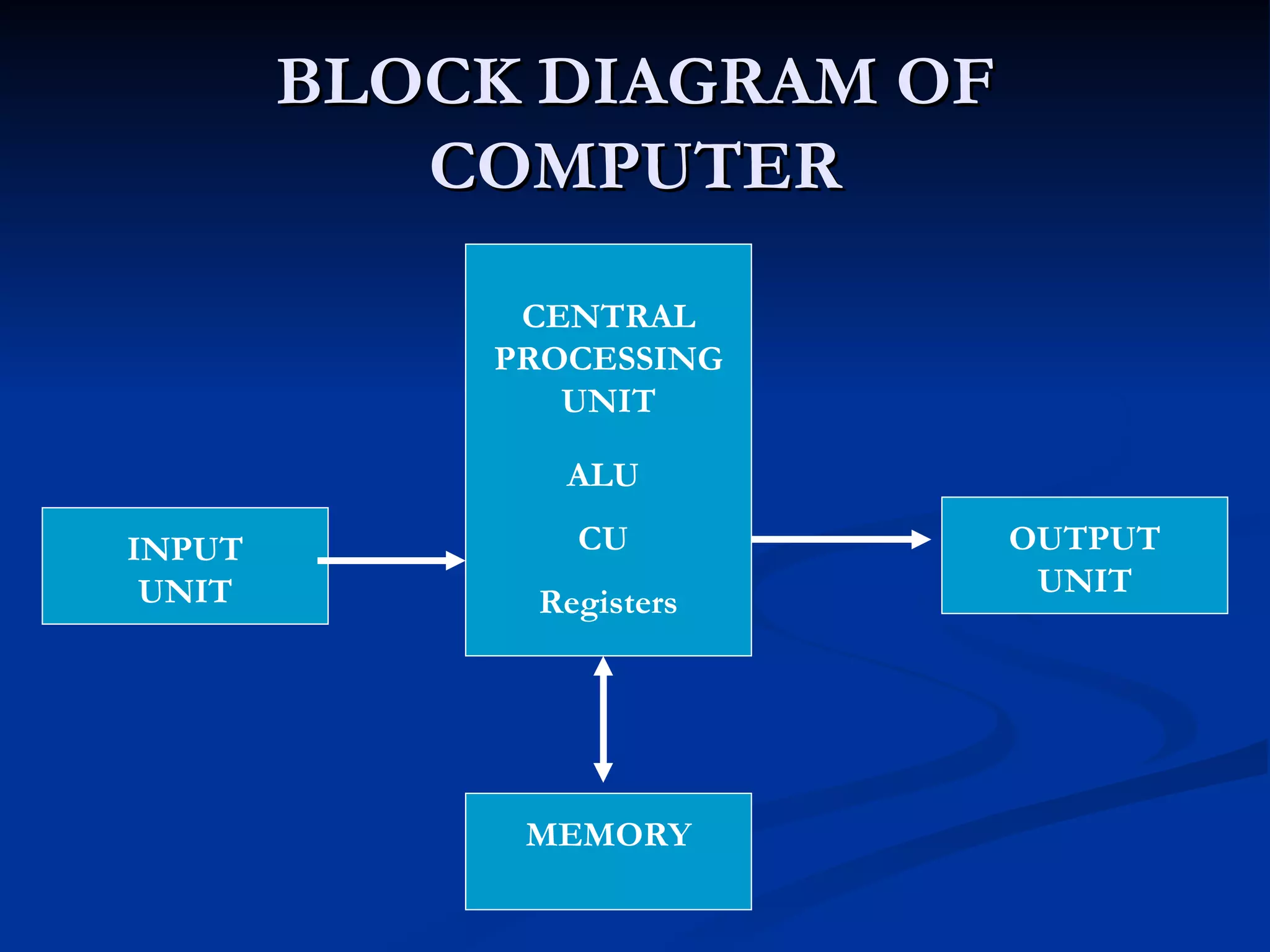
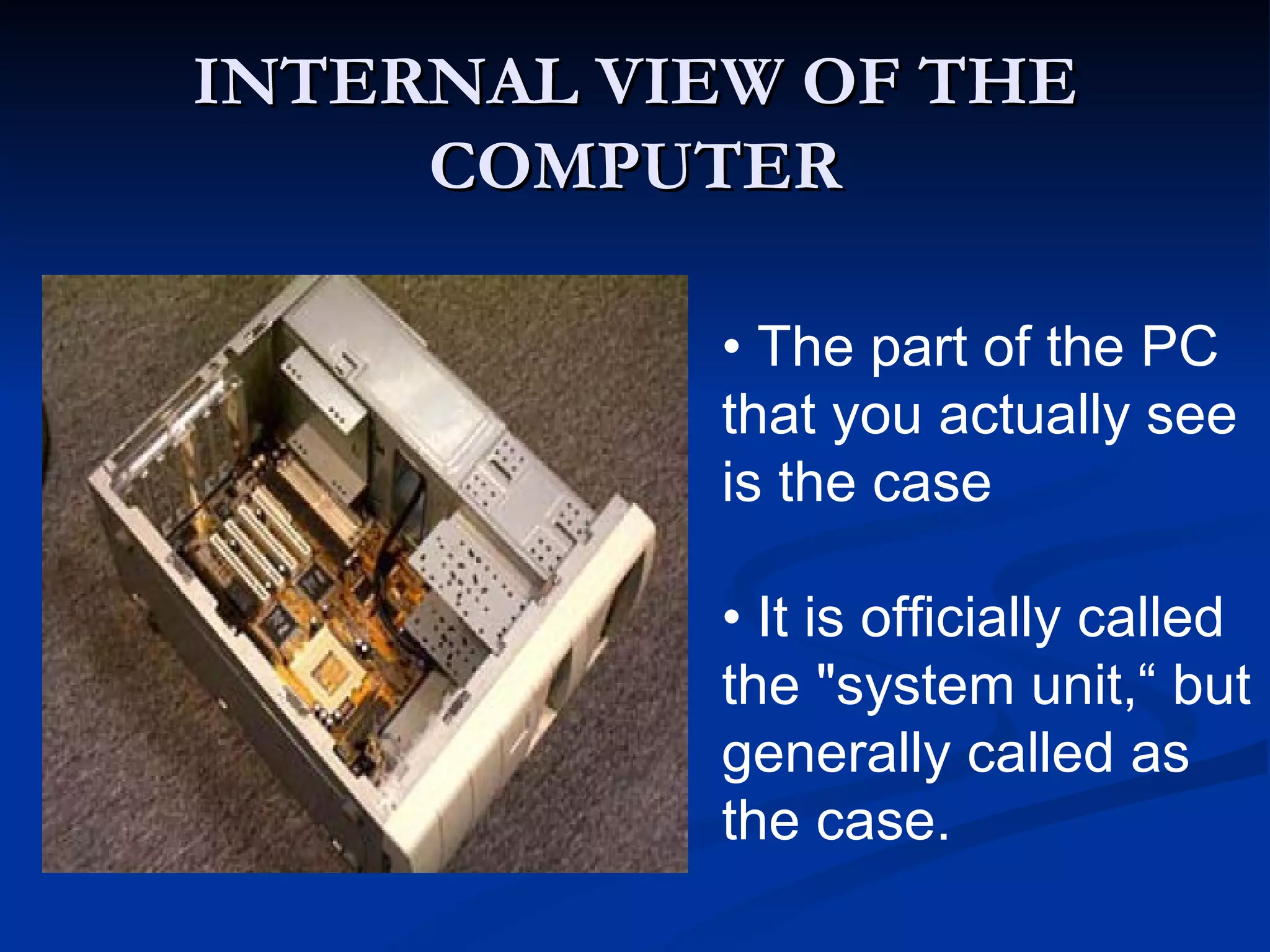
