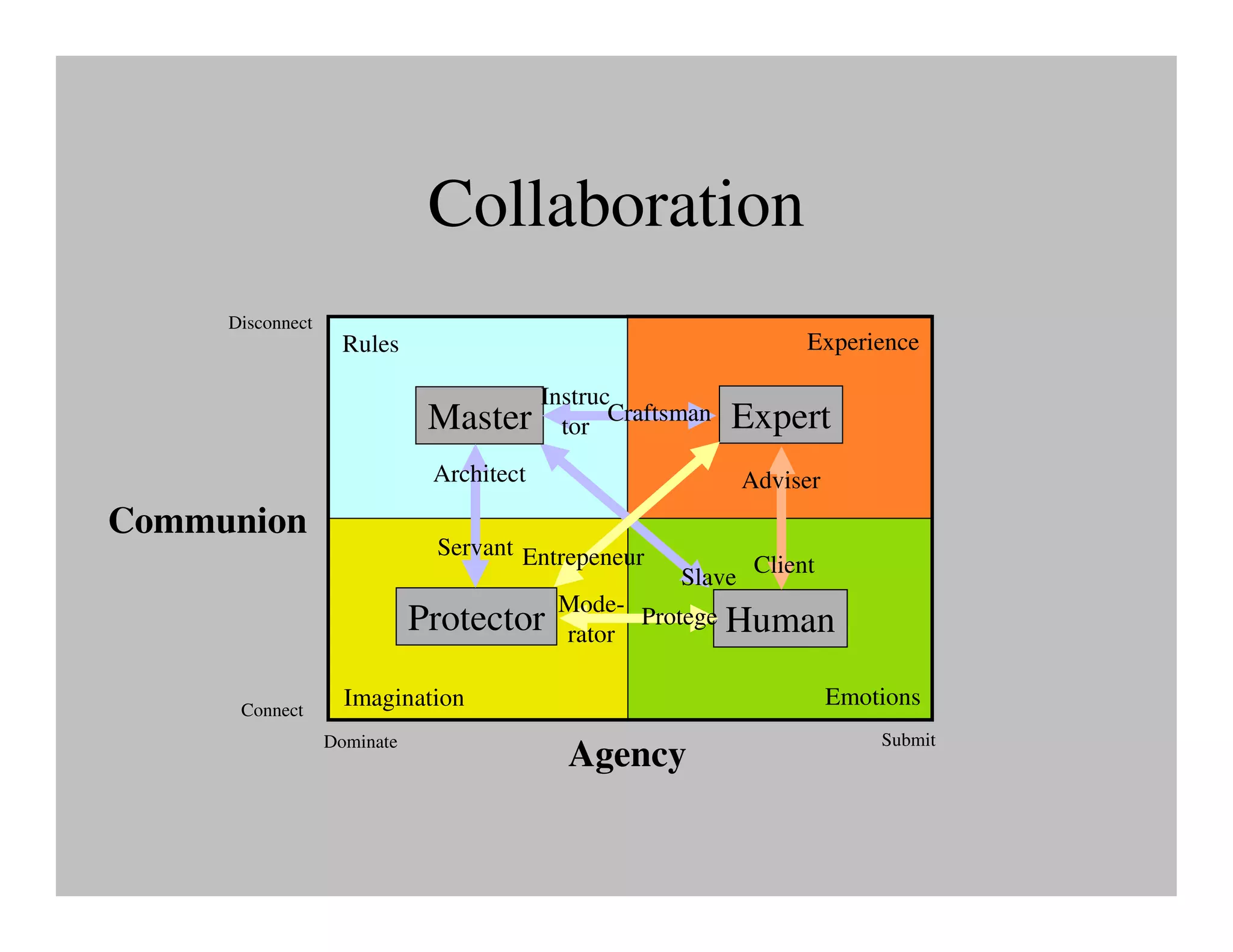
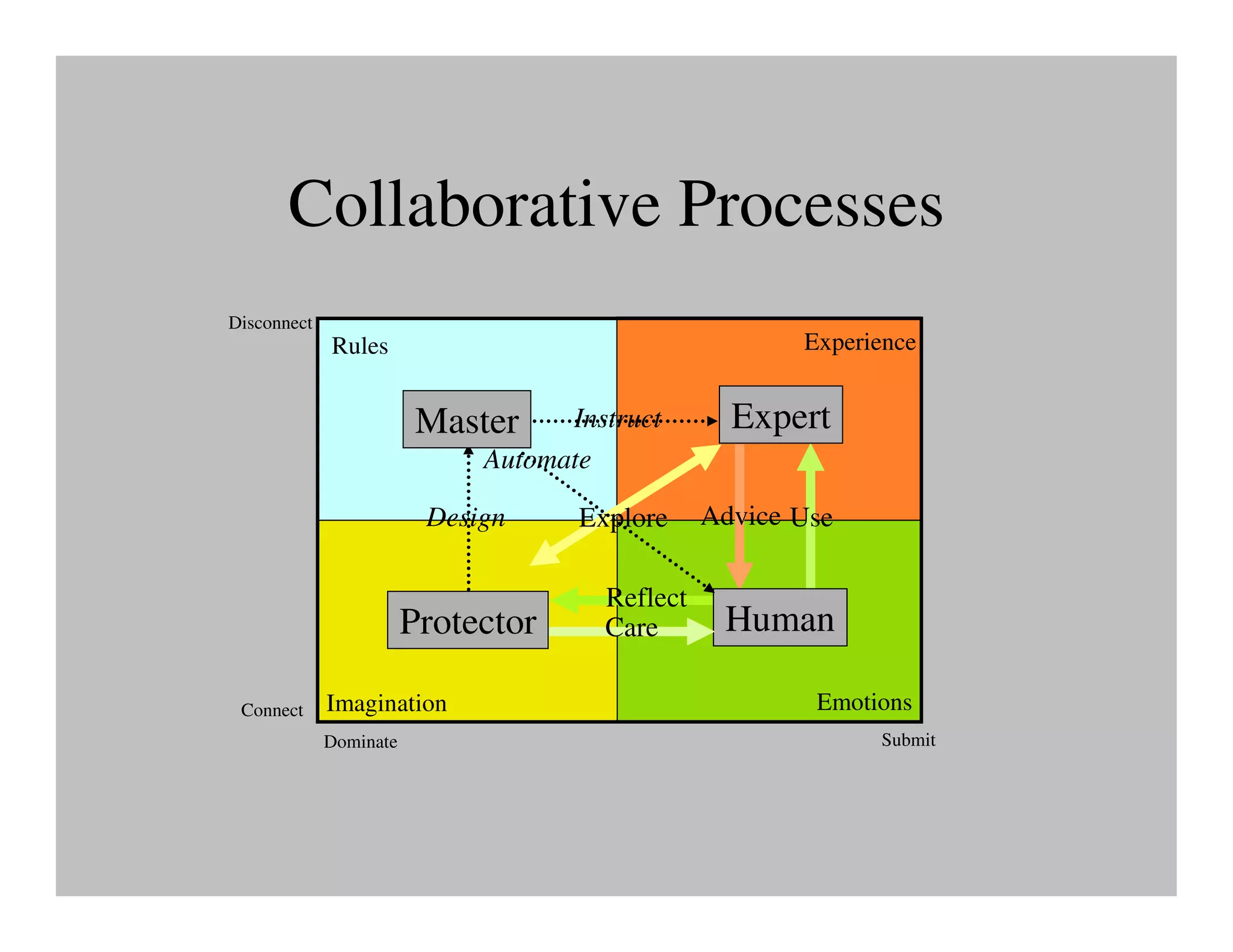
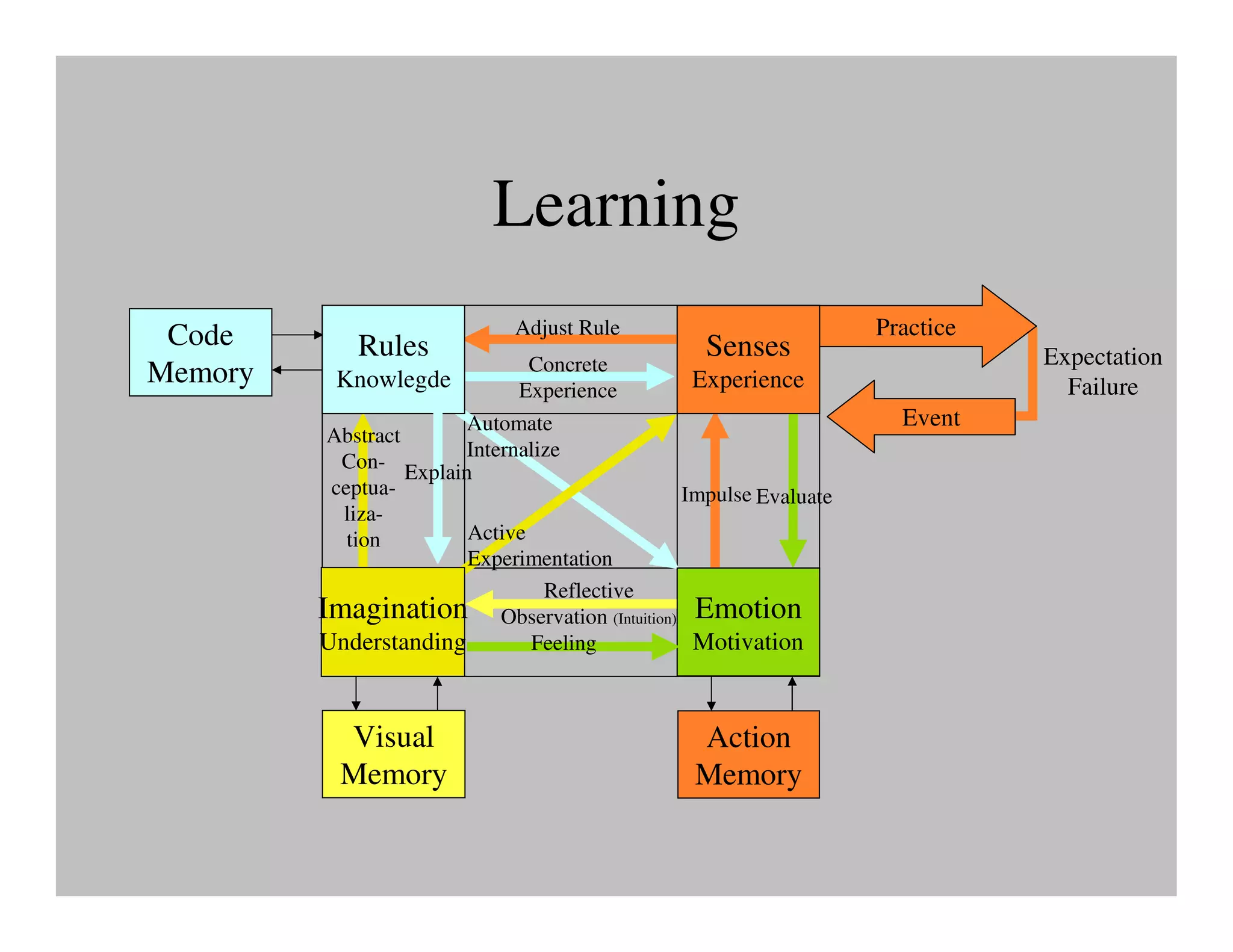
