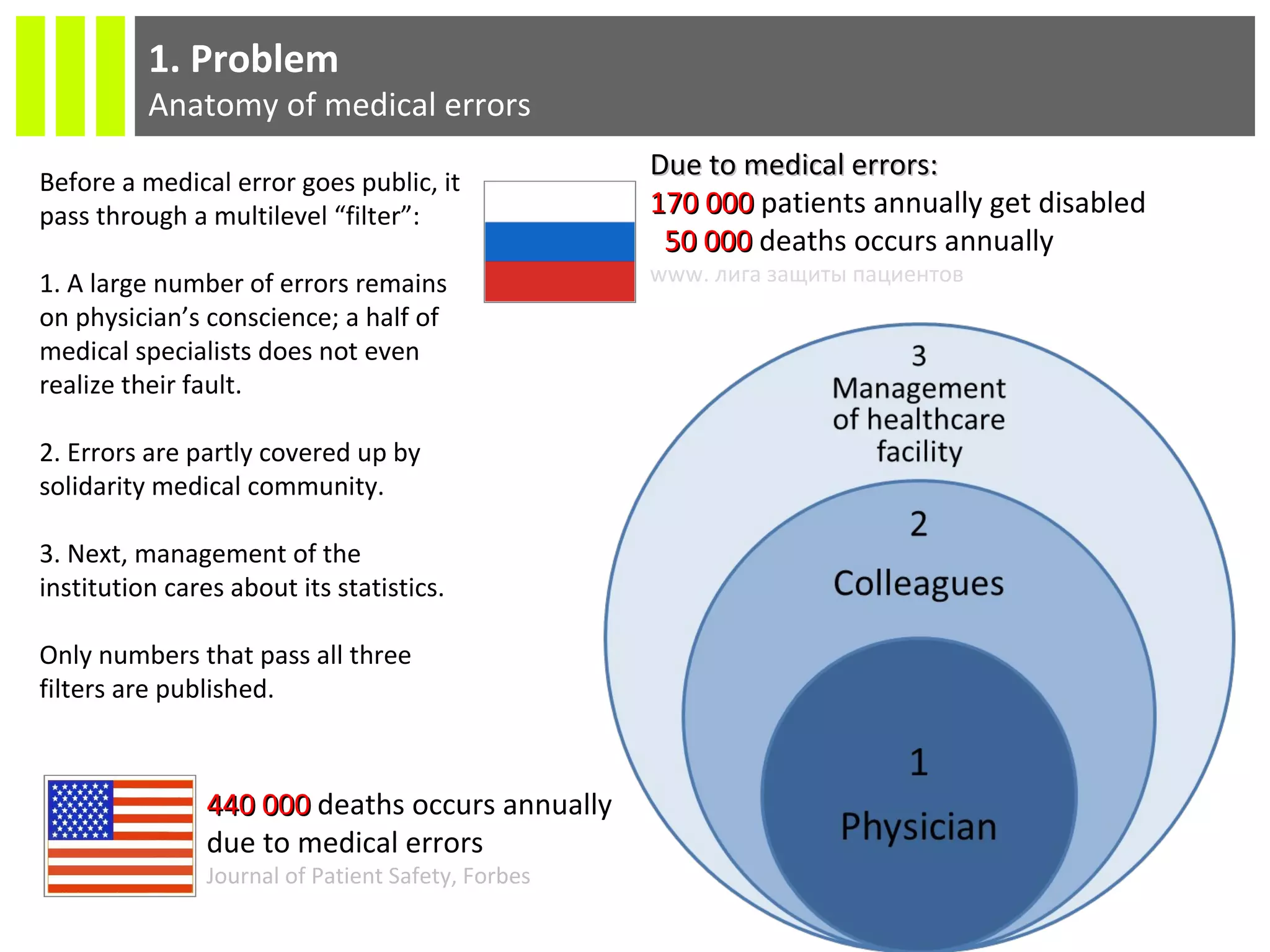
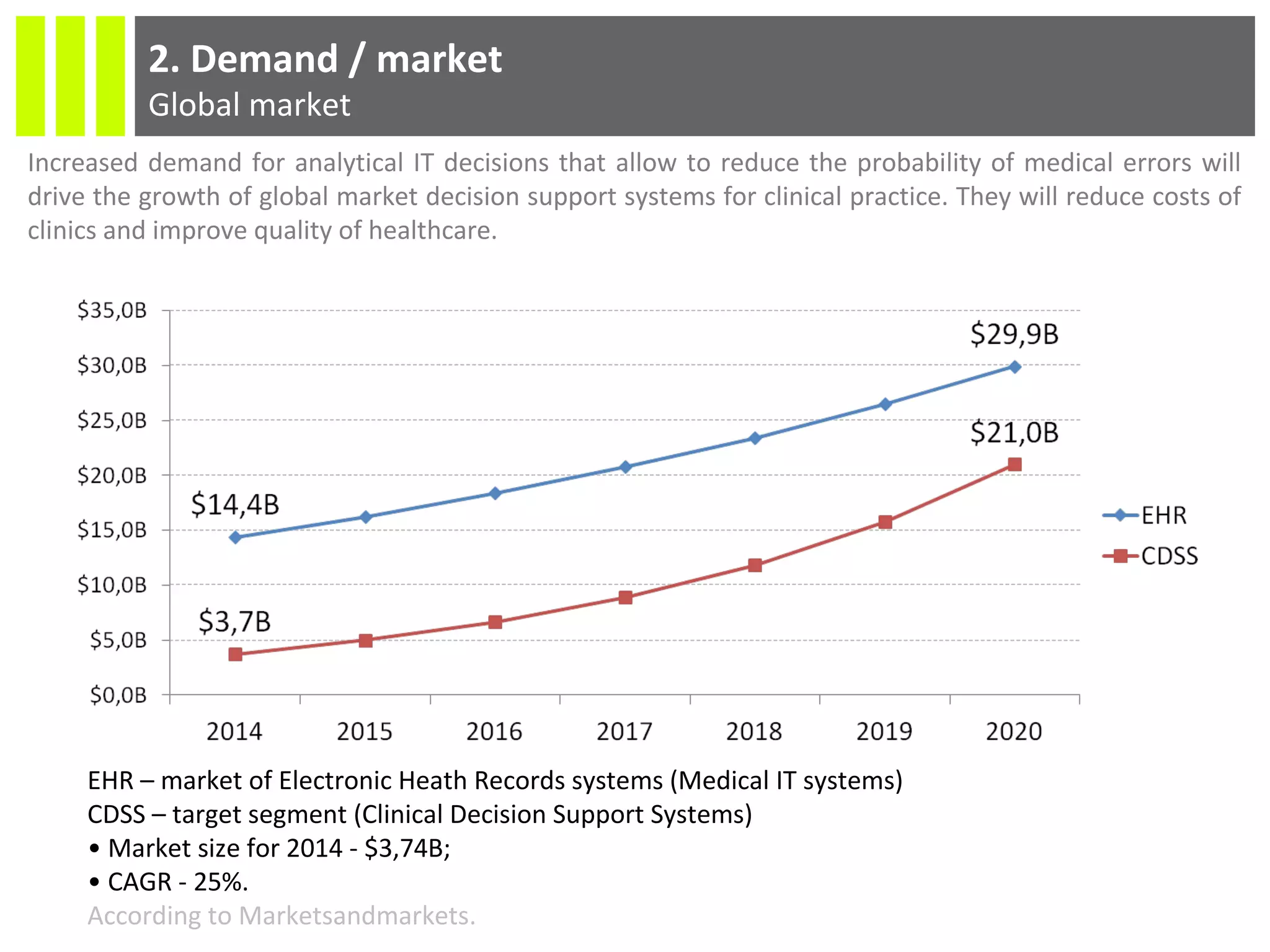
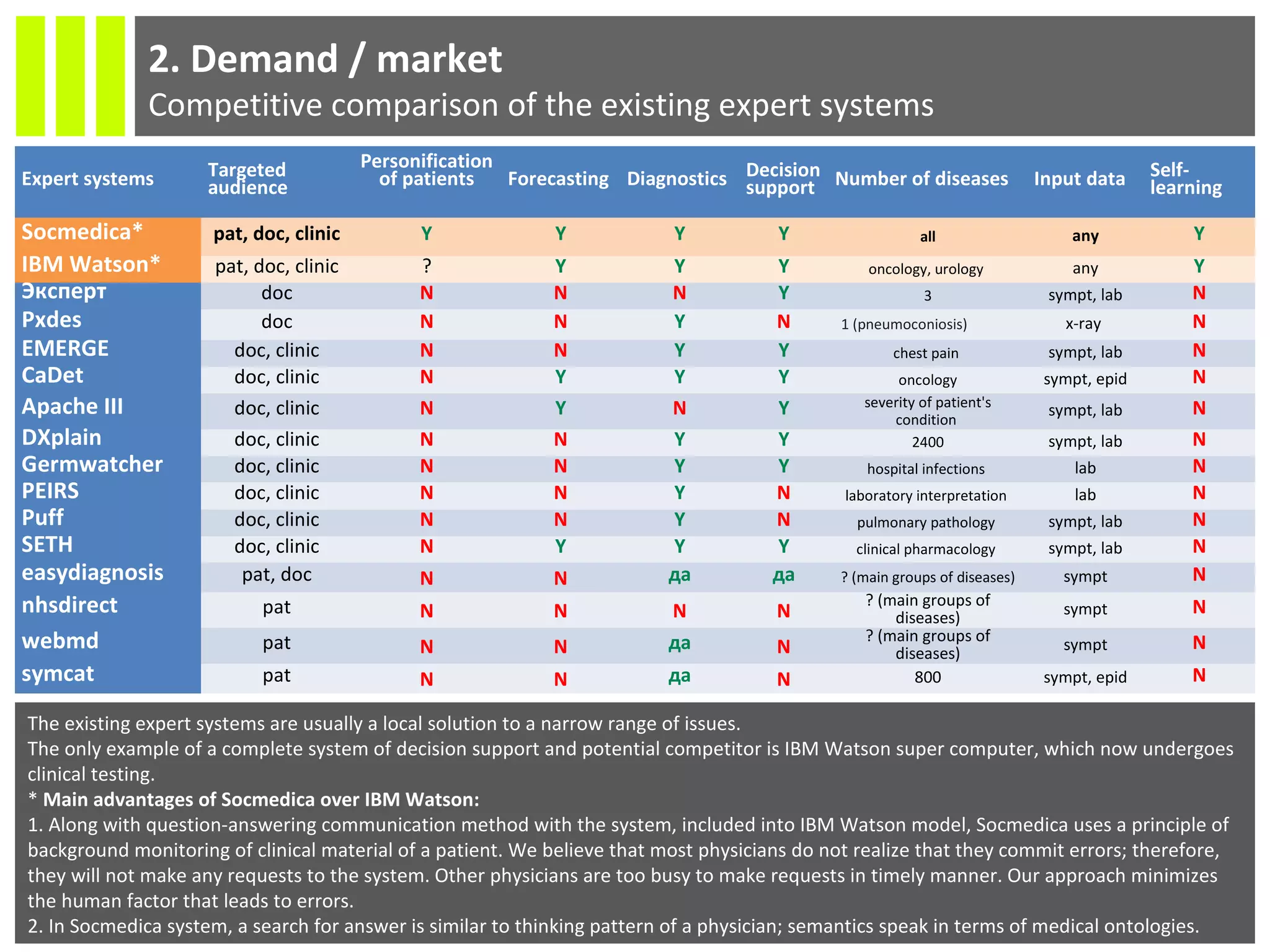
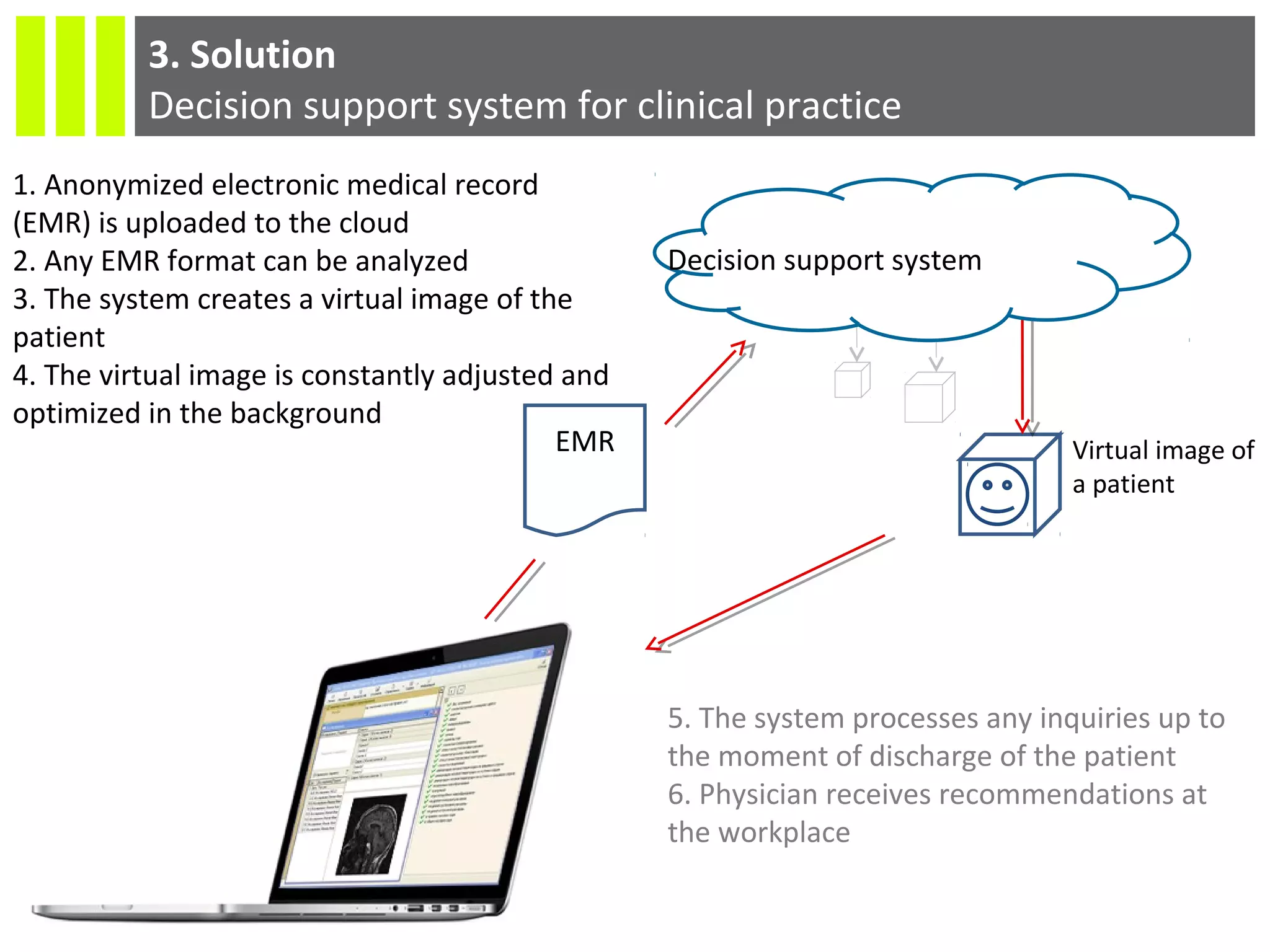
