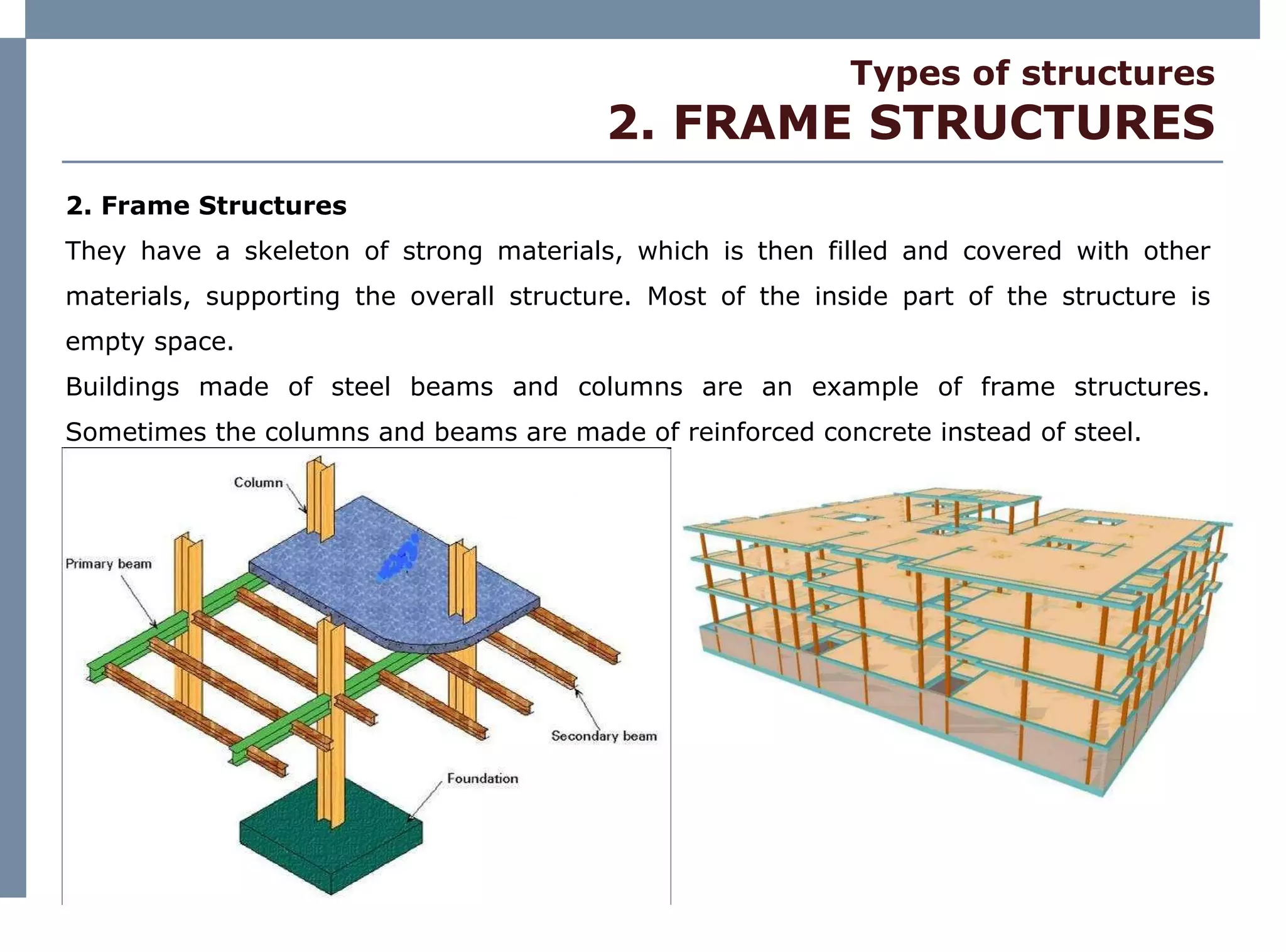
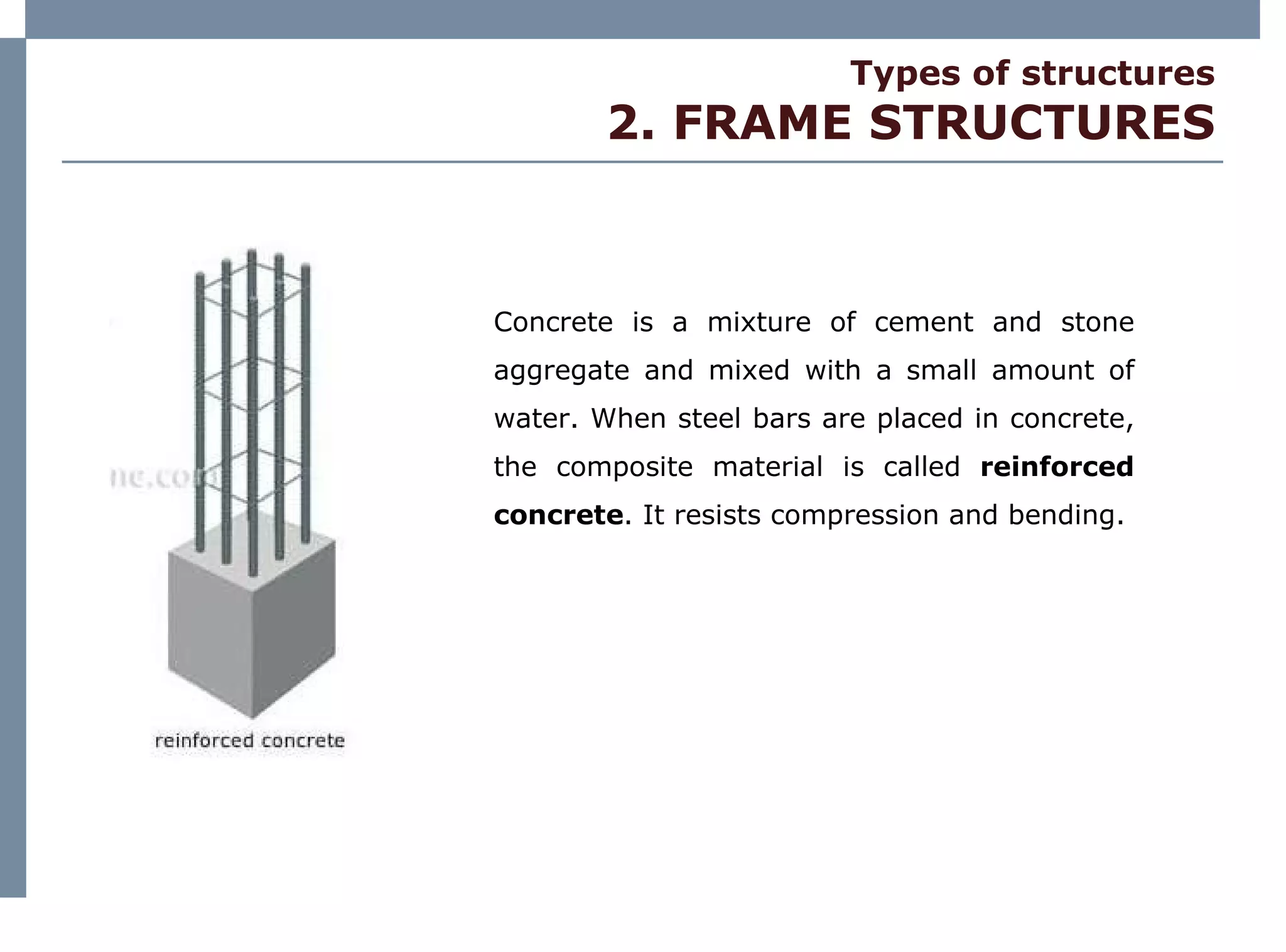
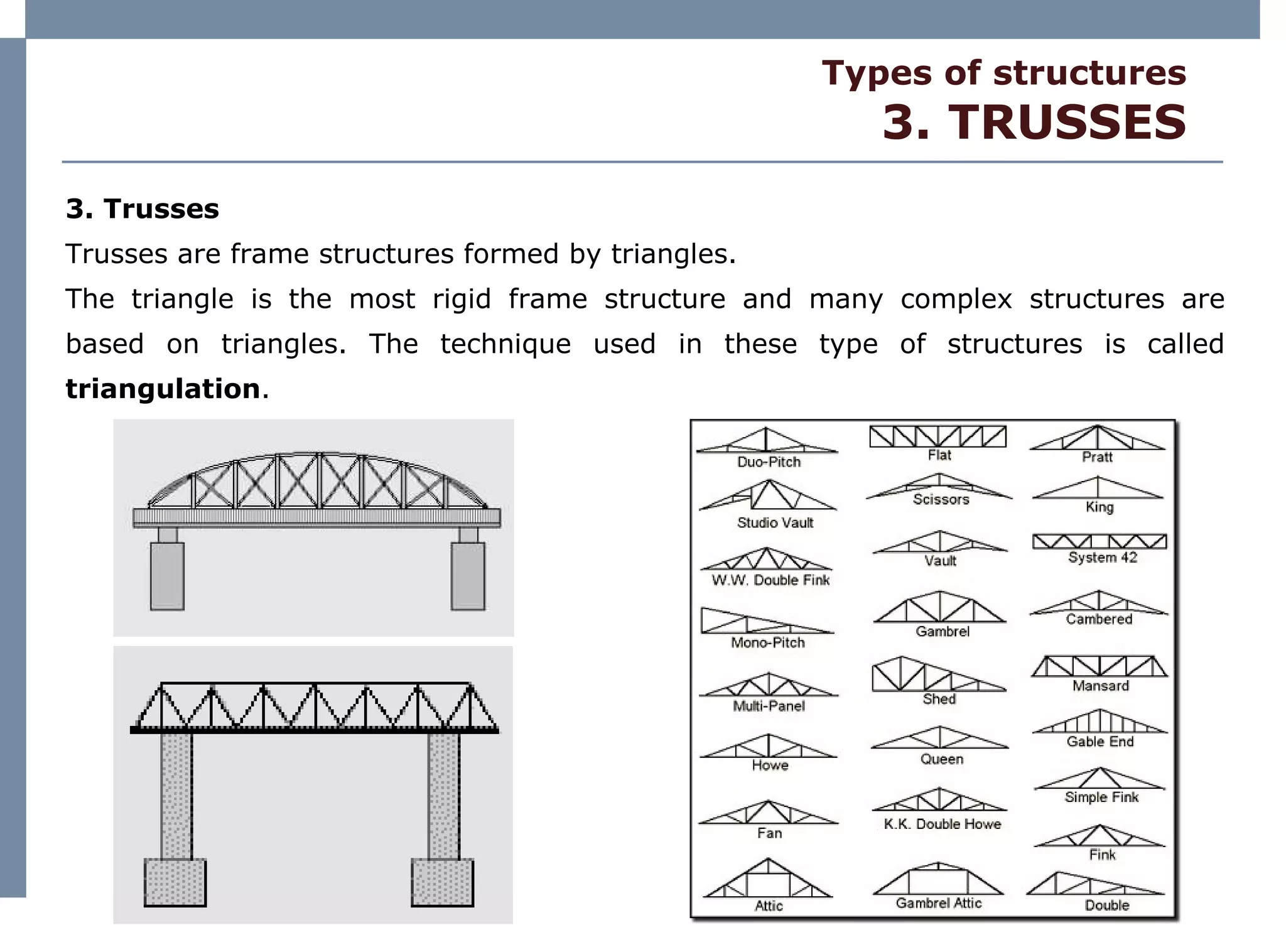