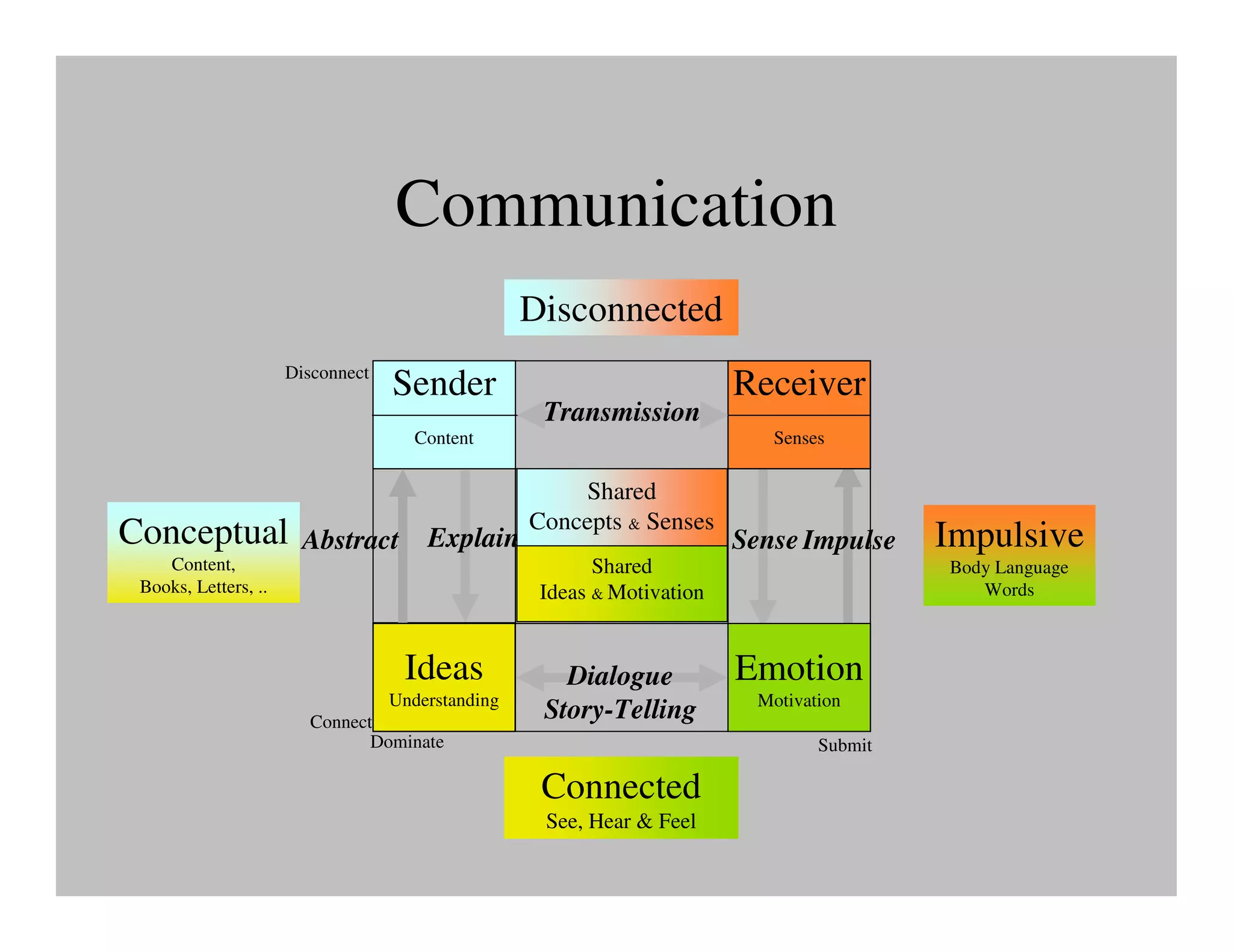
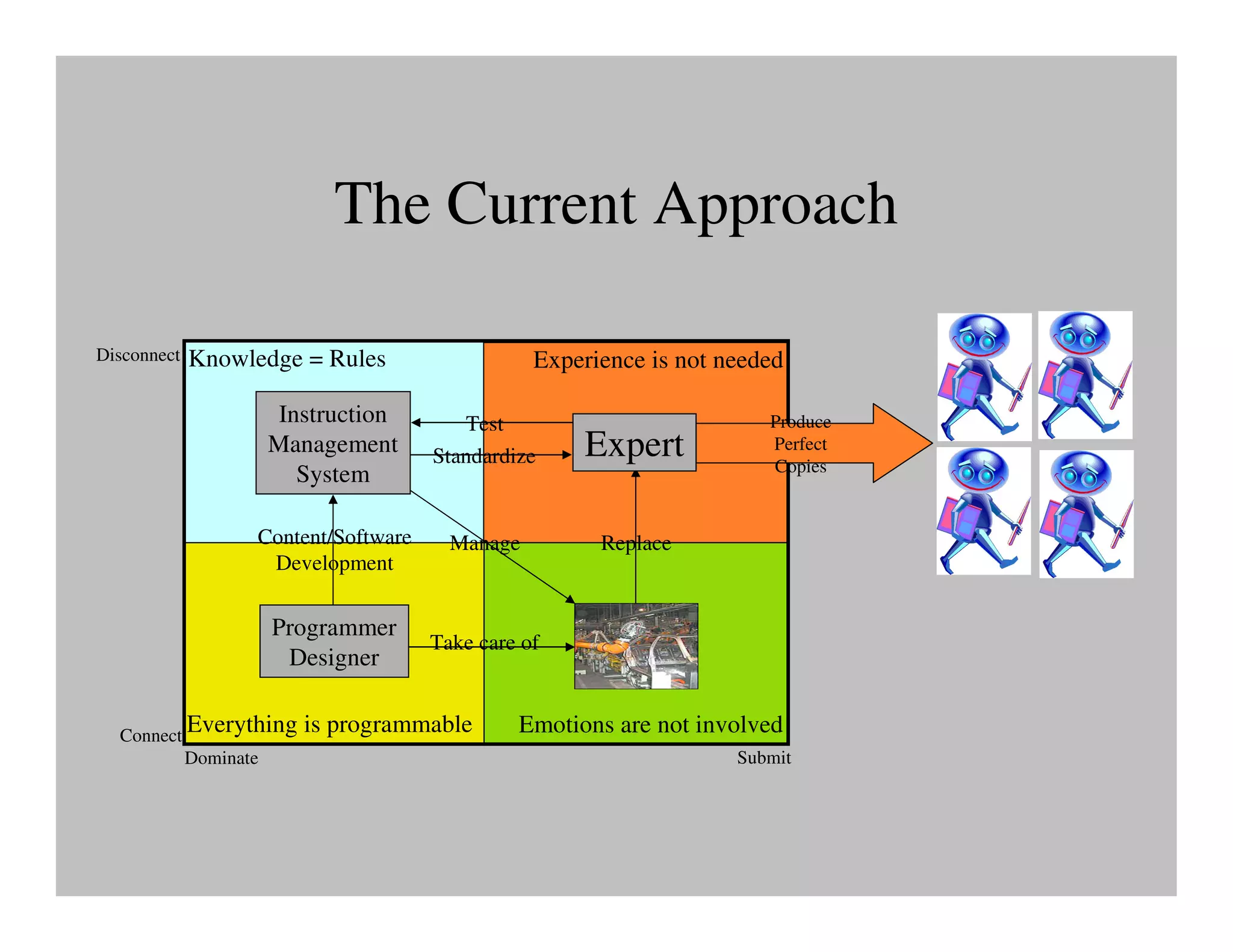