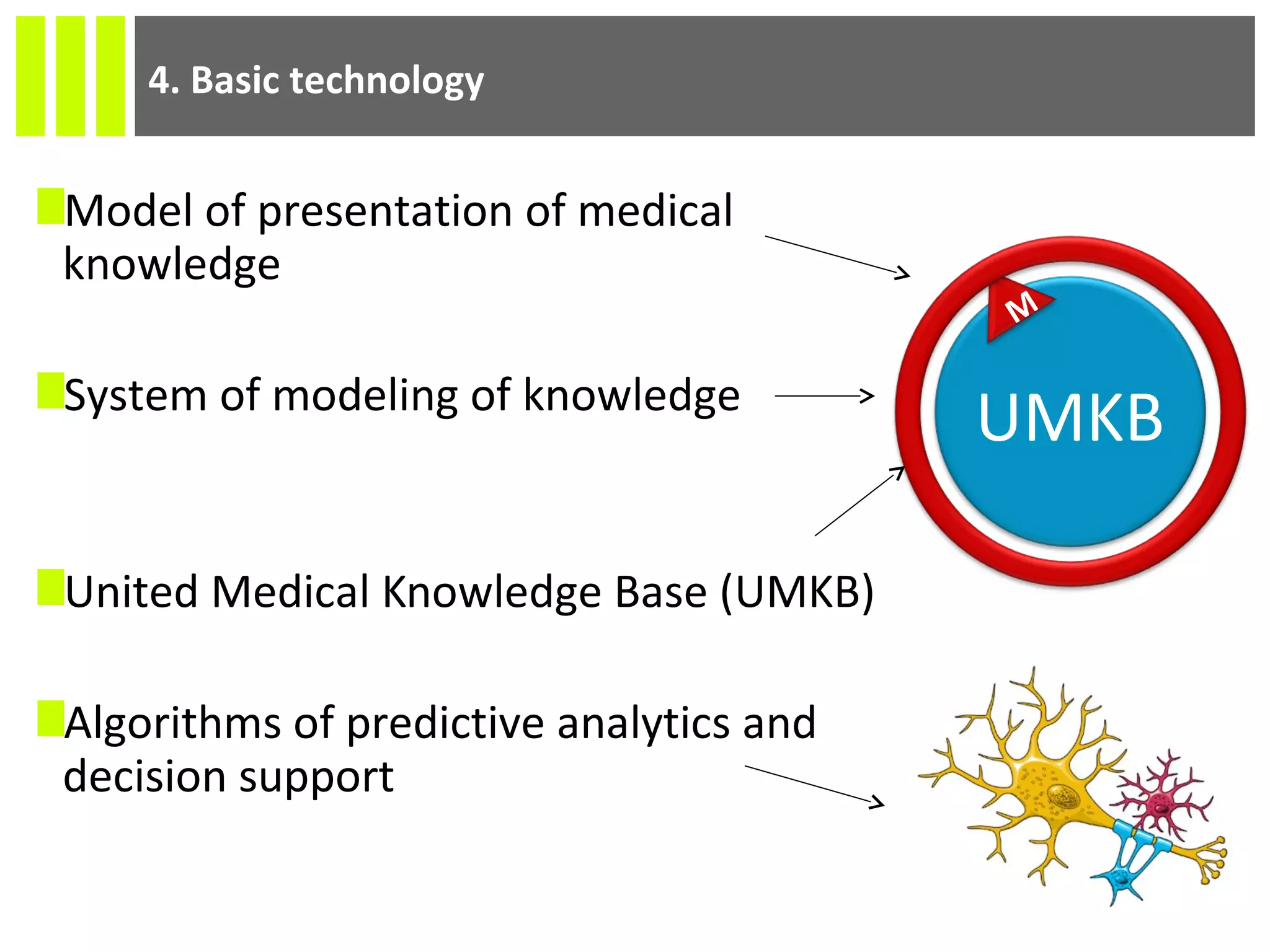
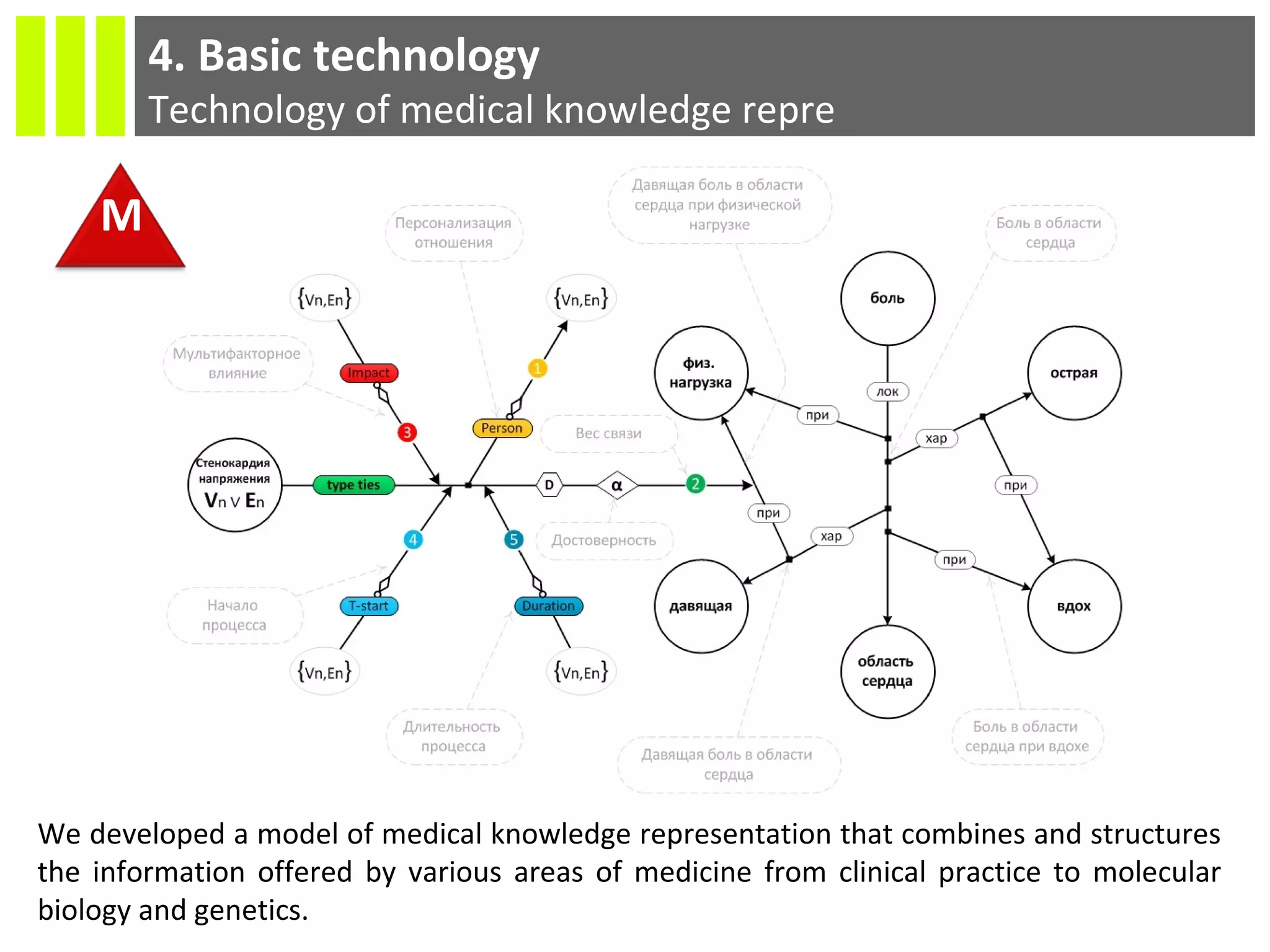
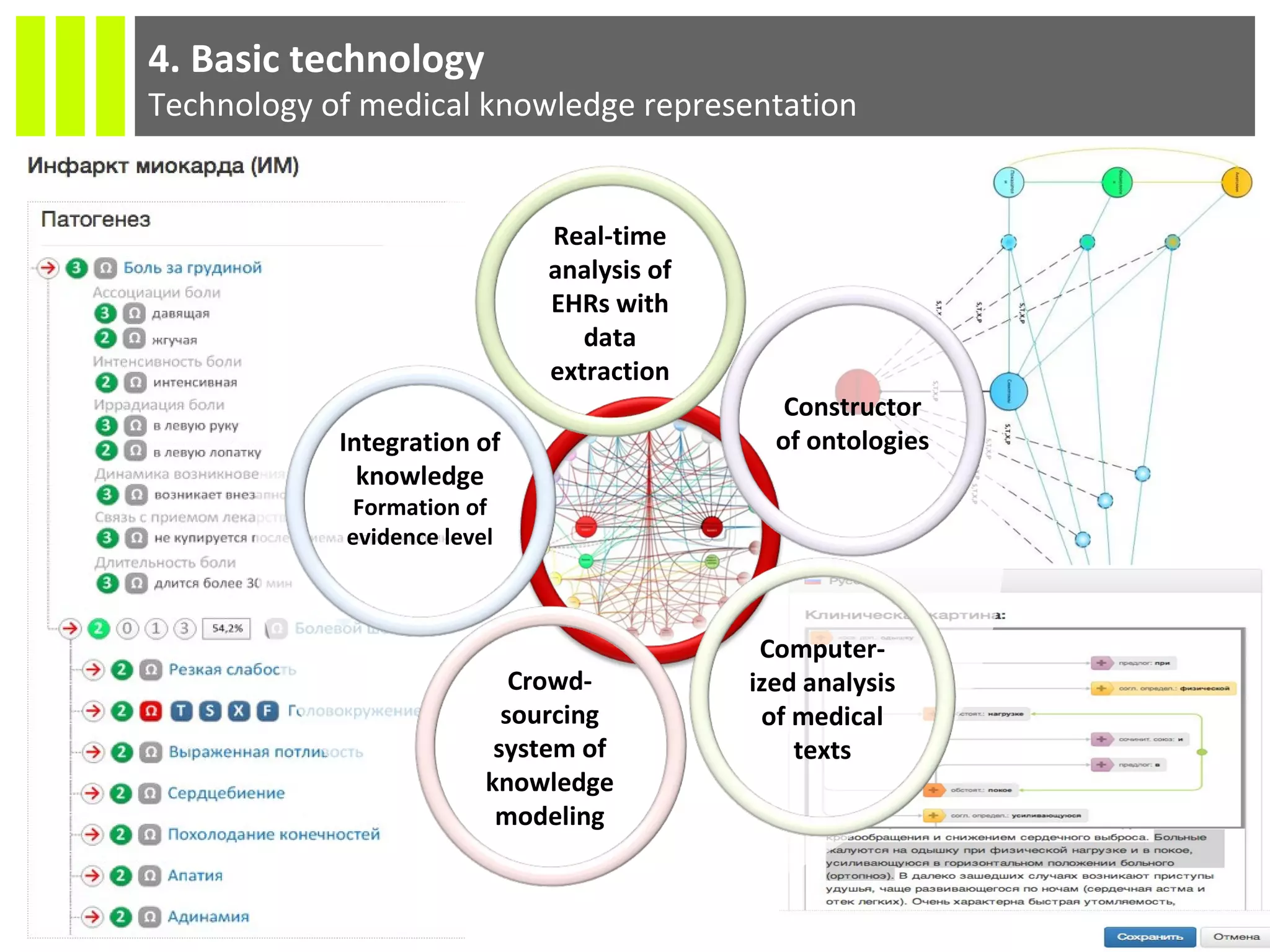
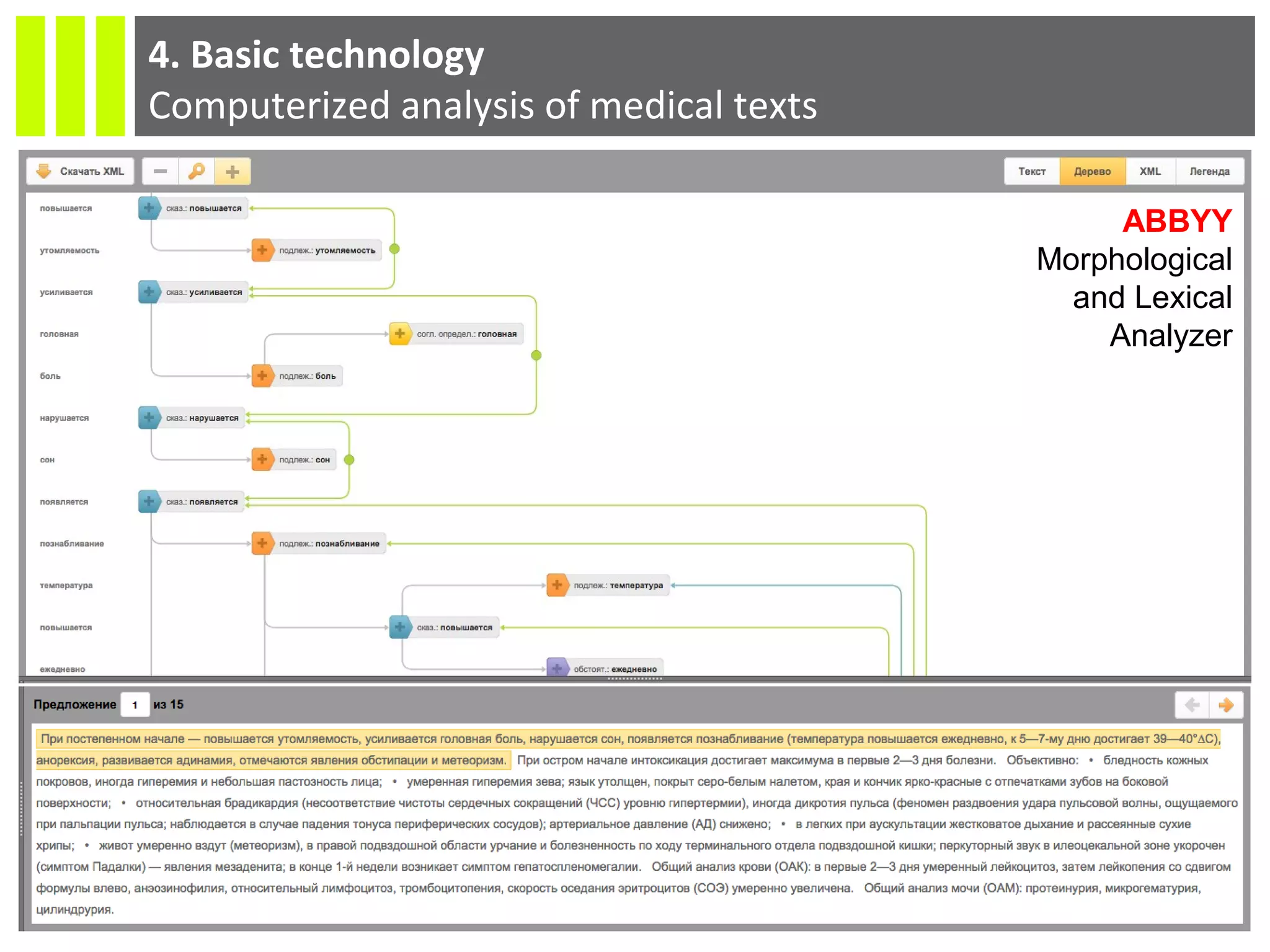
