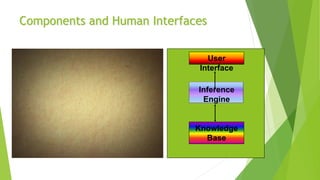
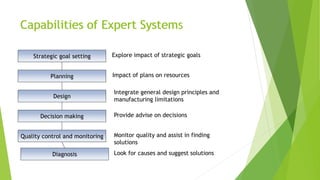
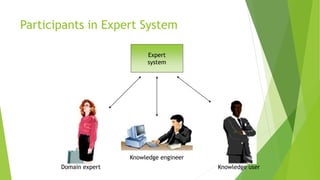
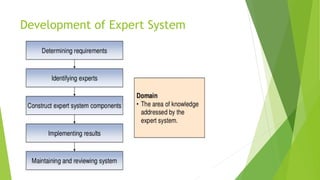
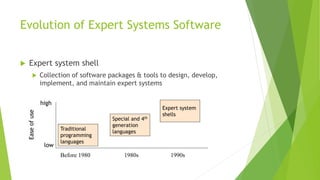
This document discusses AI with expert systems. It begins with an introduction to AI, noting its branches include game playing, expert systems, natural language processing, neural networks, and robotics. It then introduces expert systems, which emulate human decision making through knowledge bases and inference engines. The components of expert systems are described as the knowledge base, inference engine, and rules. Capabilities include strategic decision making, planning, and diagnosis. Expert system development involves domain experts, knowledge engineers, and knowledge users. The document traces the evolution of expert system software from traditional programming to expert system shells. It concludes with potential applications in fields like banking, healthcare, and customer service.