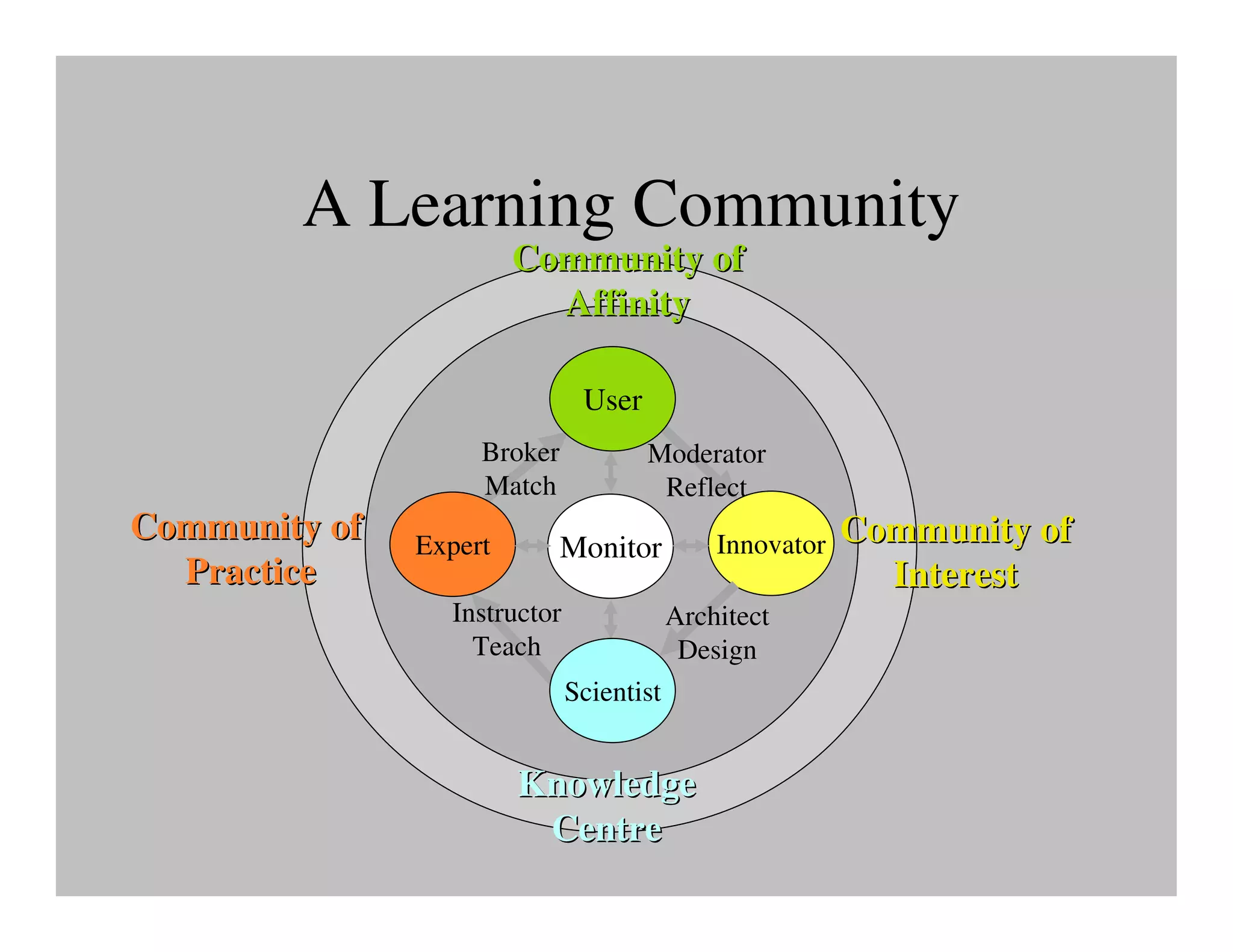
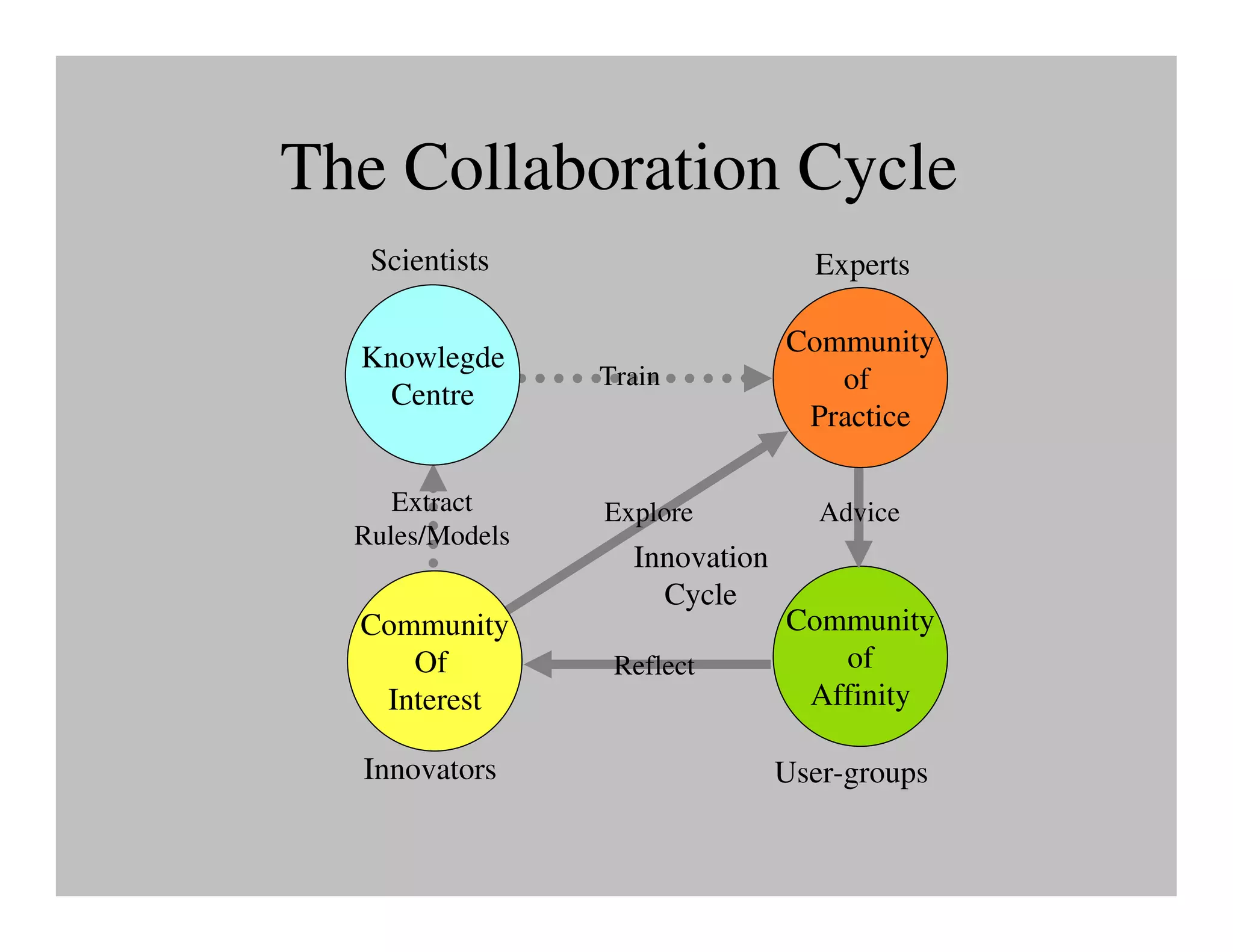
The document discusses collaborative learning and the dynamics between various roles such as master, protector, expert, and human within collaborative processes. It emphasizes the importance of agency and communion in learning, where mastery can lead to innovation cycles that encourage reflection and adaptation. Furthermore, it critiques current educational approaches that treat students as objects rather than as engaged participants in a learning community.