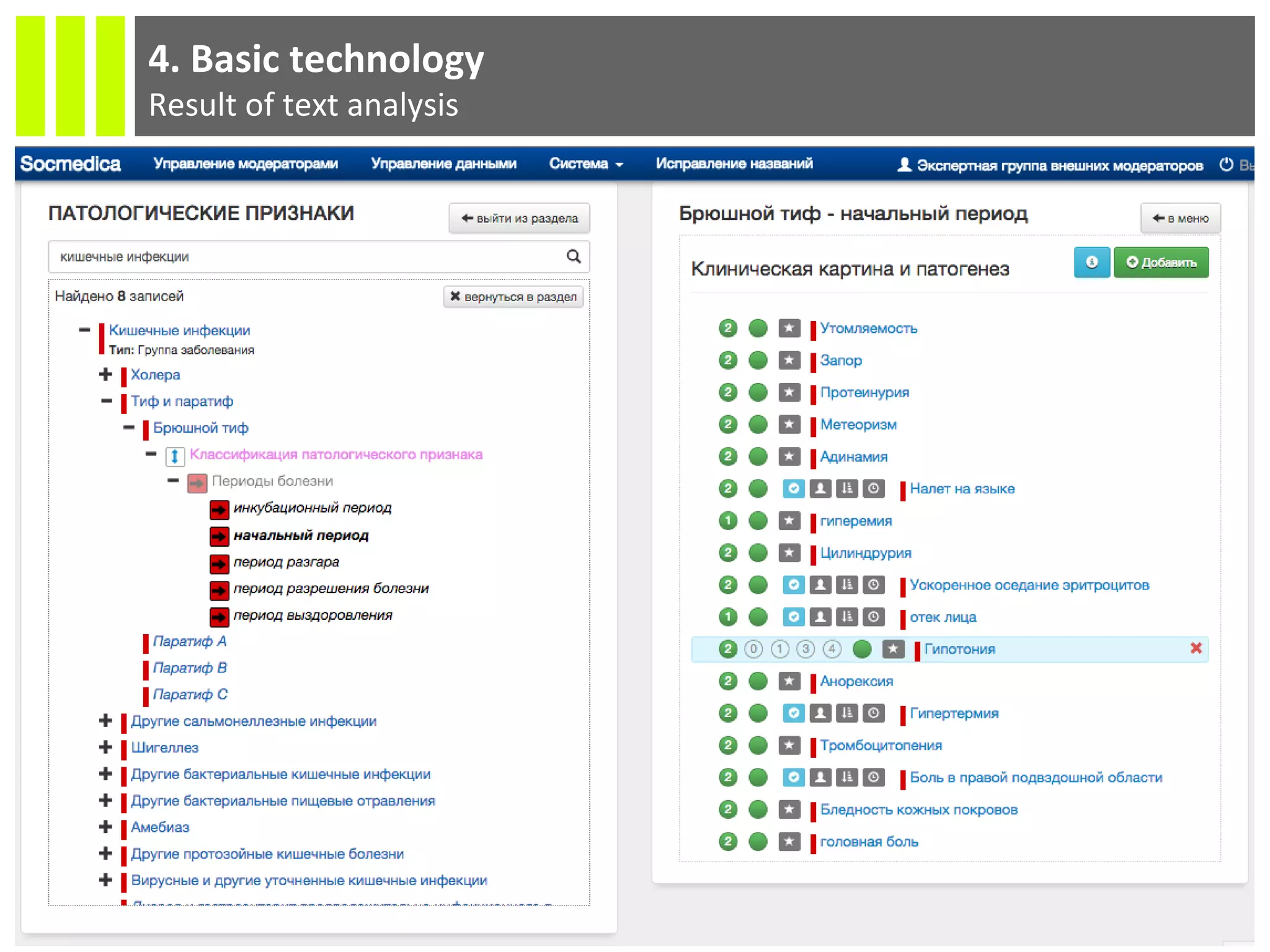
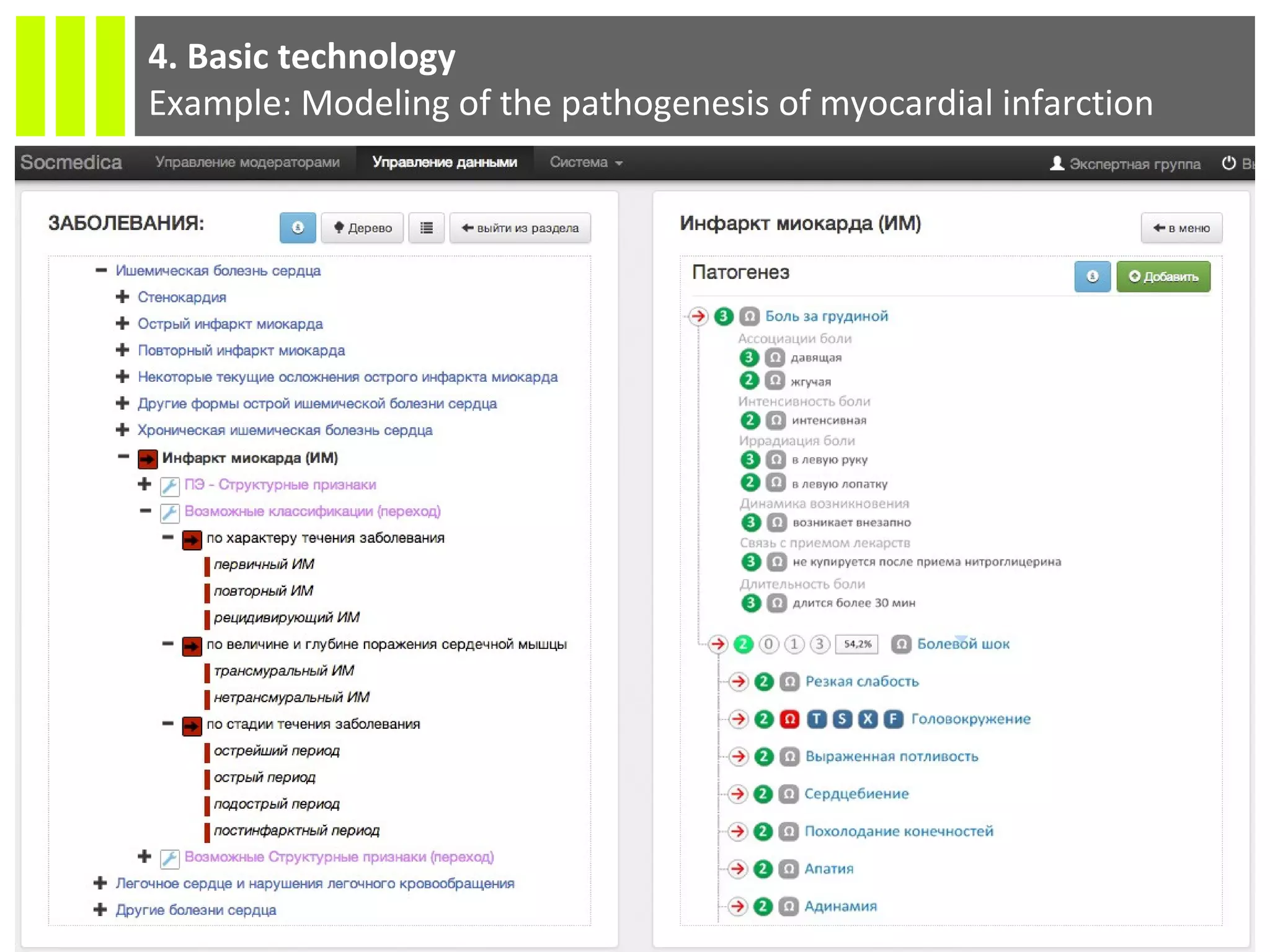
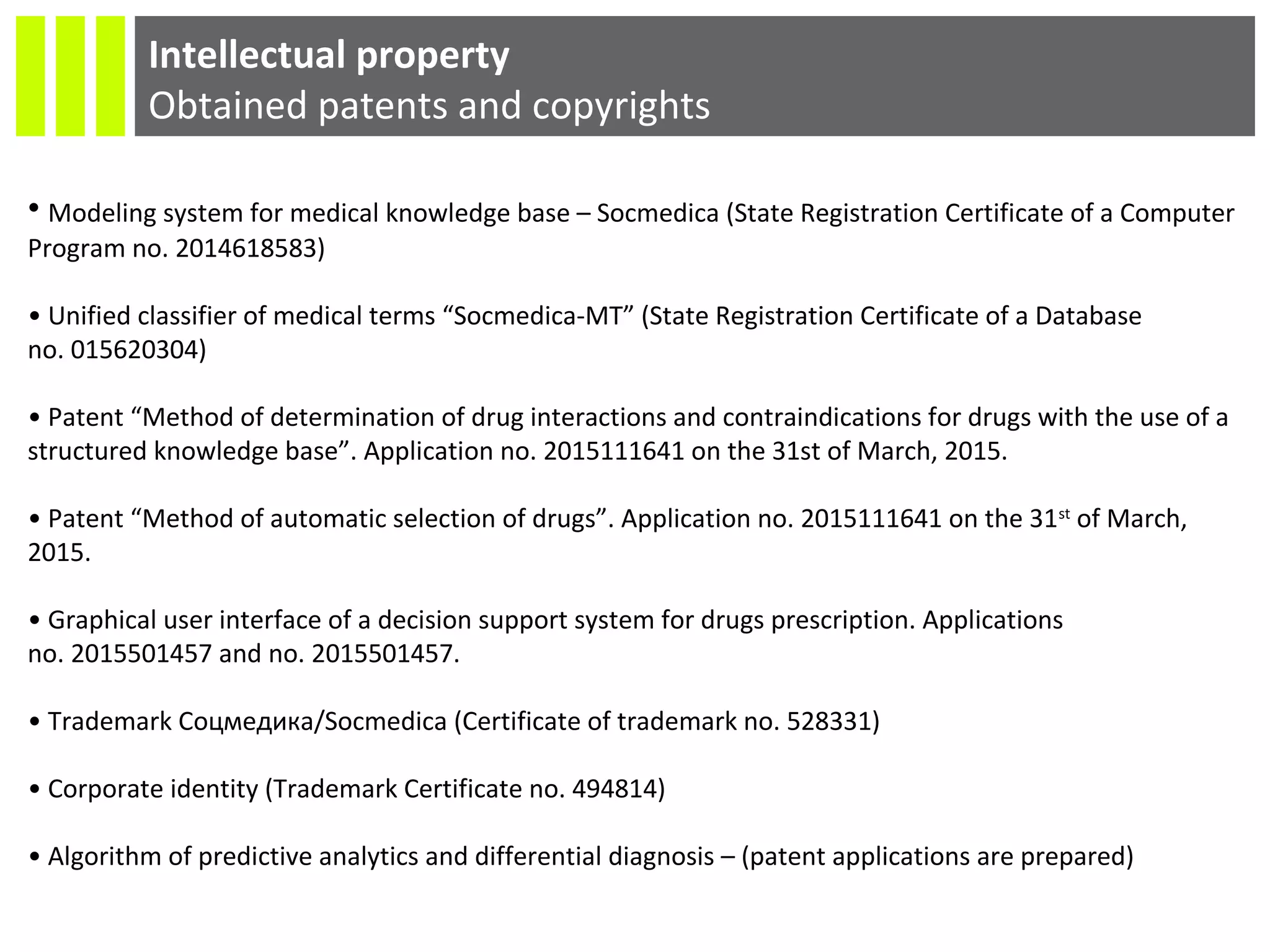
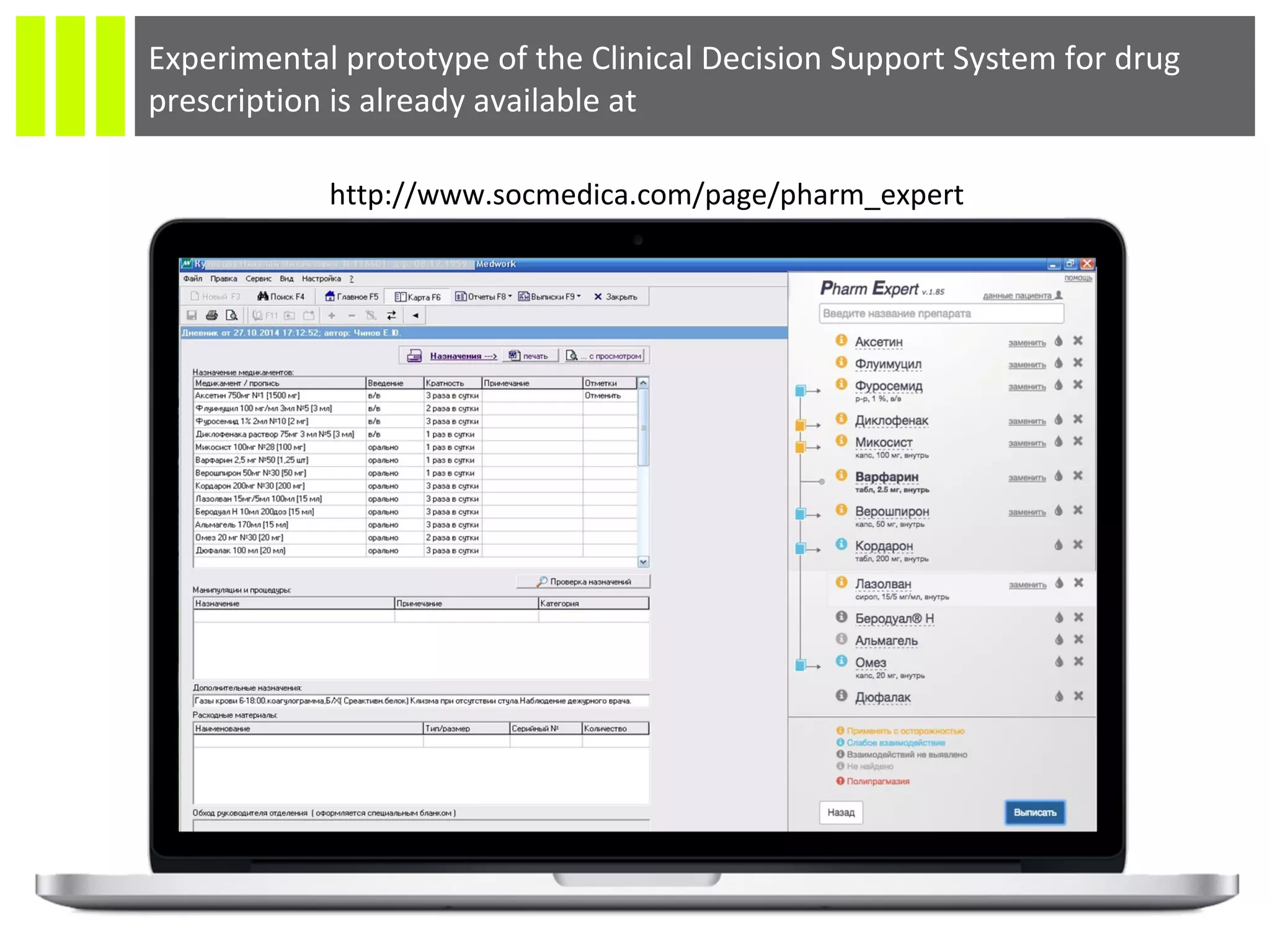
