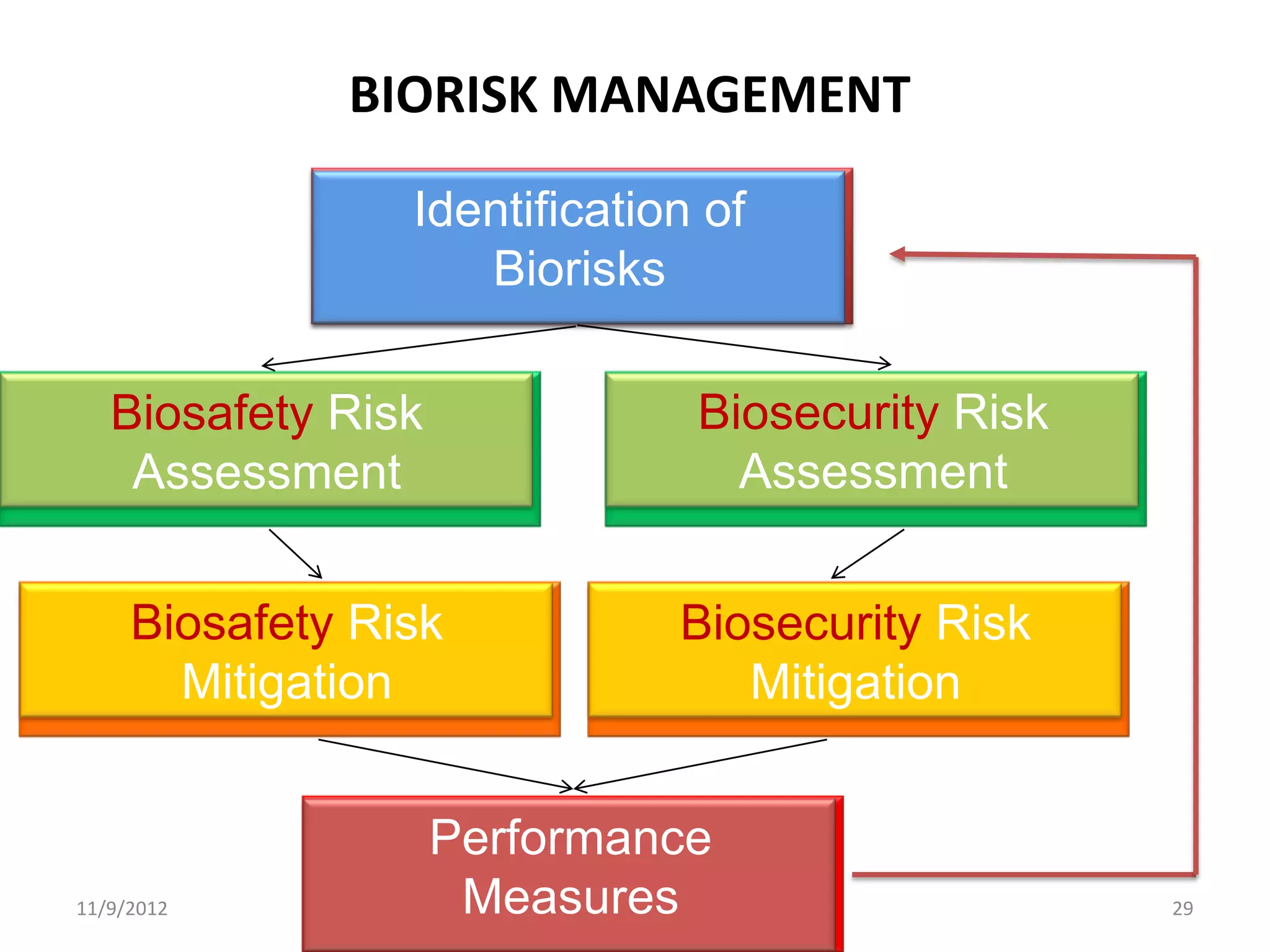
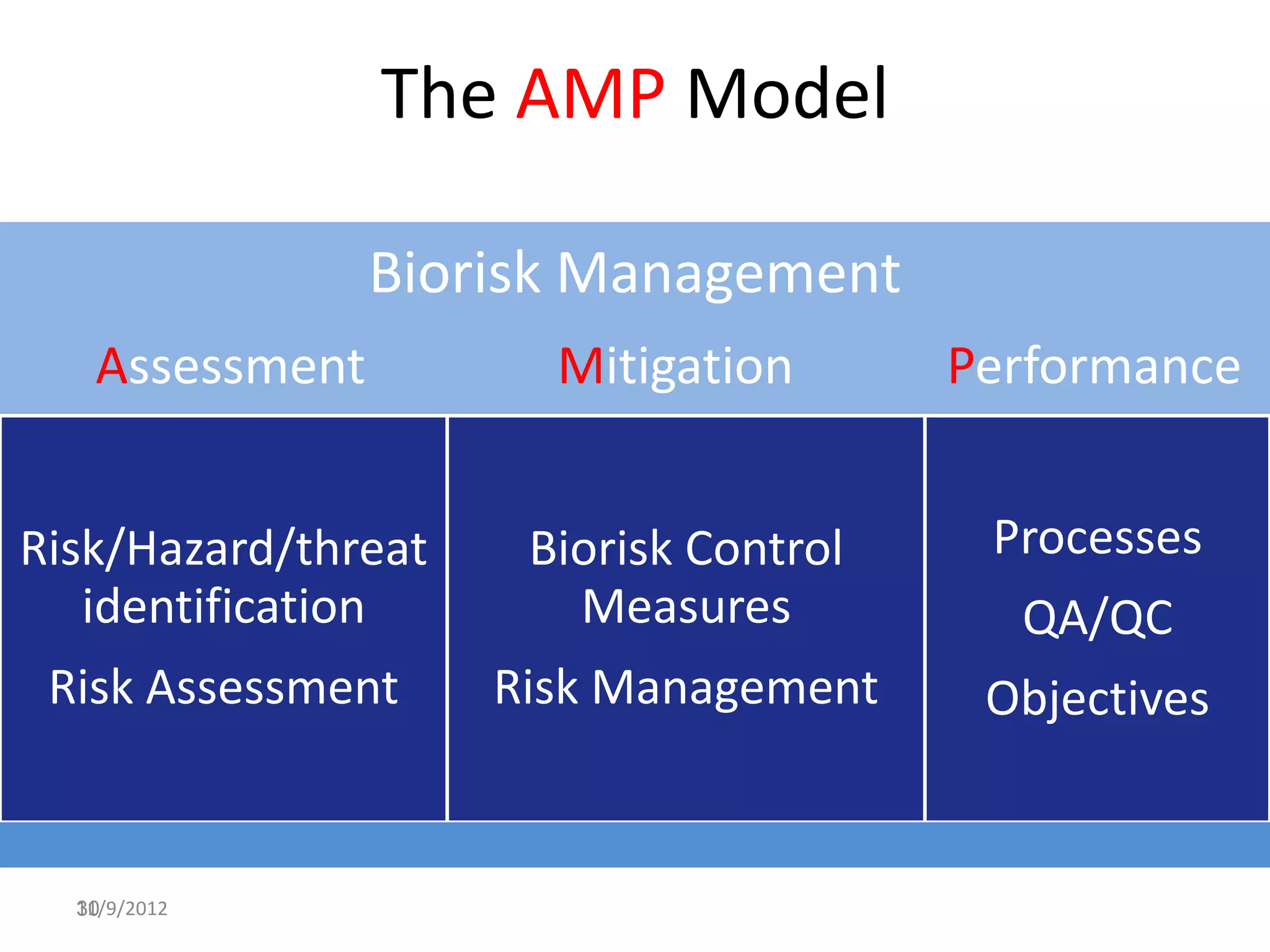
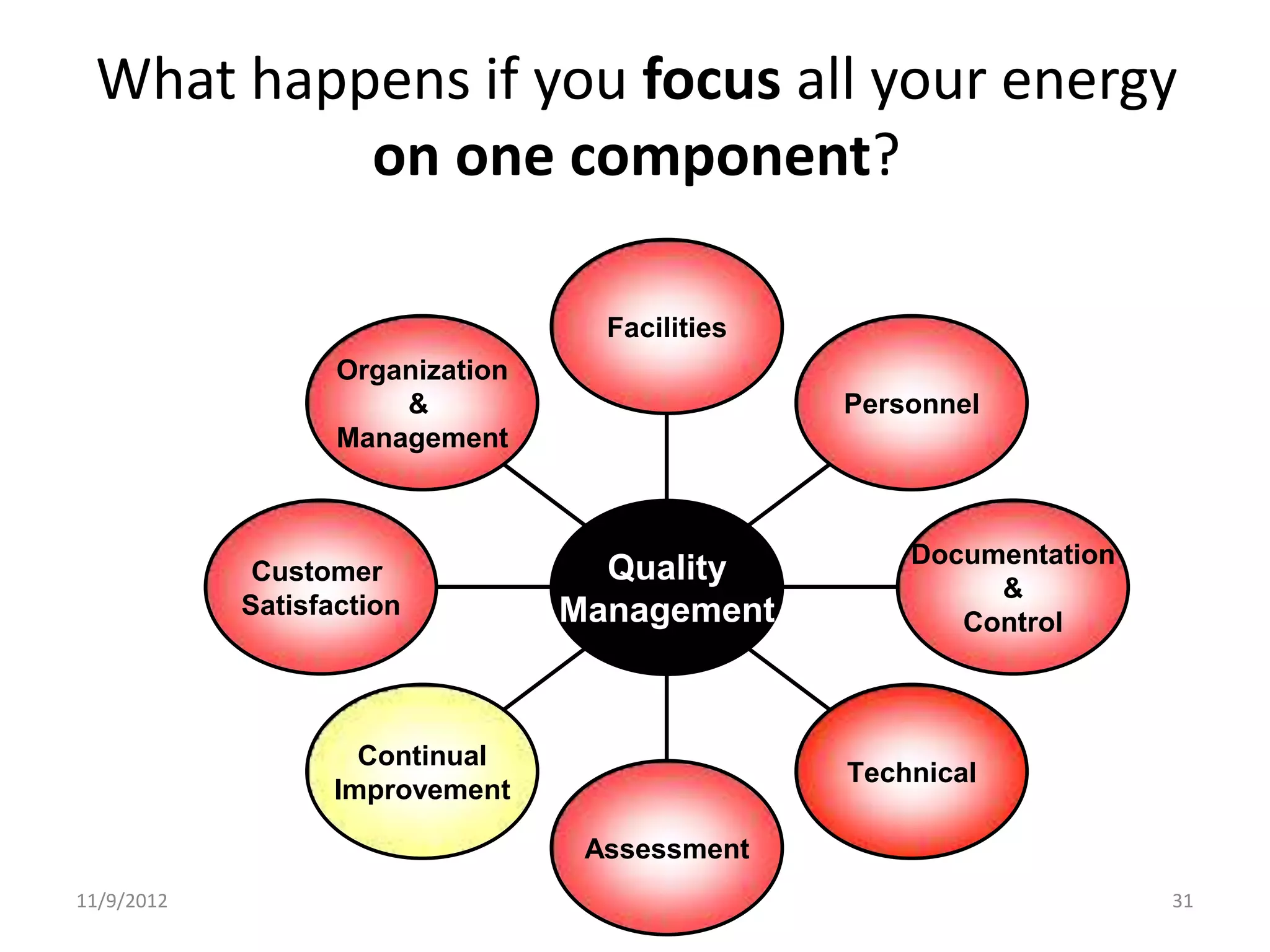
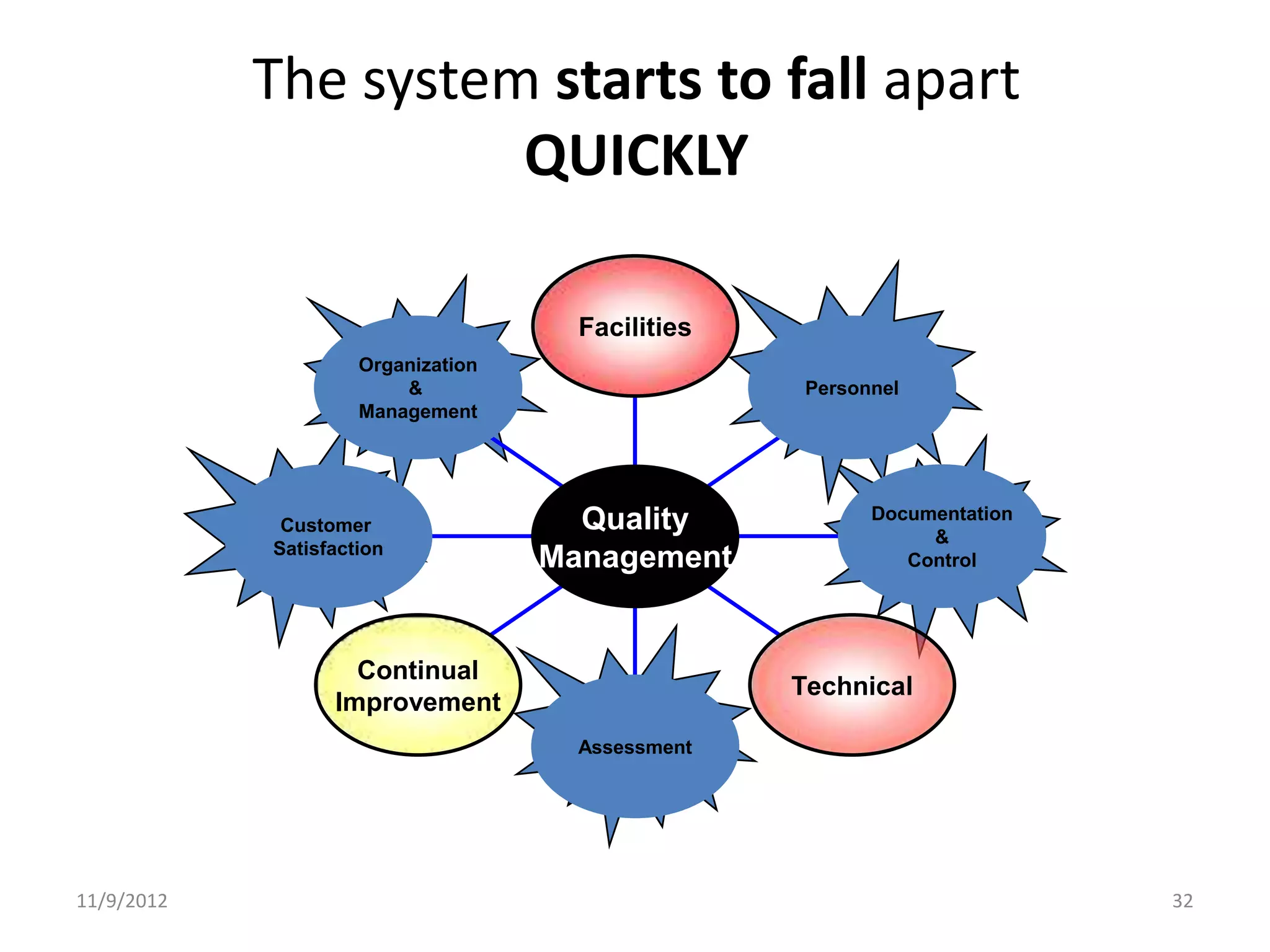
Biorisk management involves three key components: assessment, mitigation, and performance. Assessment identifies risks and hazards, mitigation develops control measures to reduce risks, and performance monitoring ensures the system is working properly through techniques like audits, inspections, and continuous improvement. Neglecting any one component can compromise the overall effectiveness of the biorisk management system.