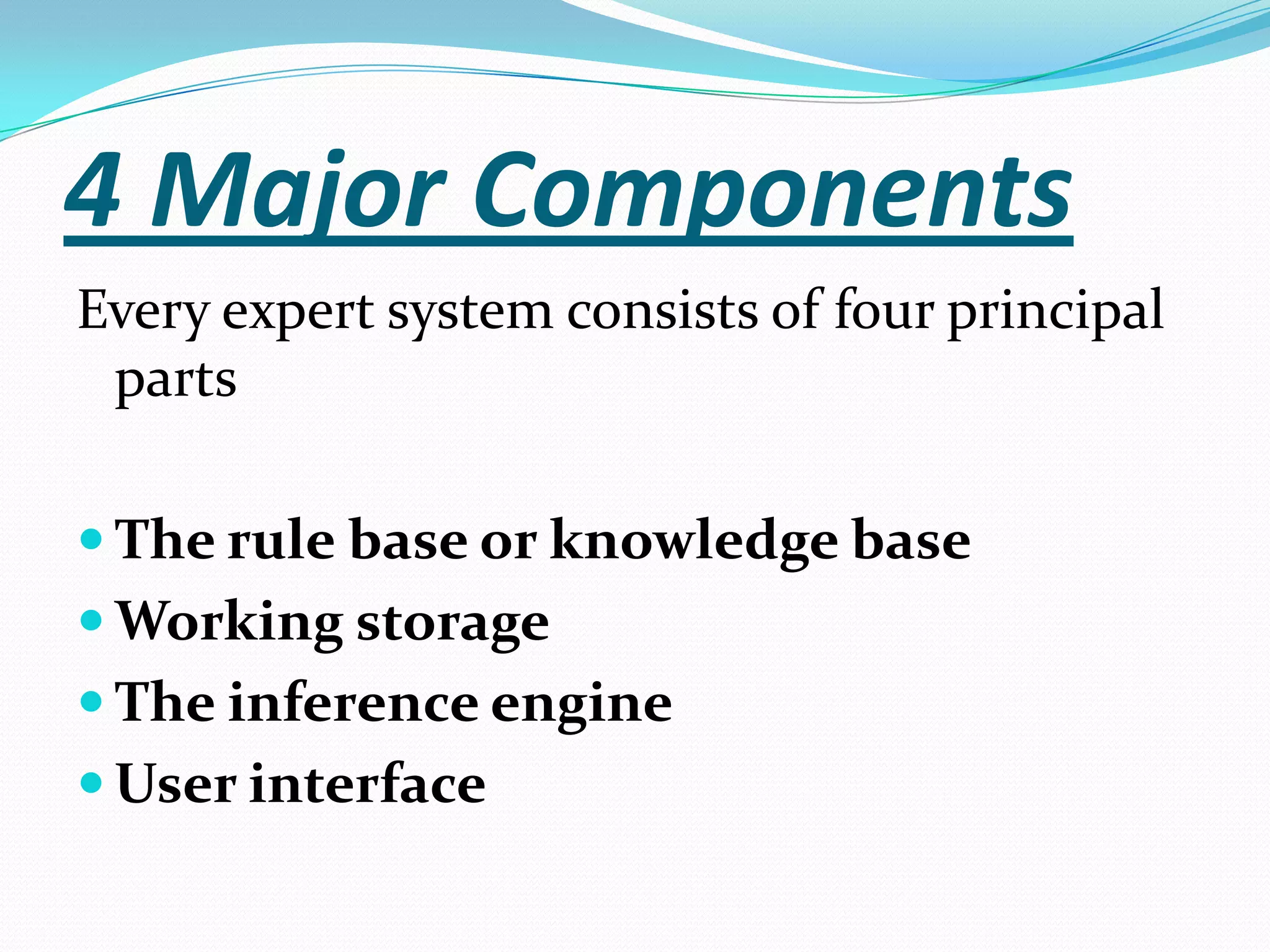
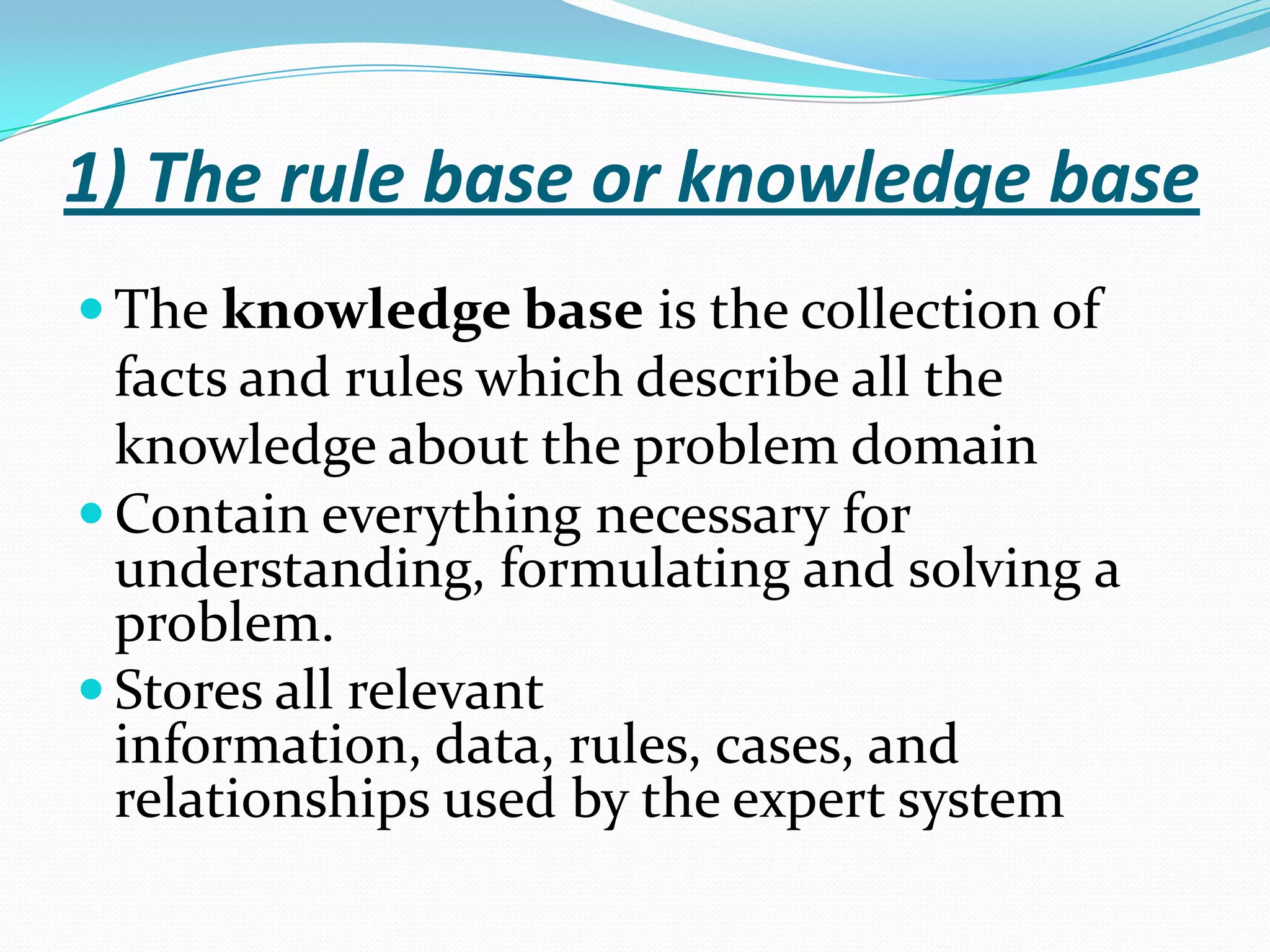
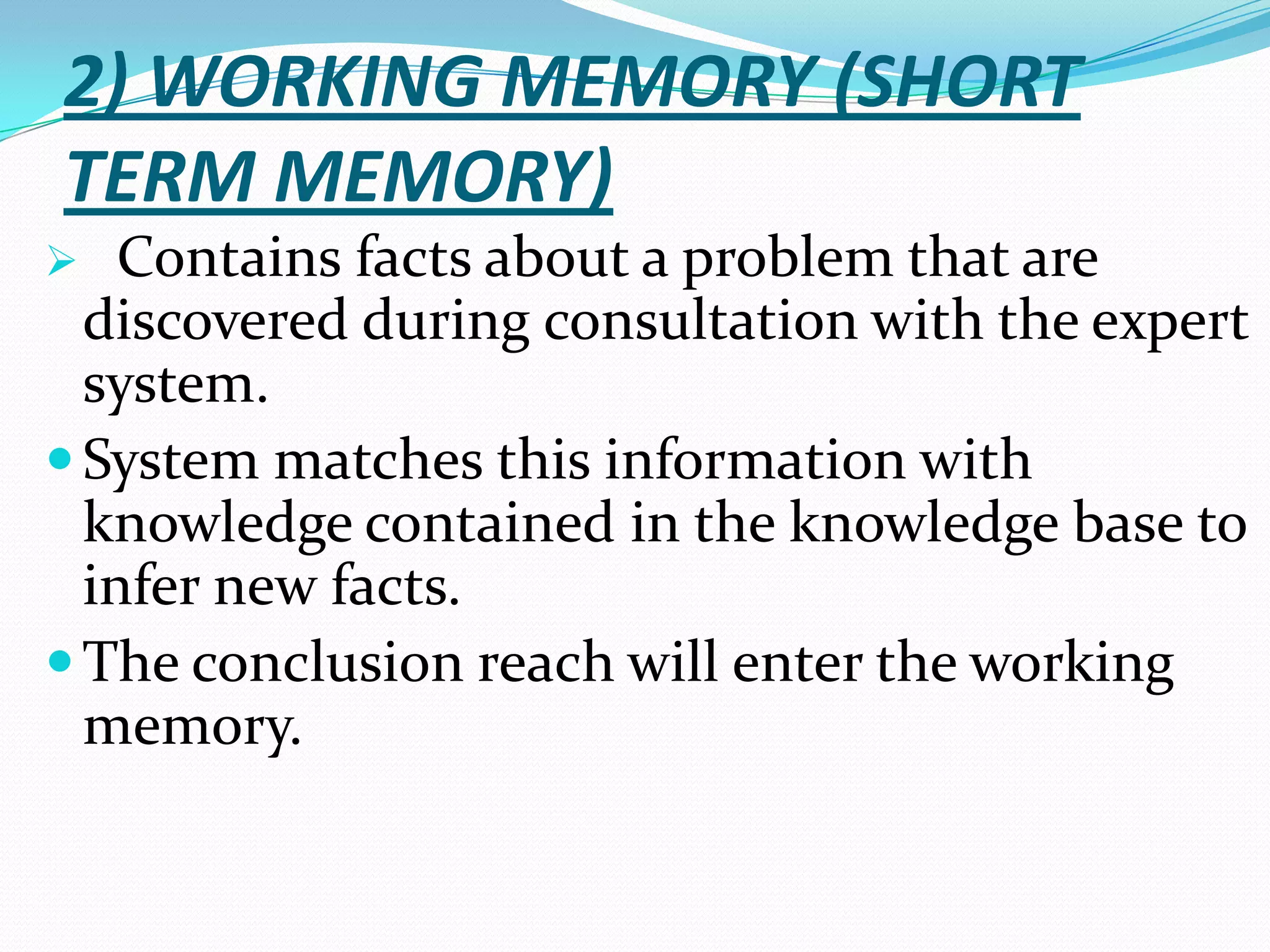