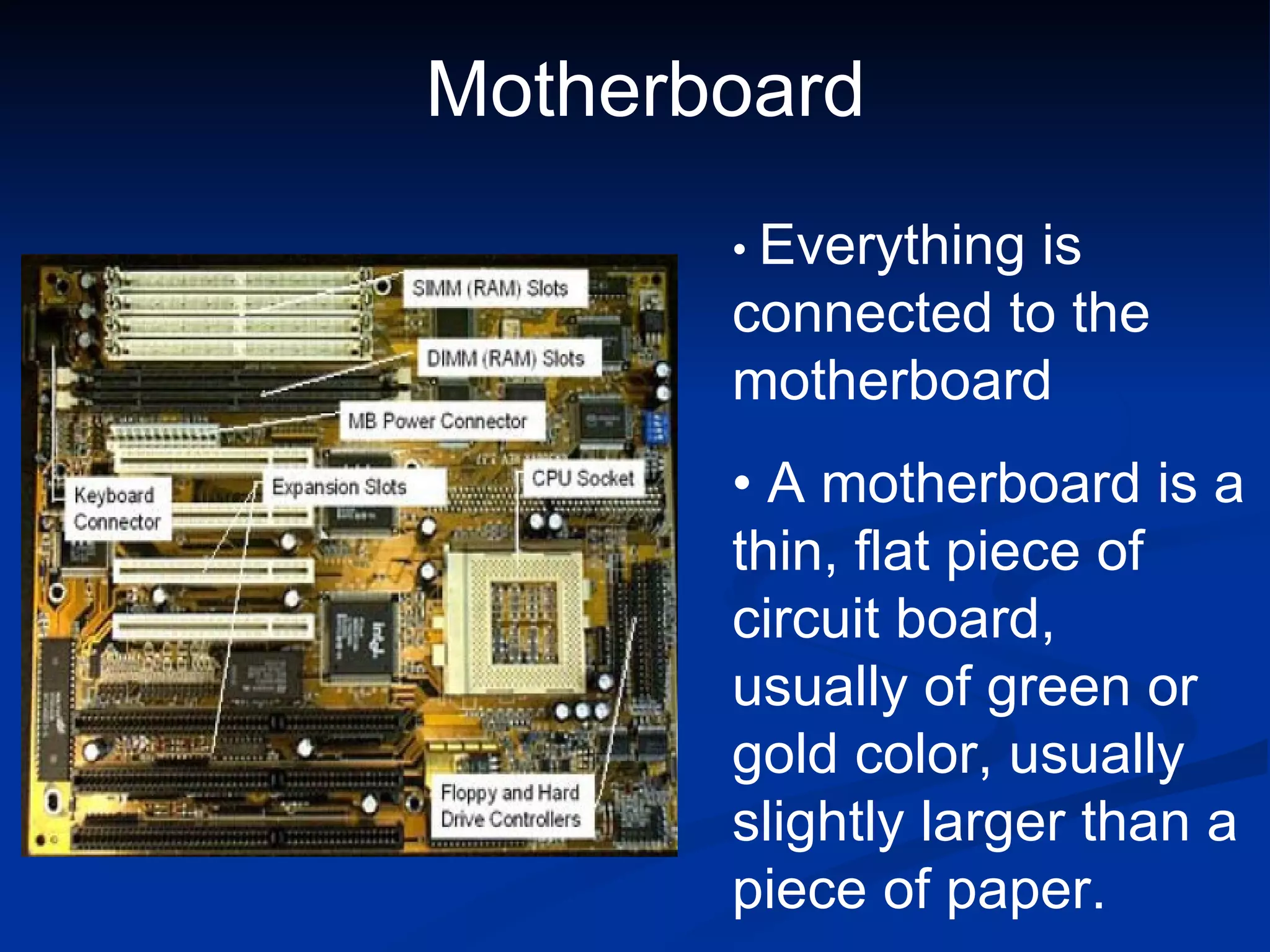
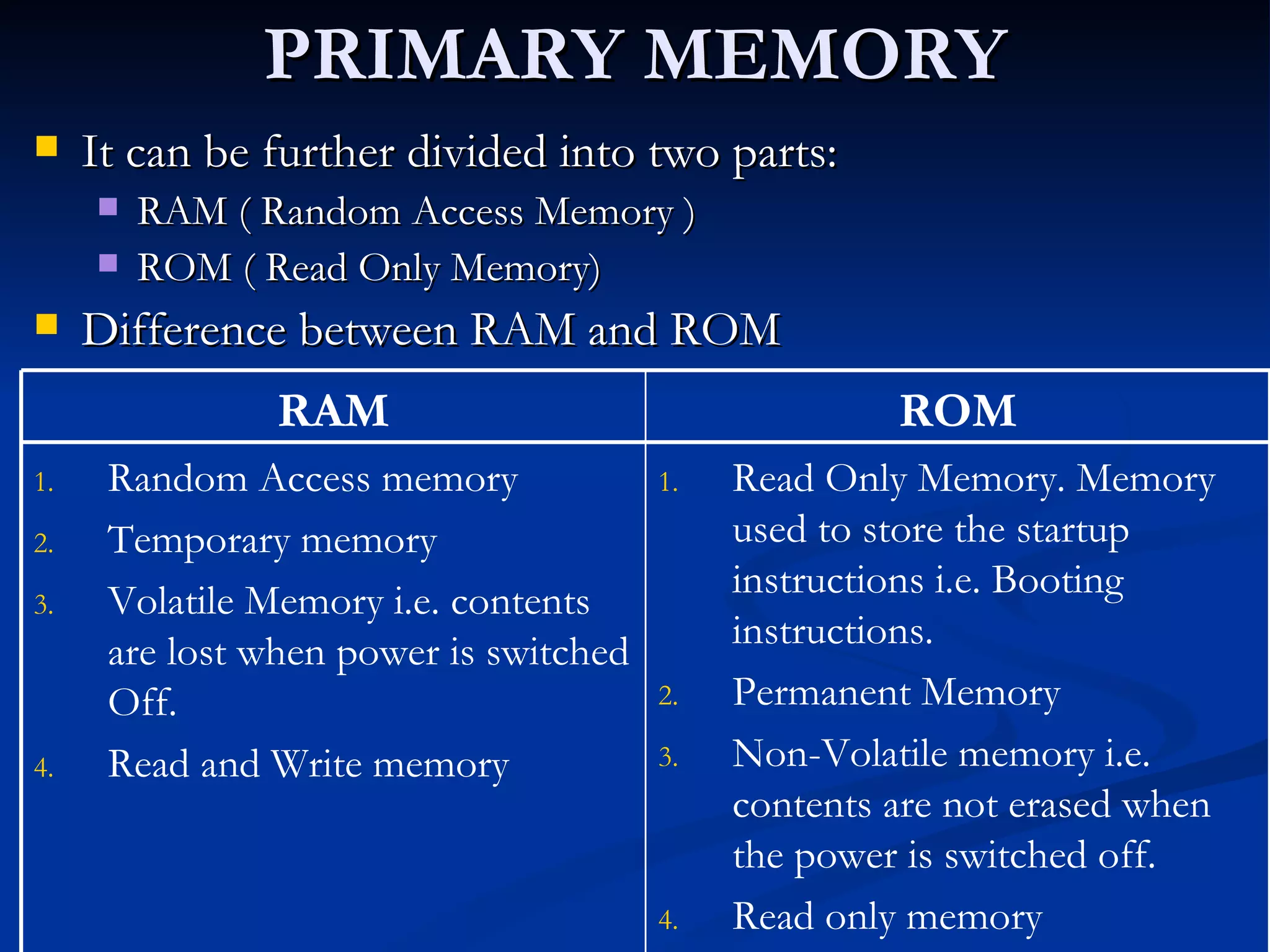
