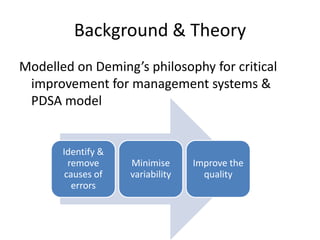
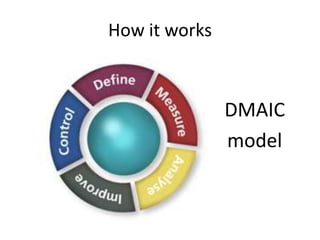
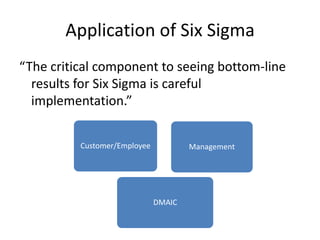
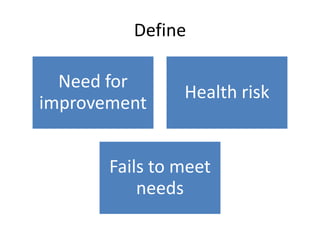
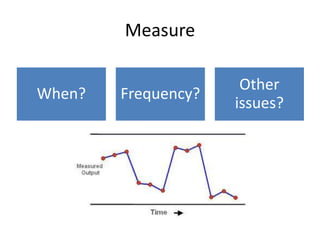
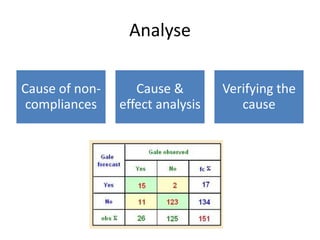
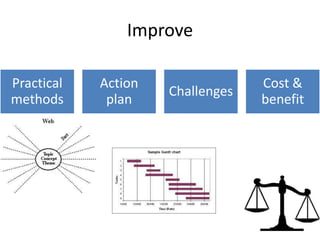
The document discusses using Six Sigma and the DMAIC model to improve PPE compliance on a surgical ward. It describes conducting an audit that found the ward's hand hygiene was not compliant with WHO guidelines. To address this, the DMAIC process would be used to define the problem, measure compliance rates and causes of non-compliance, analyze the root causes, improve practices through an action plan addressing challenges and costs/benefits, and control the process through monitoring.