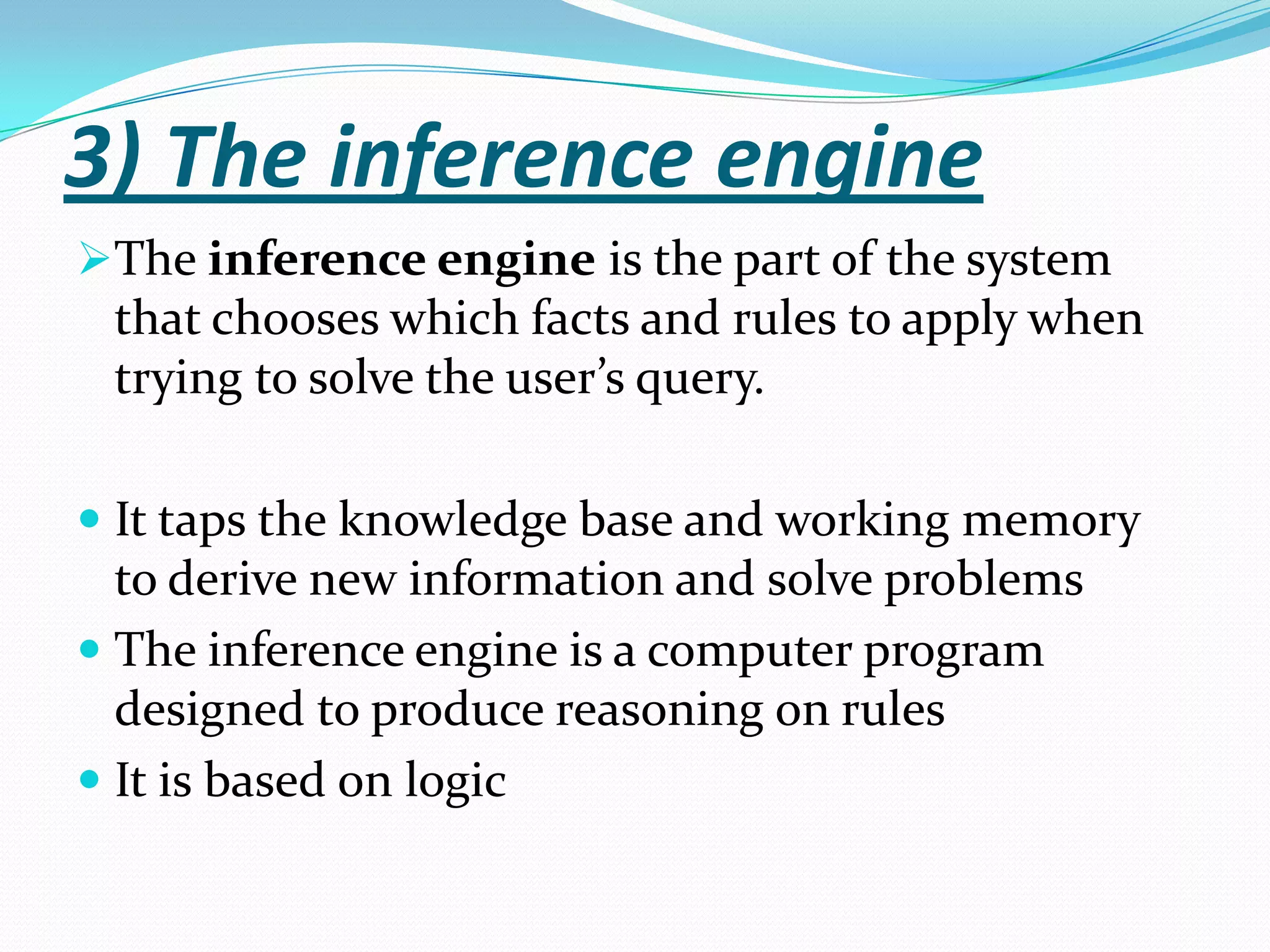
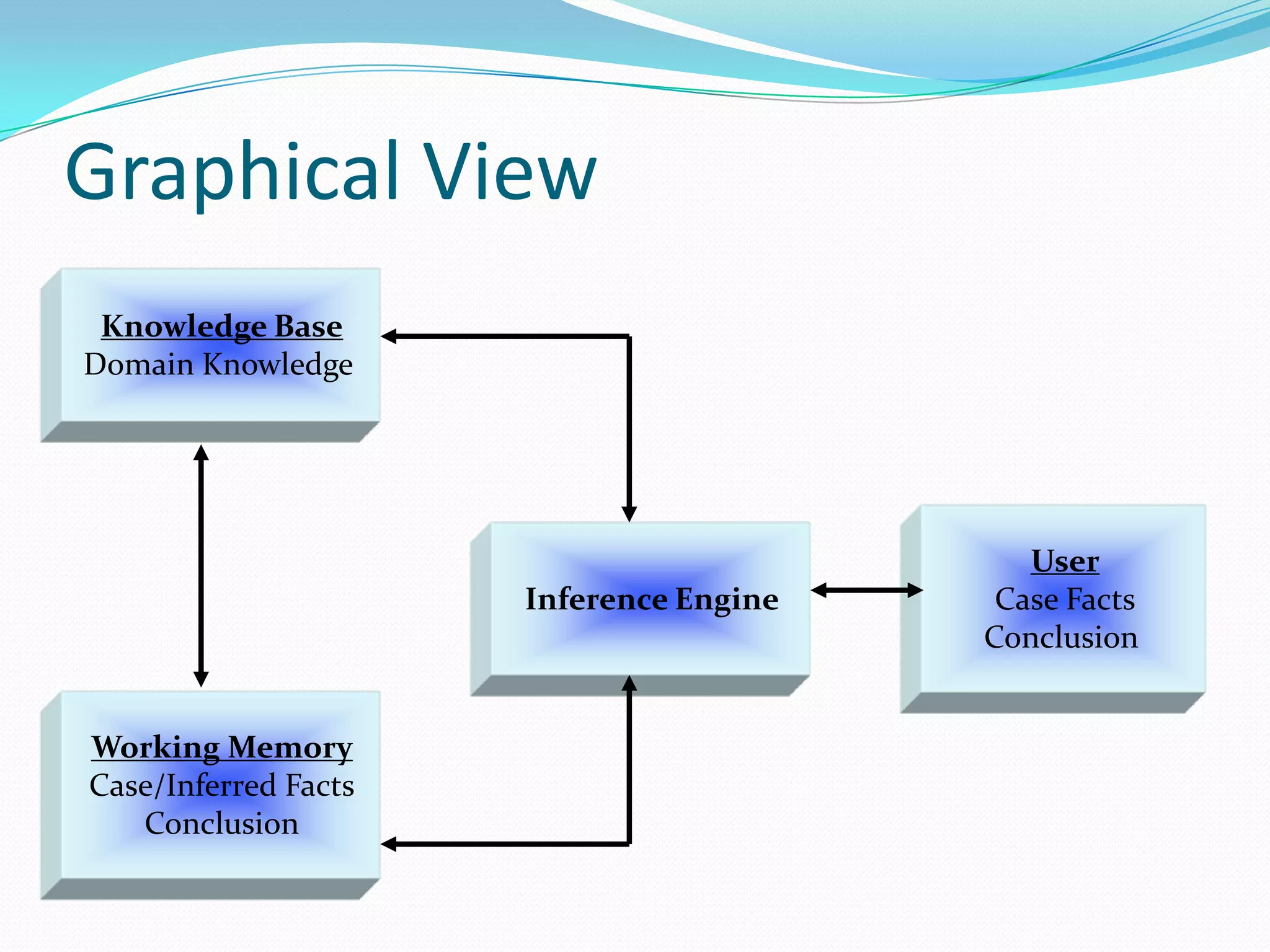
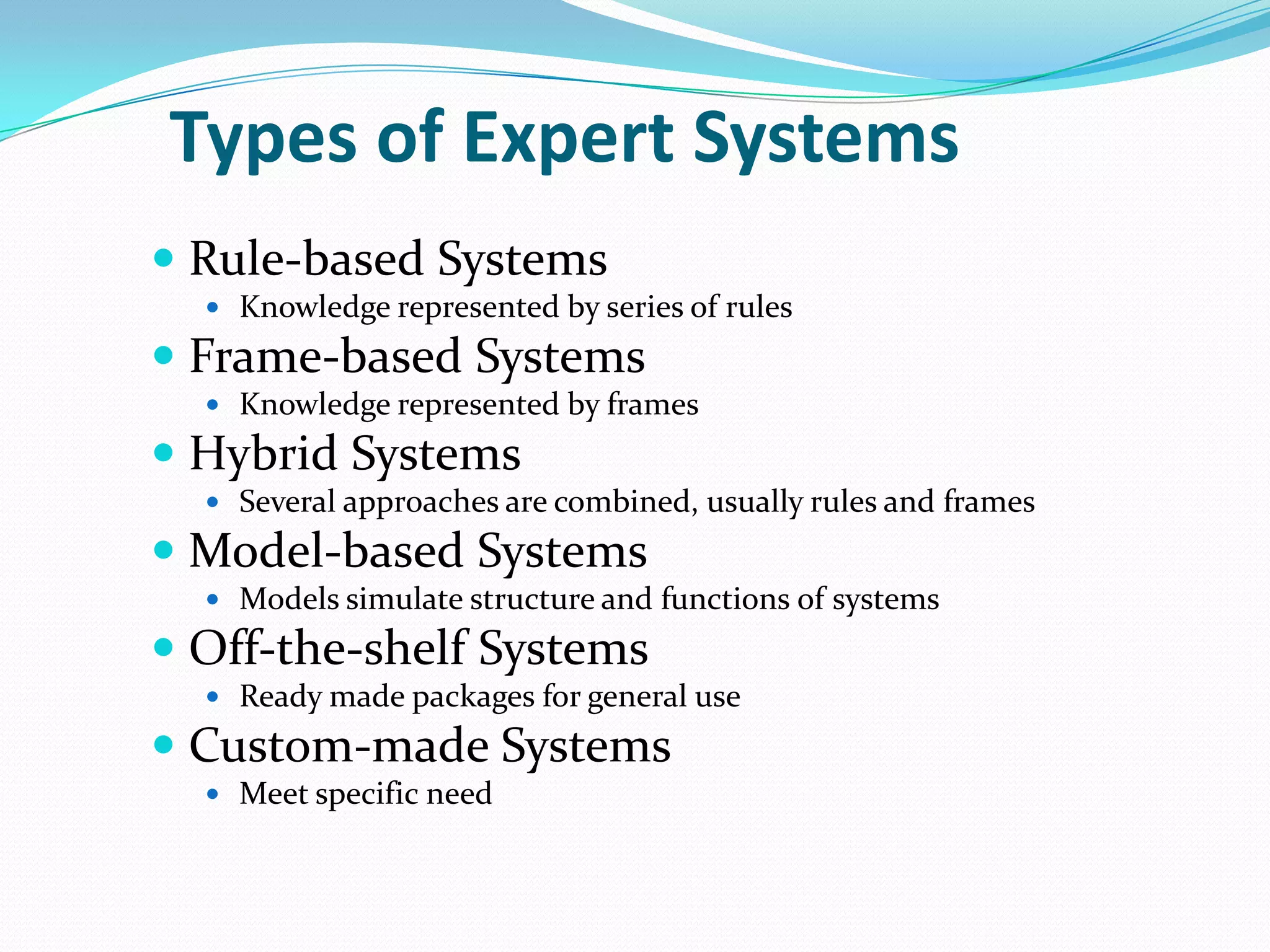