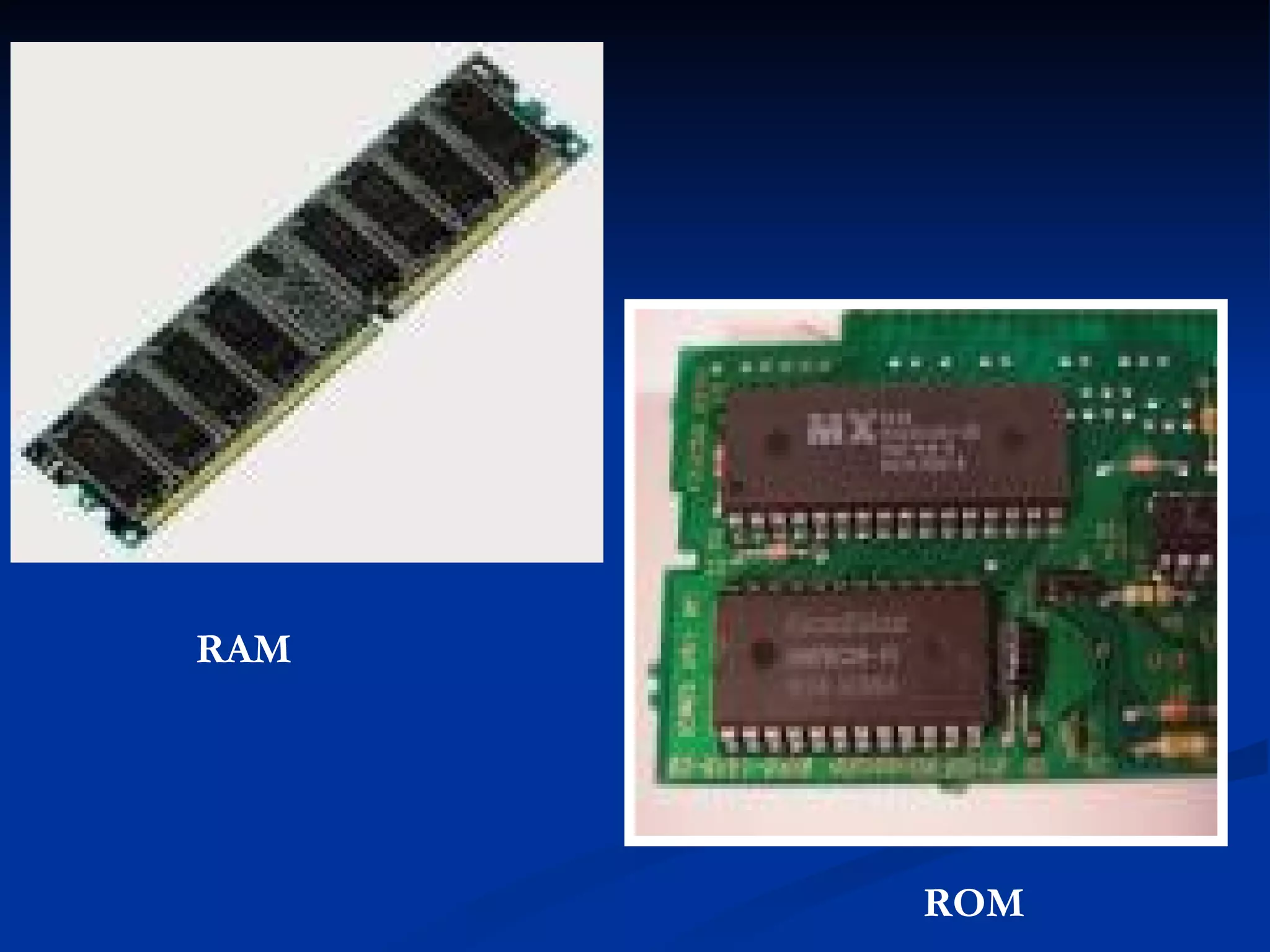
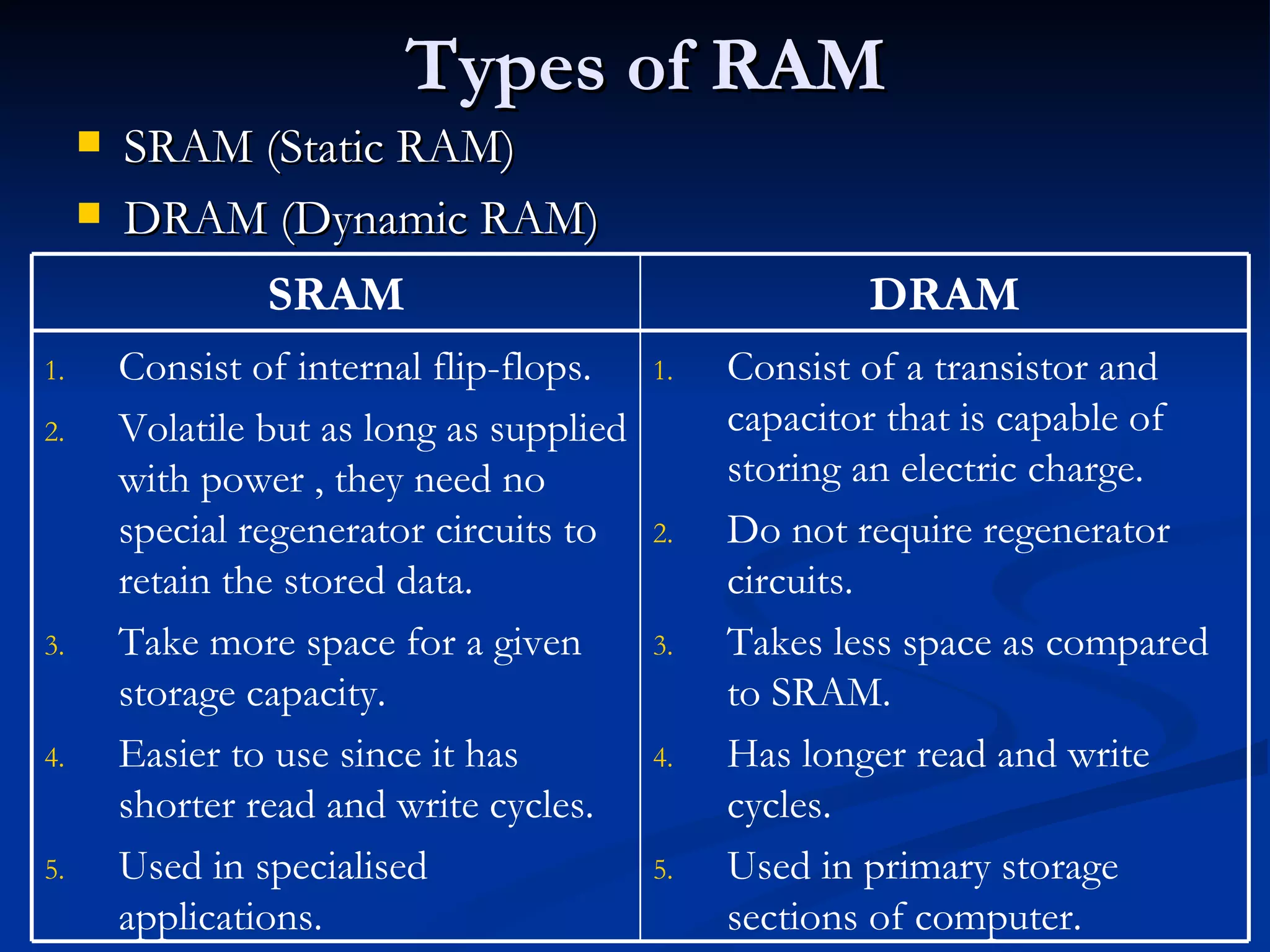
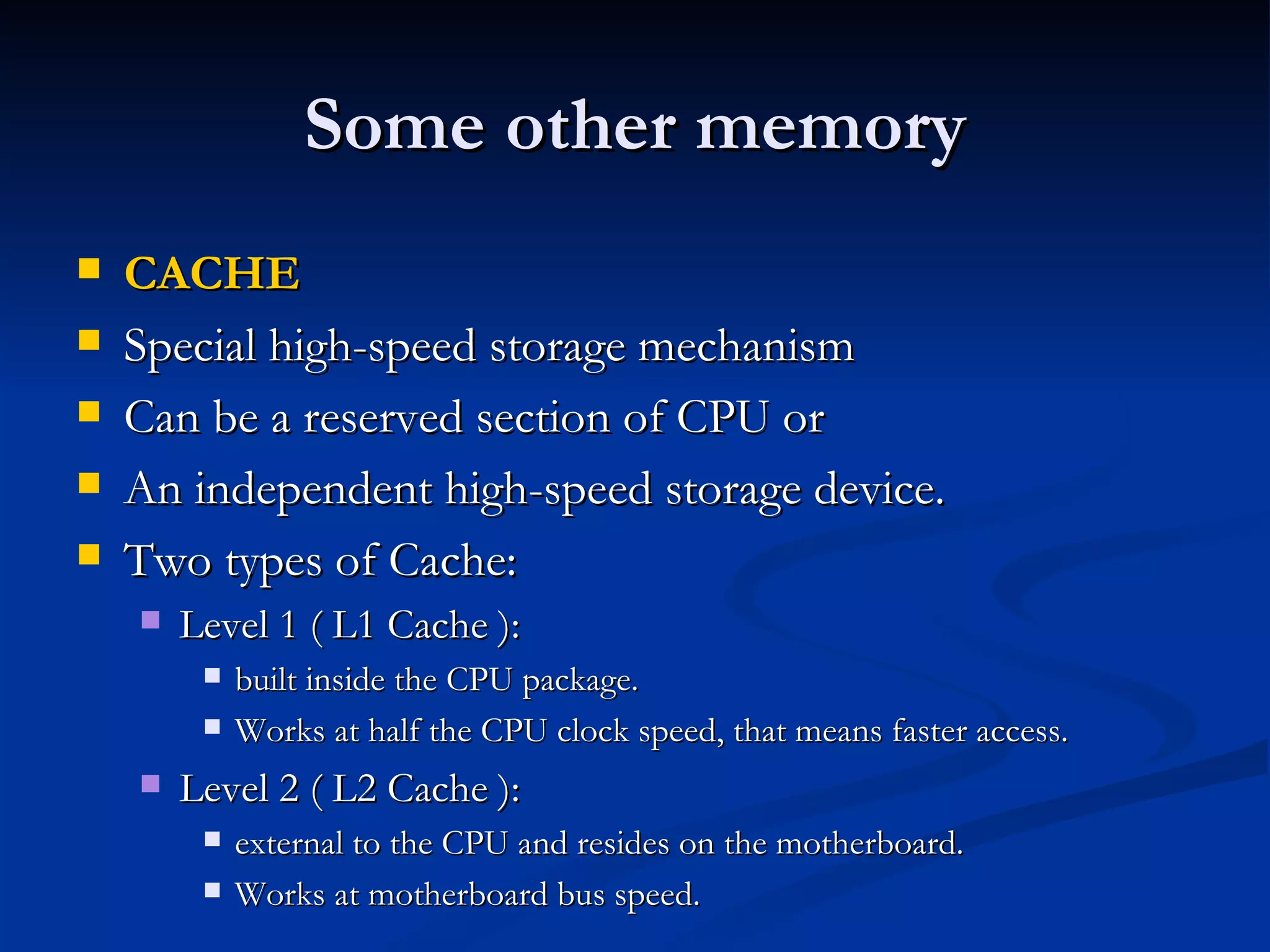