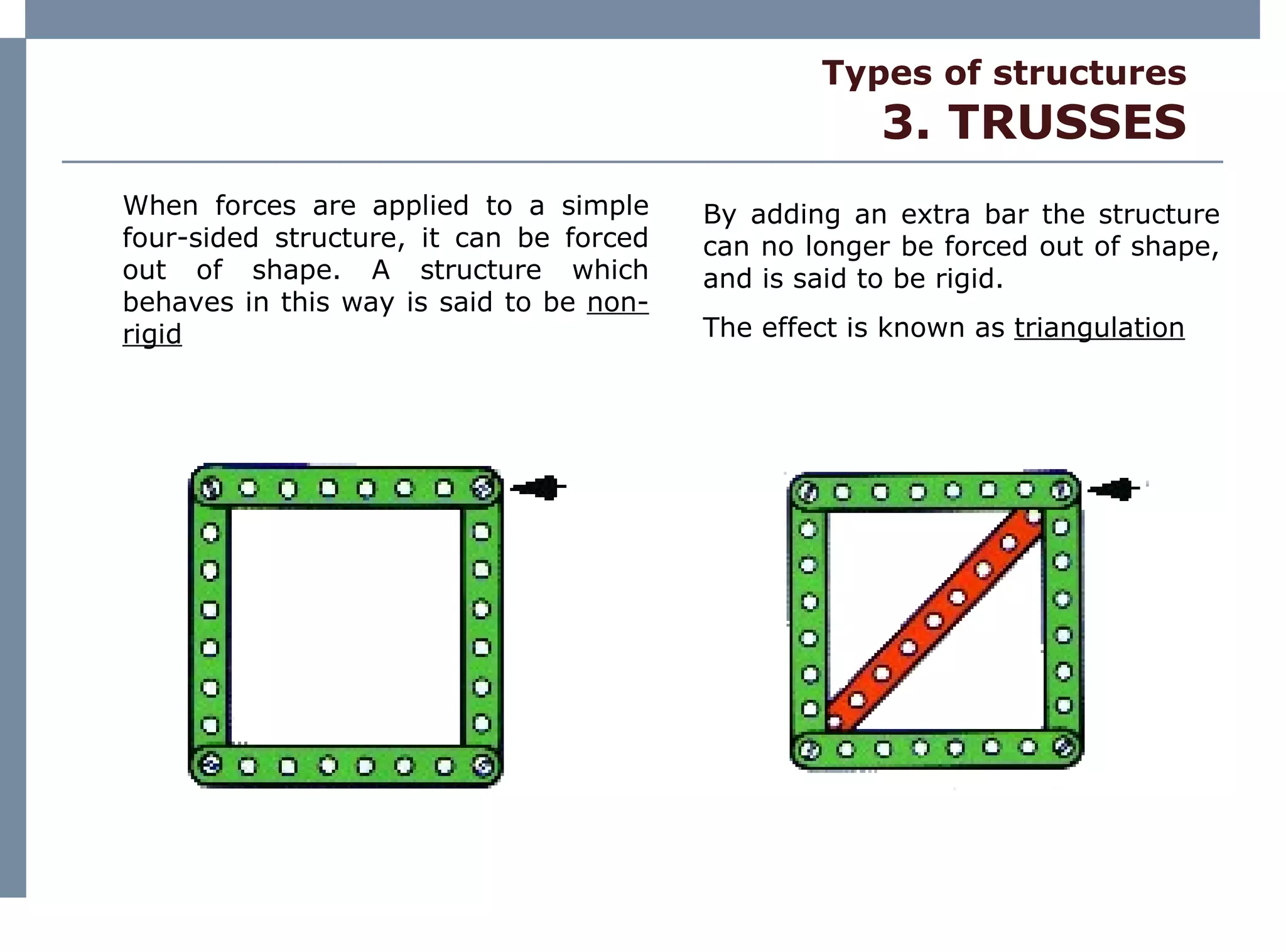
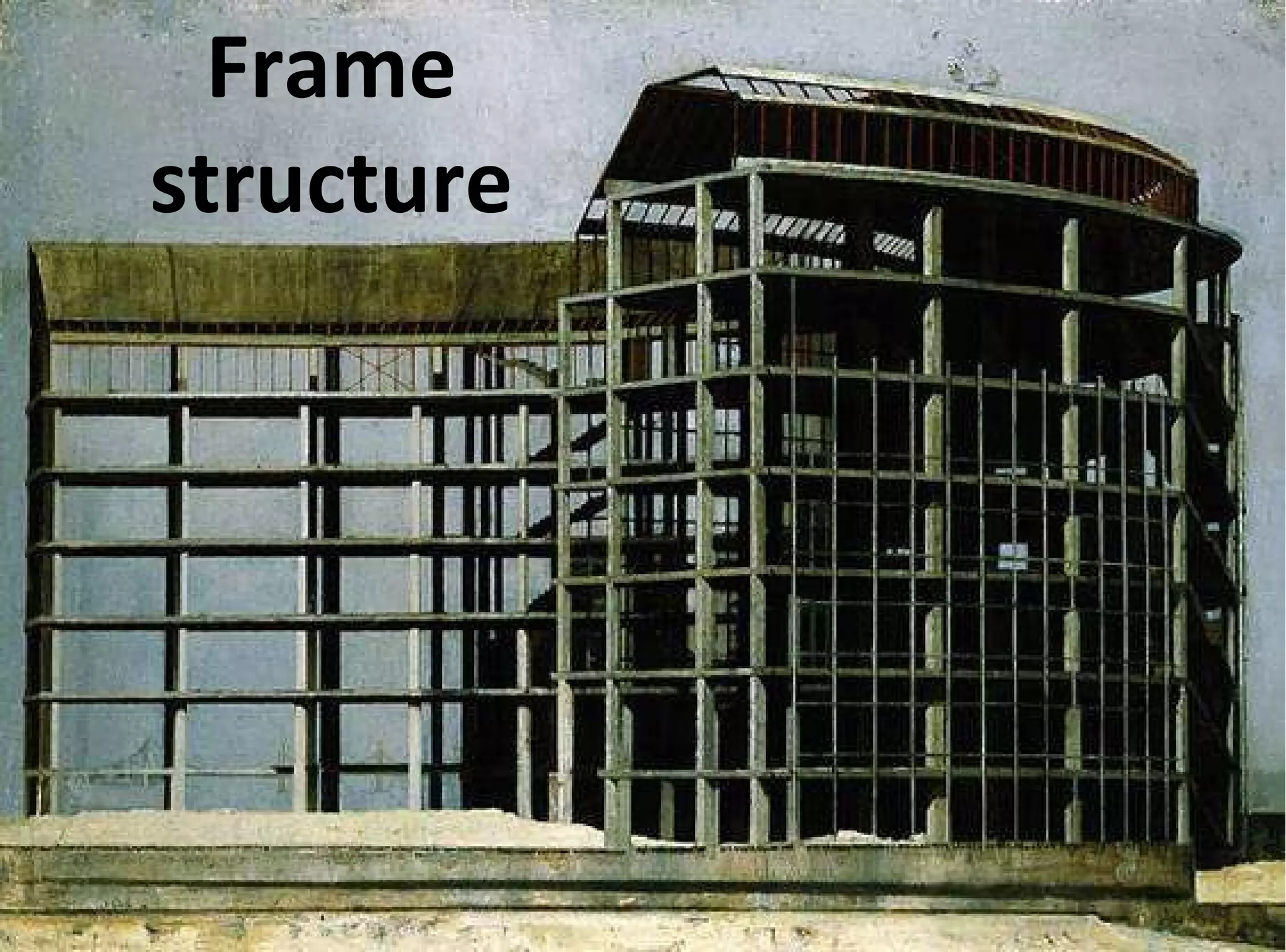
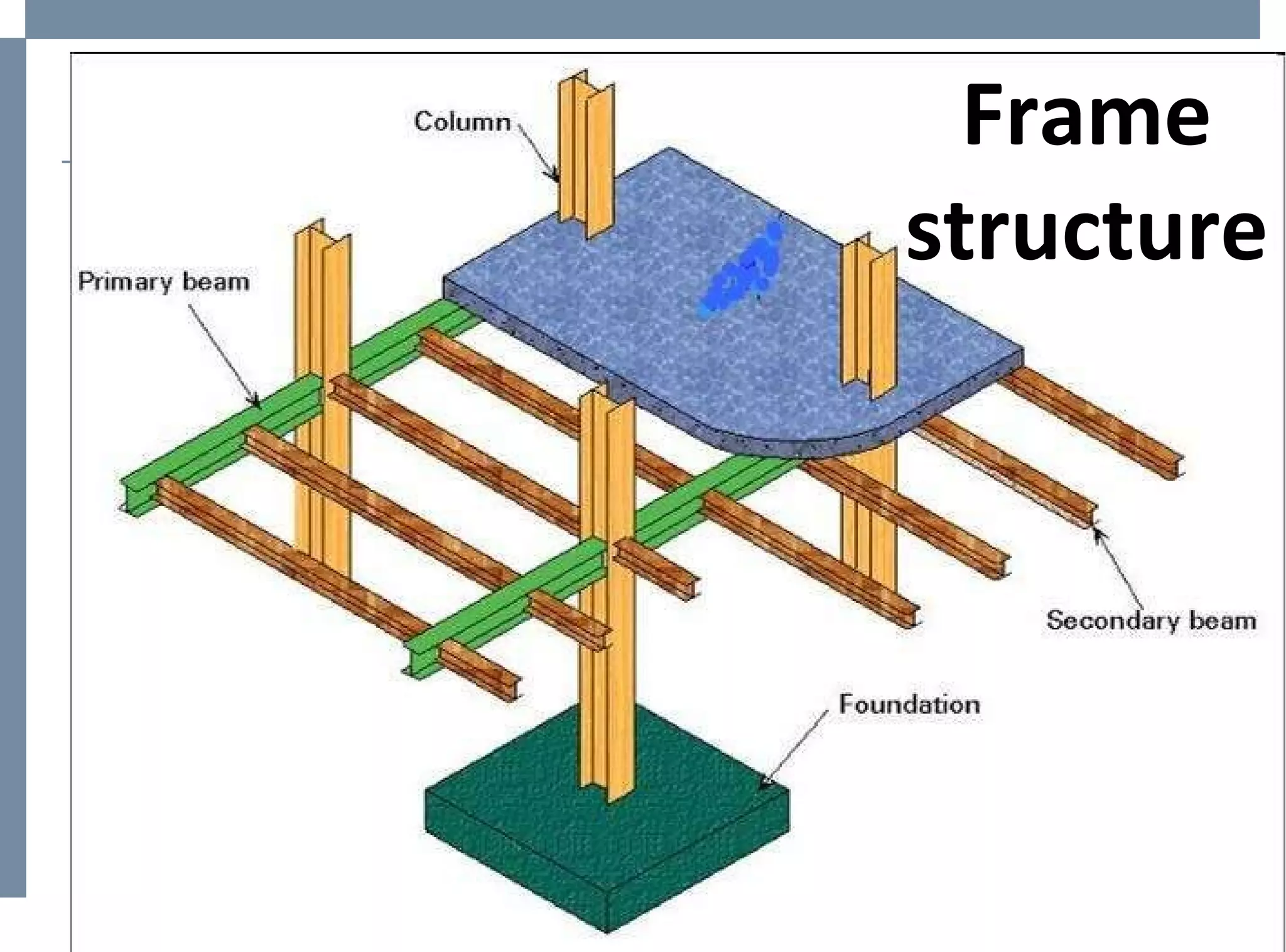