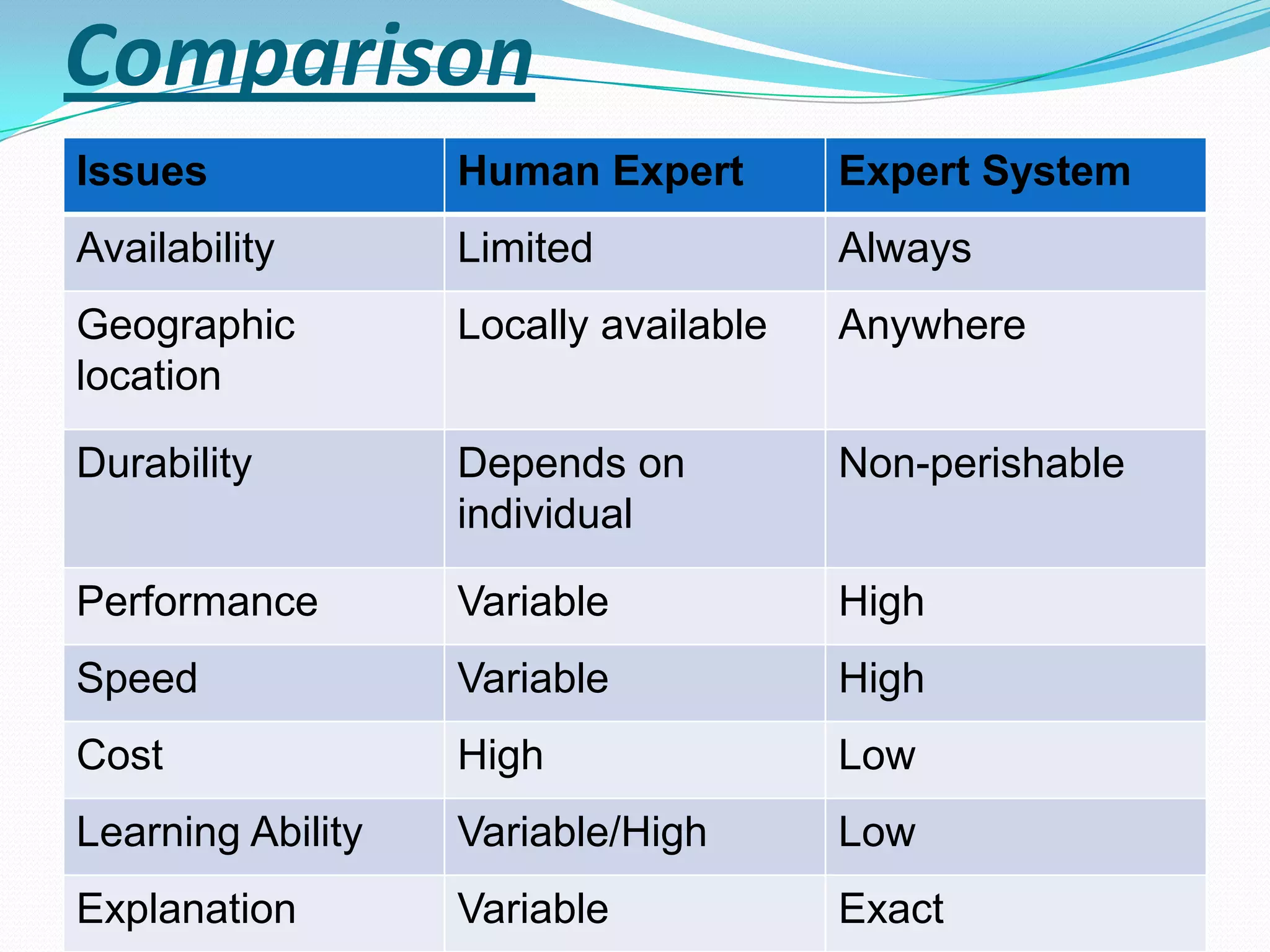
An expert system is a computer system that uses knowledge and inference rules to solve complex problems in a manner similar to a human expert. It consists of a knowledge base containing facts and rules about a problem domain, a working memory that stores facts about the current problem, an inference engine that applies rules to derive new facts and solve problems, and a user interface for communicating with users. Expert systems are designed to emulate the decision-making of human experts and provide consistent, fast solutions to problems in a domain.