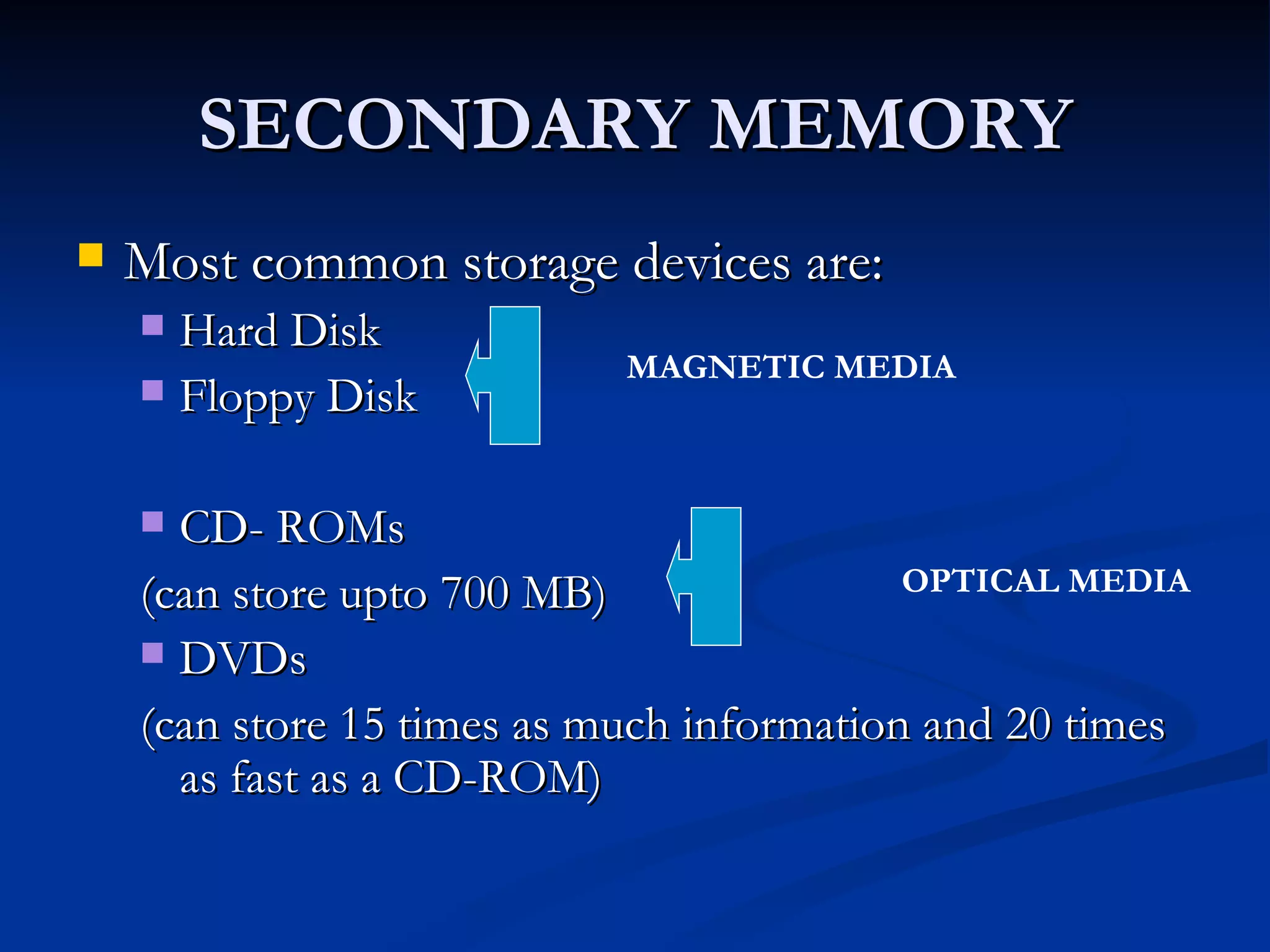
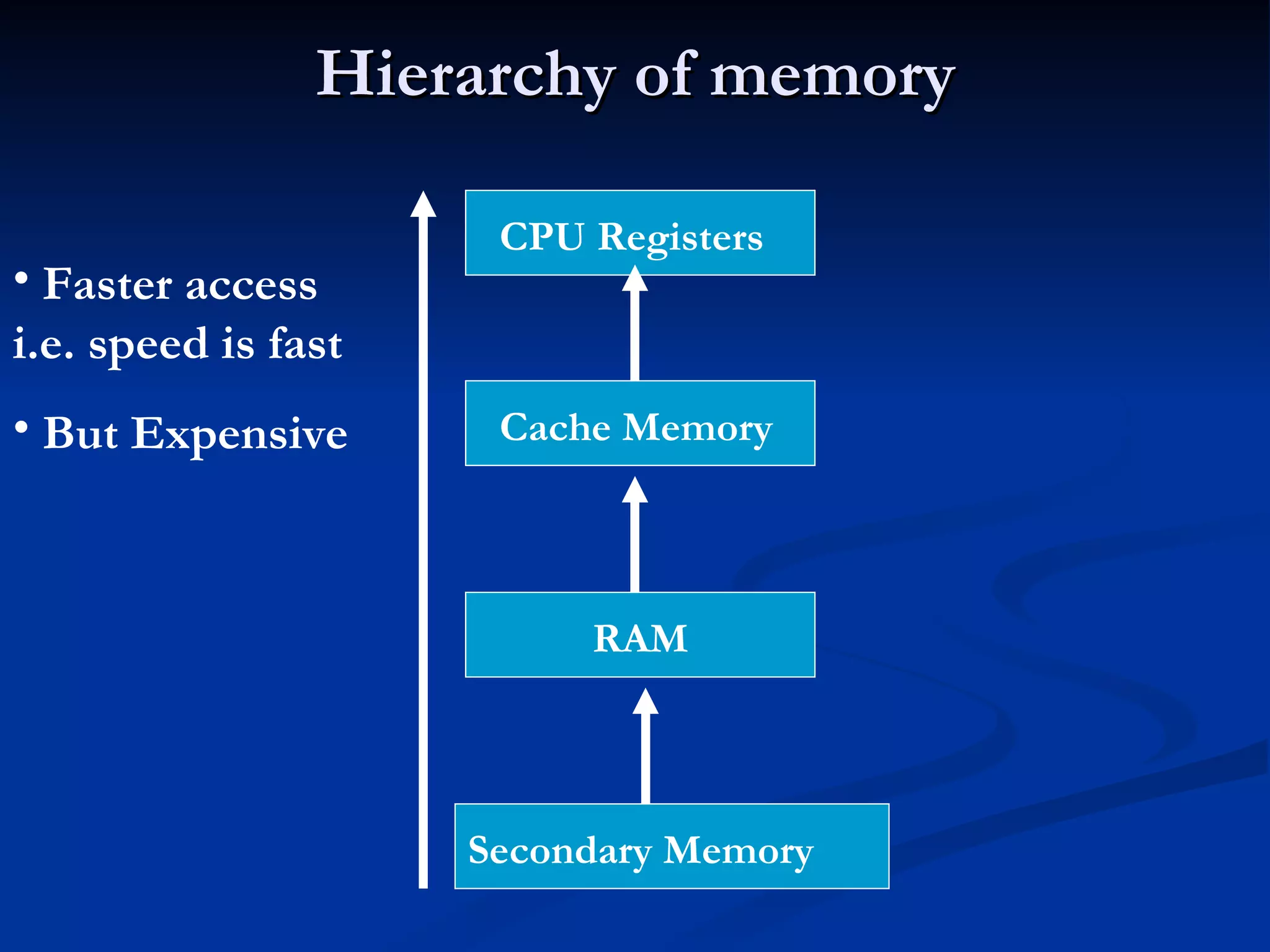