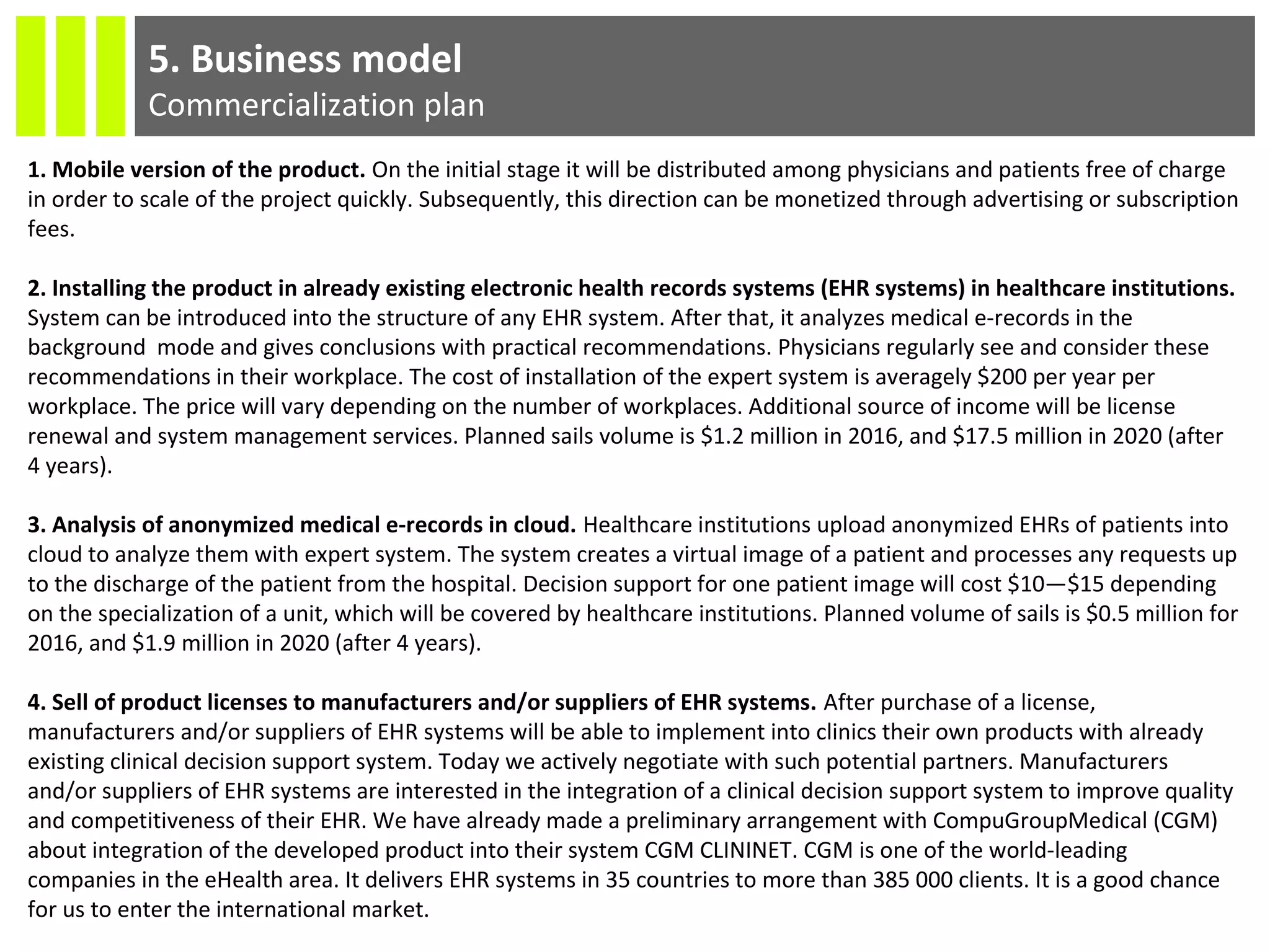
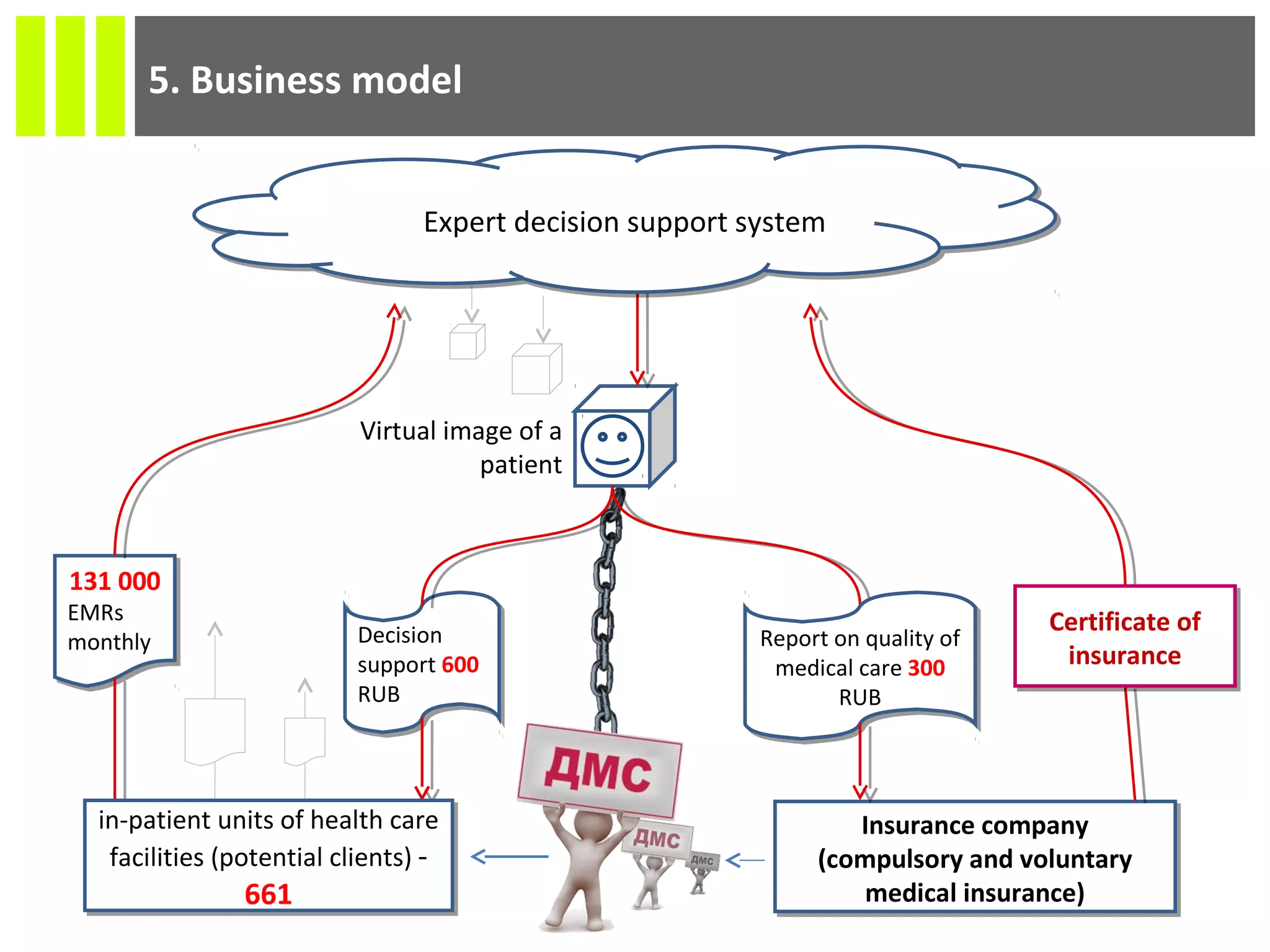
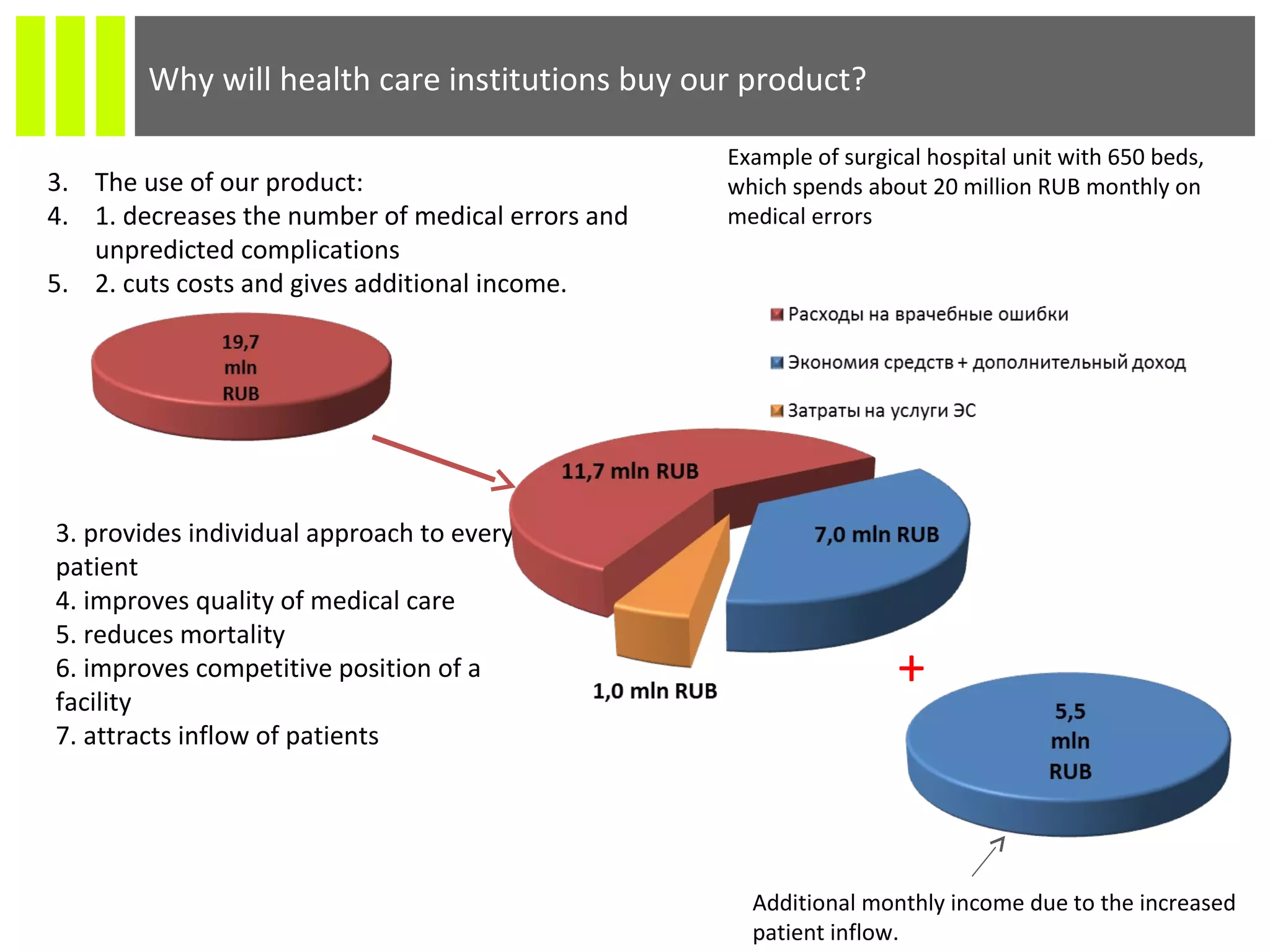
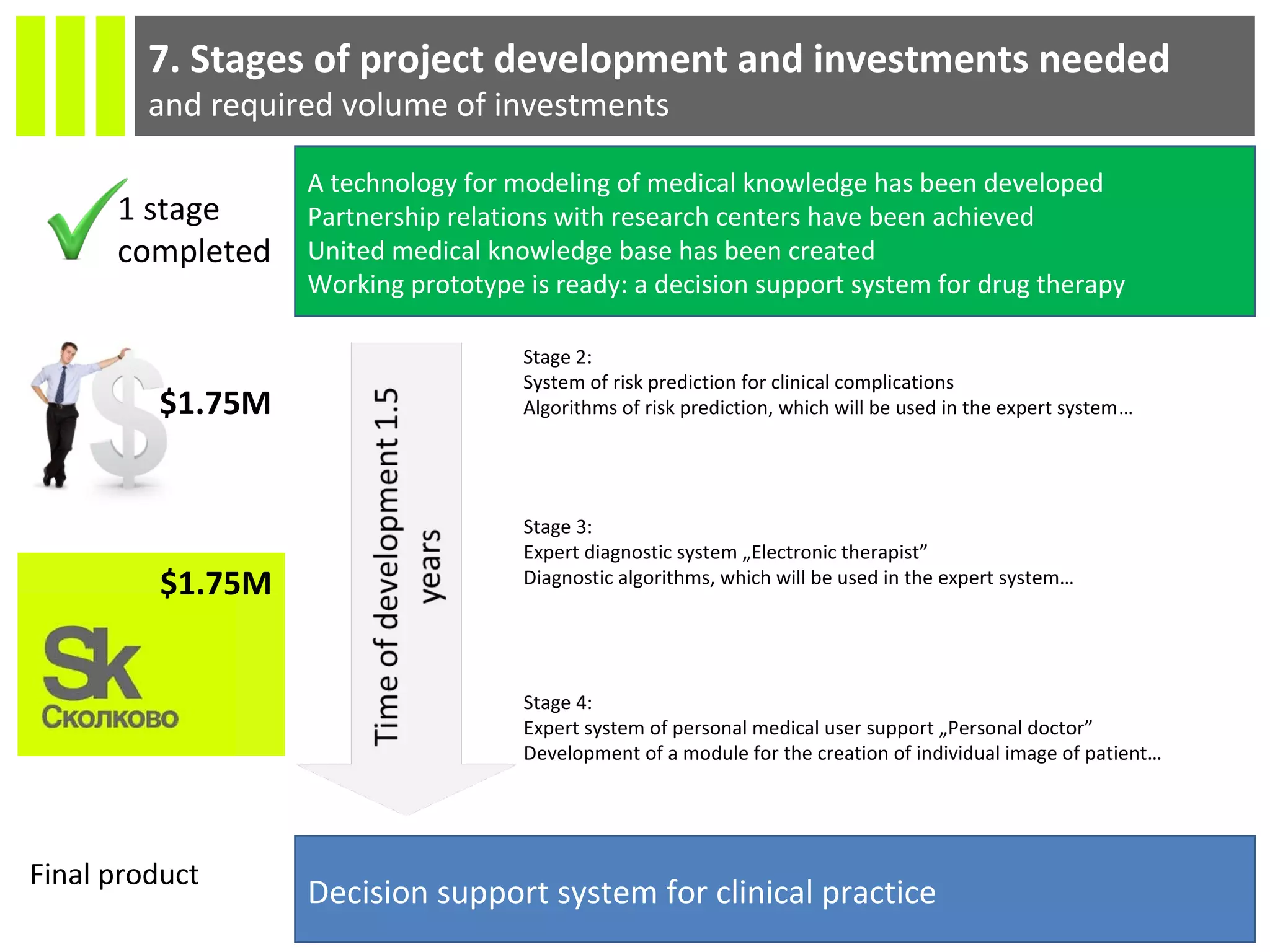
