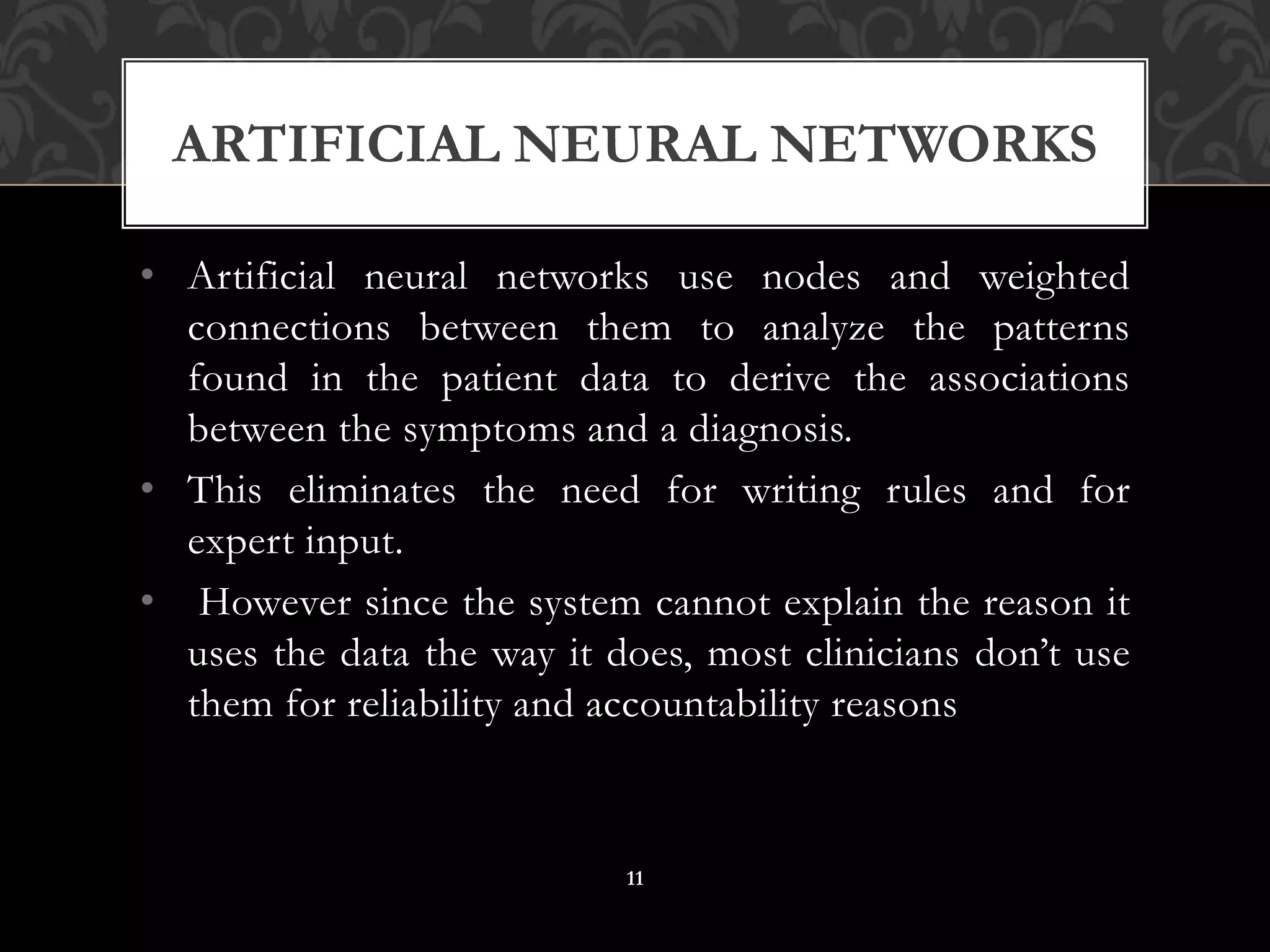
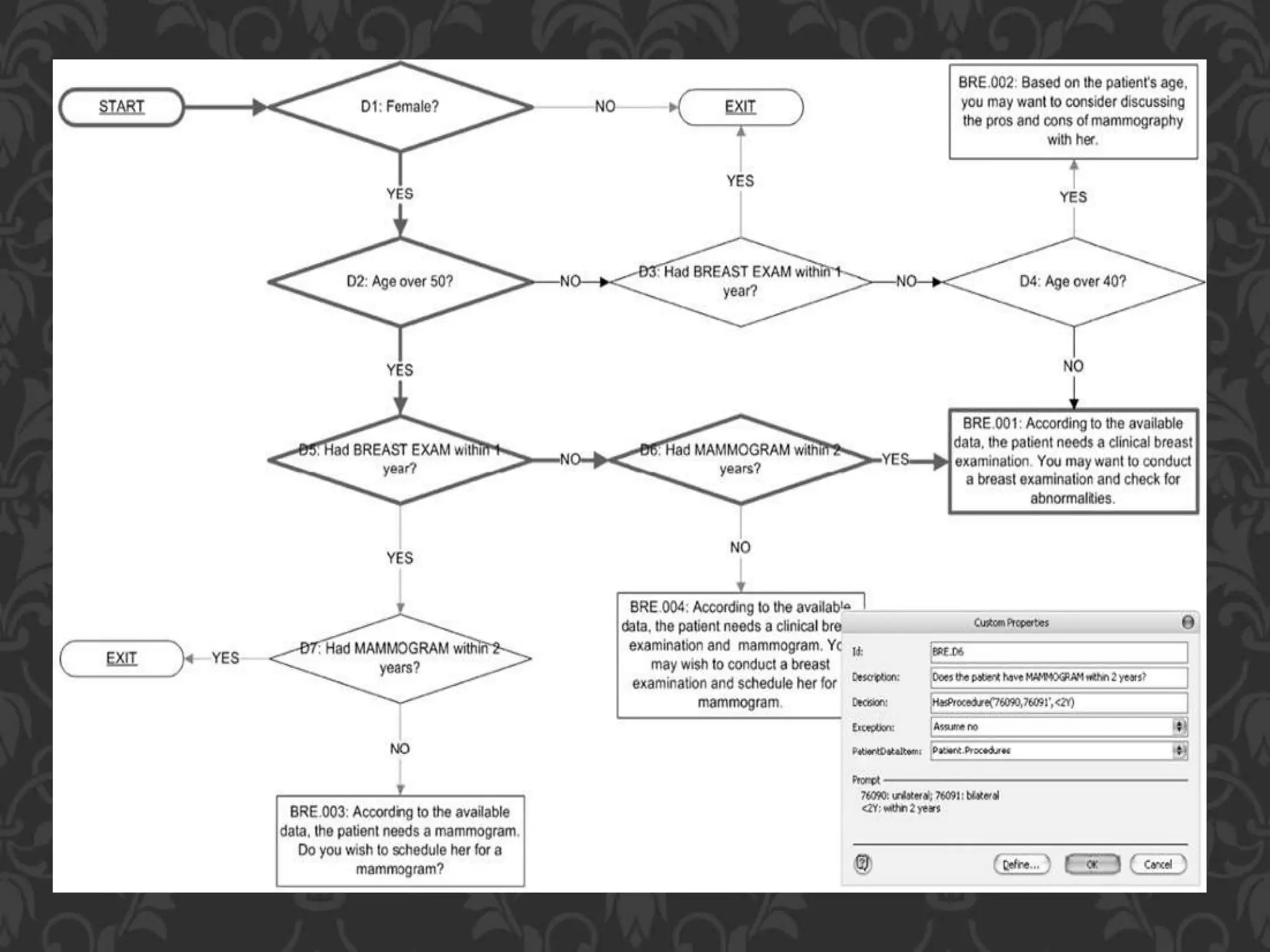
This document discusses clinical decision support systems (CDSS). It begins by defining CDSS as systems that apply medical knowledge to patient data to generate recommendations. It then provides an example of how CDSS could help prevent drug interactions. The document outlines different types of CDSS, including knowledge-based and non-knowledge-based systems using machine learning. It also discusses the history and examples of CDSS, highlighting their role in improving healthcare quality and reducing errors.