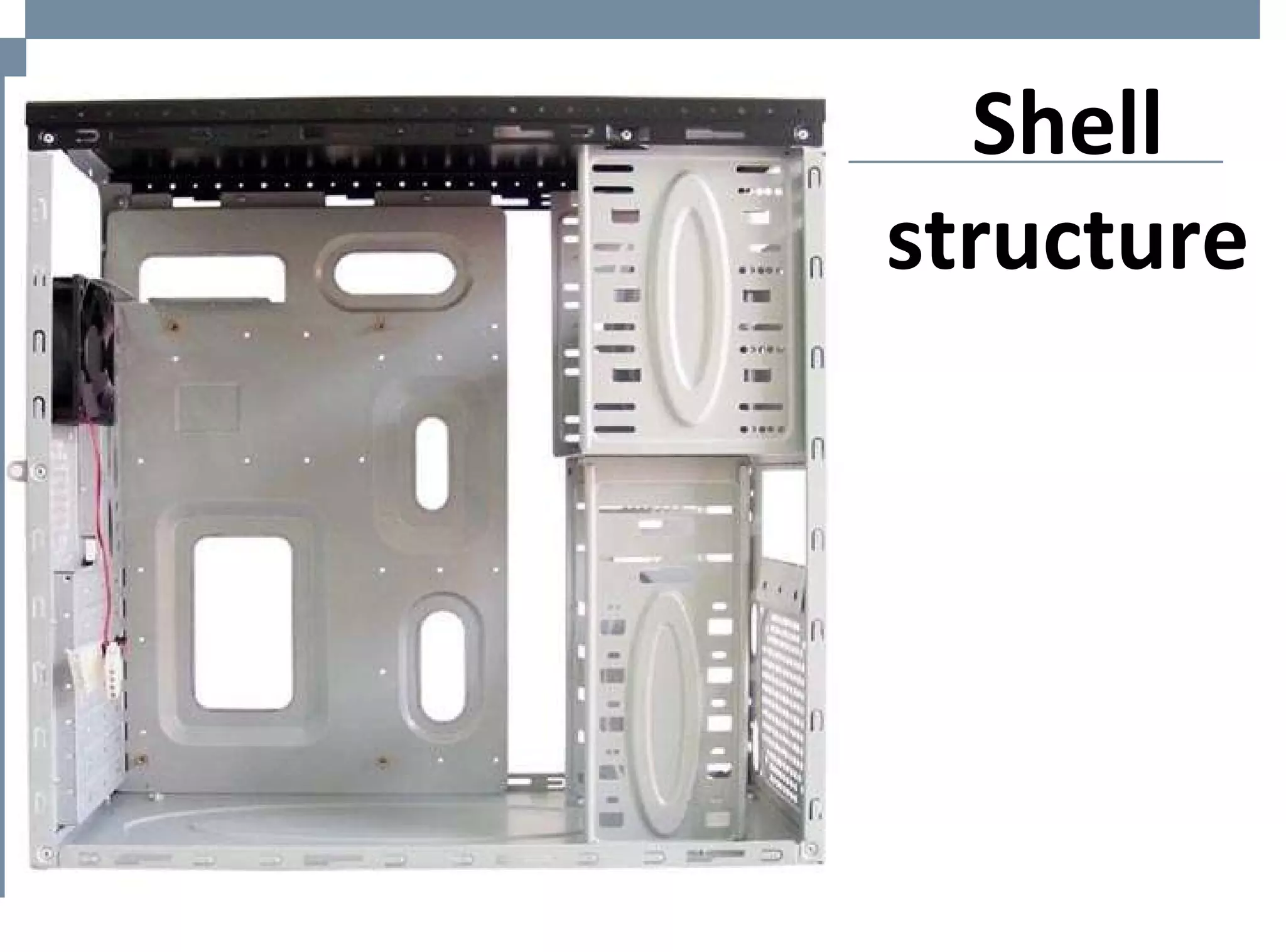
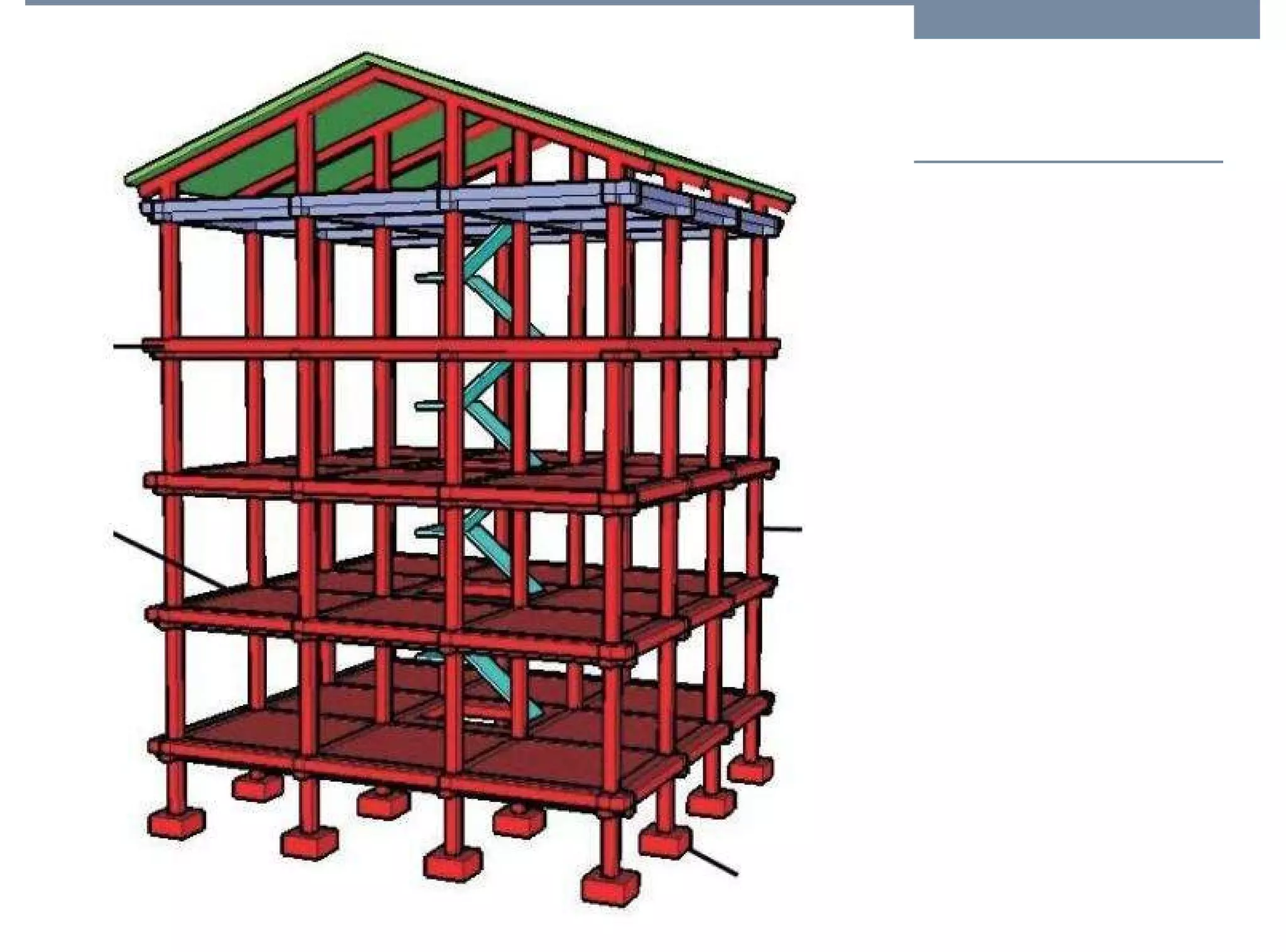
The document discusses different types of structures including mass structures, frame structures, trusses, shell structures, suspension structures, vaulted structures, and geodesic structures. It provides examples and descriptions of each type as well as their advantages. Mass structures use weight to hold themselves together while frame structures have a skeleton that supports an empty interior space. Trusses form rigid structures using triangles. Shell structures derive strength from an outer layer while suspension structures use cables to support horizontal planes. Vaulted structures use arches to provide space and geodesic domes form shell structures from polygons.