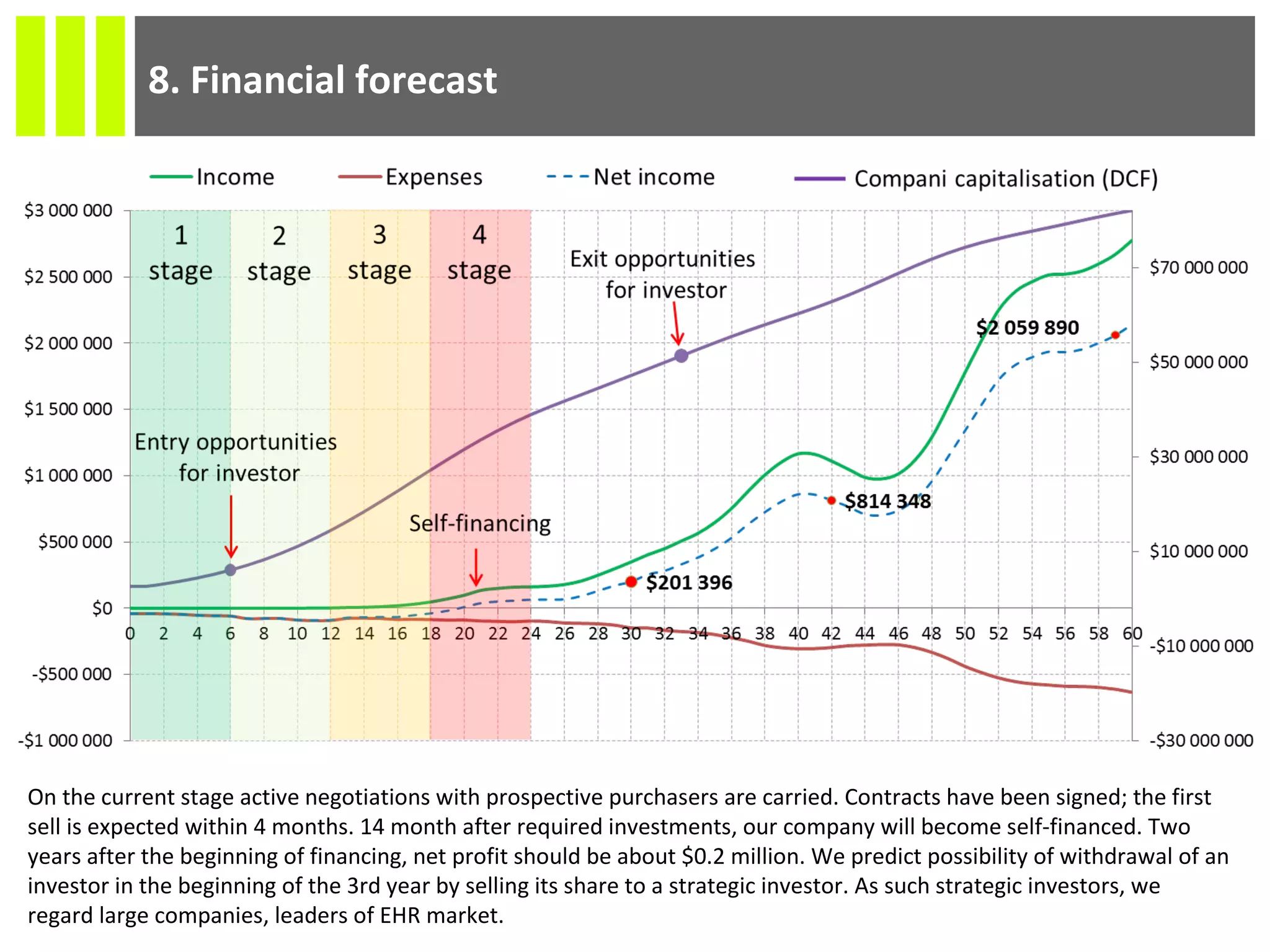
The document discusses the Socmedica decision support system designed to reduce medical errors and complications in clinical practice, highlighting the significant annual costs and mortality rates associated with medical errors. It outlines the demand for electronic health record (EHR) systems and clinical decision support systems (CDSS) in healthcare, emphasizing the market potential and competitive advantages of Socmedica over existing solutions like IBM Watson. The business model includes free distribution initially to scale the user base, followed by monetization through installation in EHR systems and analysis of anonymized medical records.