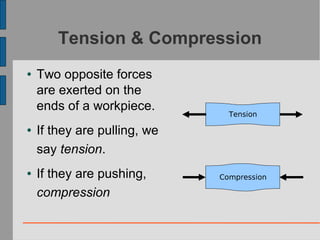
This document discusses different types of structures and structural elements. It begins by defining a structure as the part of an object that keeps its parts joined and in position. It then classifies structures into three main types - massive, casing/shell, and framework. For each type, it provides examples. It also discusses common structural elements like arches, trusses, girders and beams. It explains the six fundamental structural stresses of tension, compression, bending, shear, torsion and buckling. In closing, it provides some activities for analyzing structures.