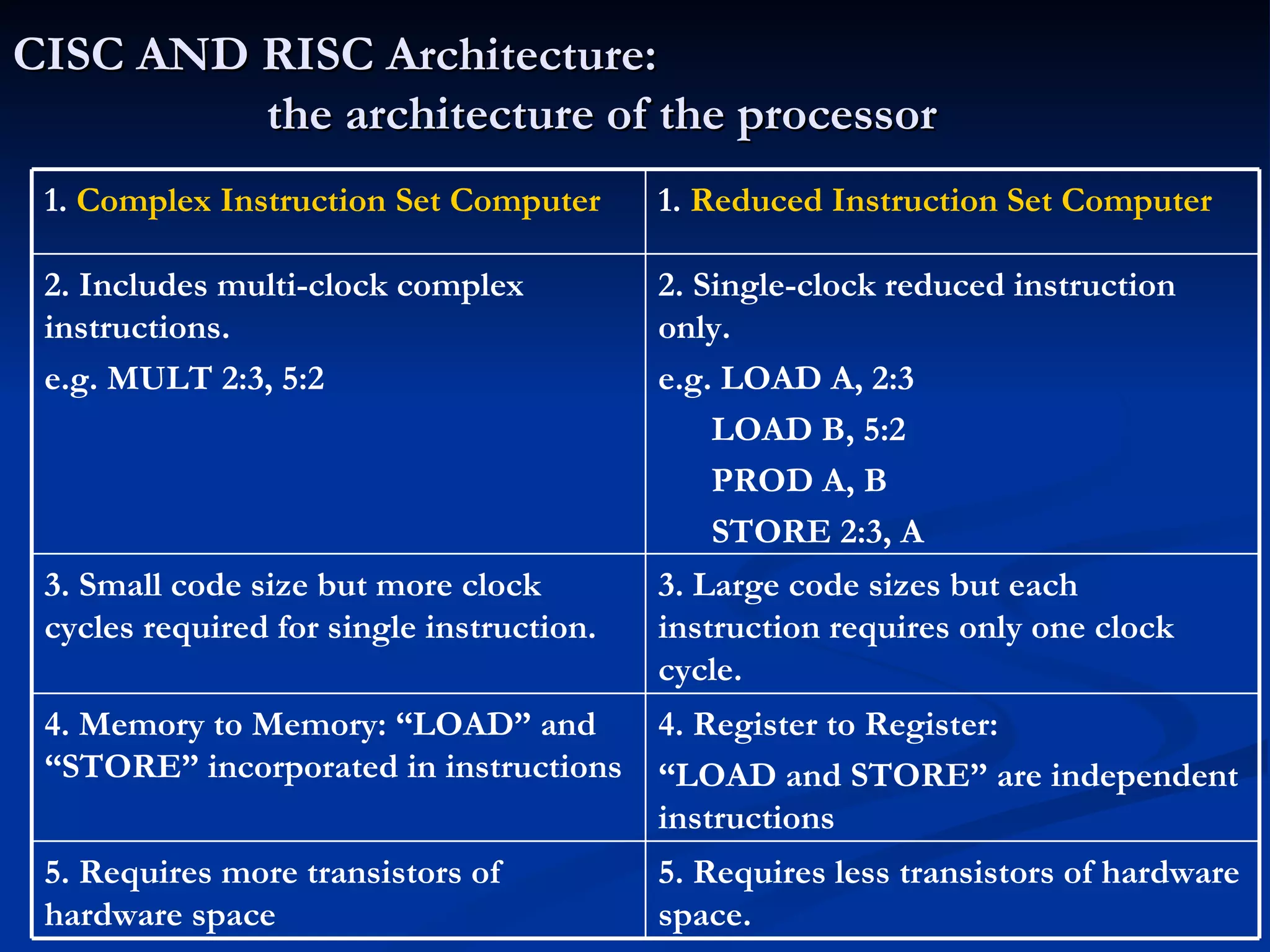
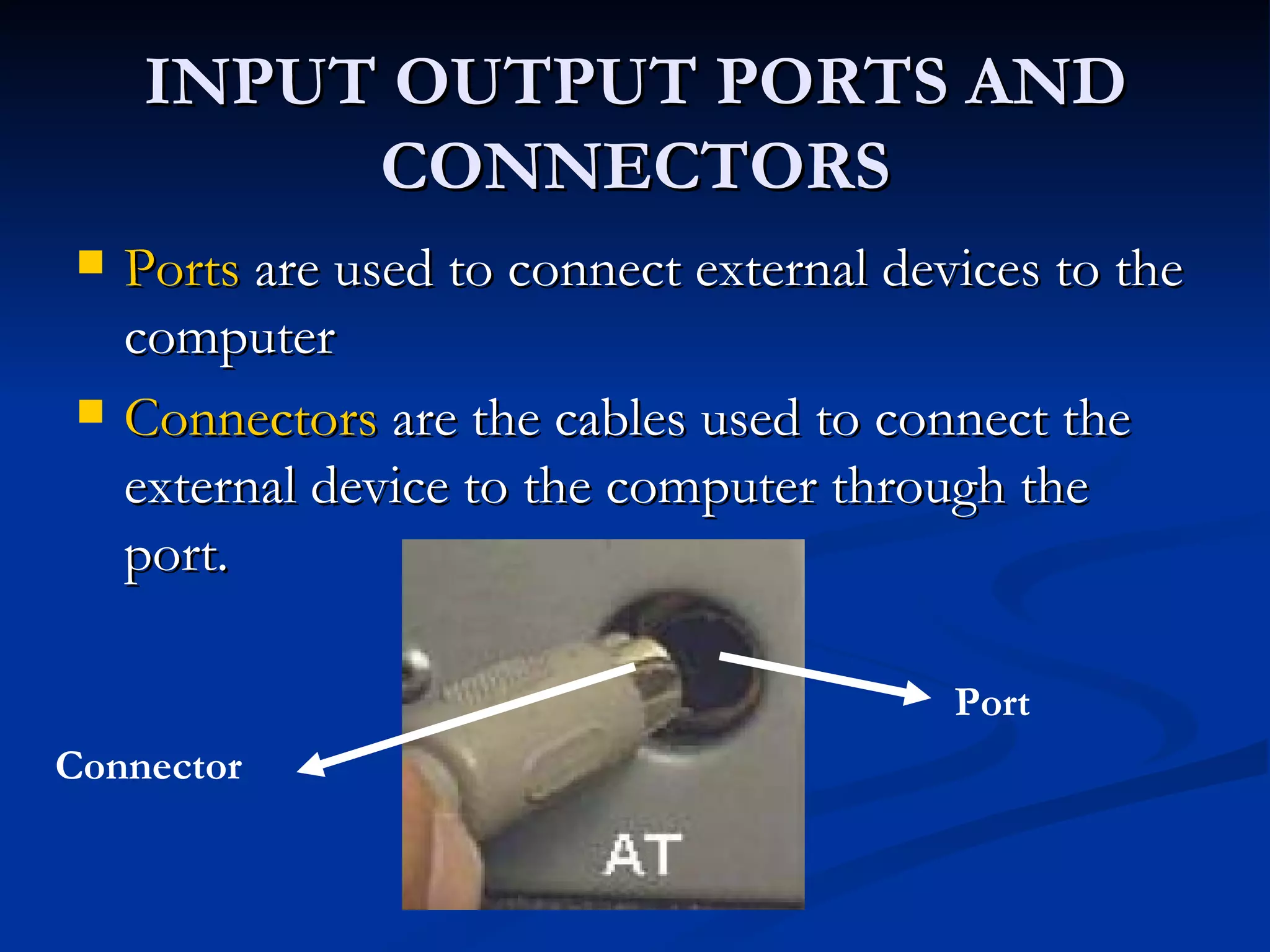
The document provides an overview of the key components of a computer system, including the input and output units, memory, central processing unit, and various ports. It describes the functions of these components and how they work together to process data and perform tasks.