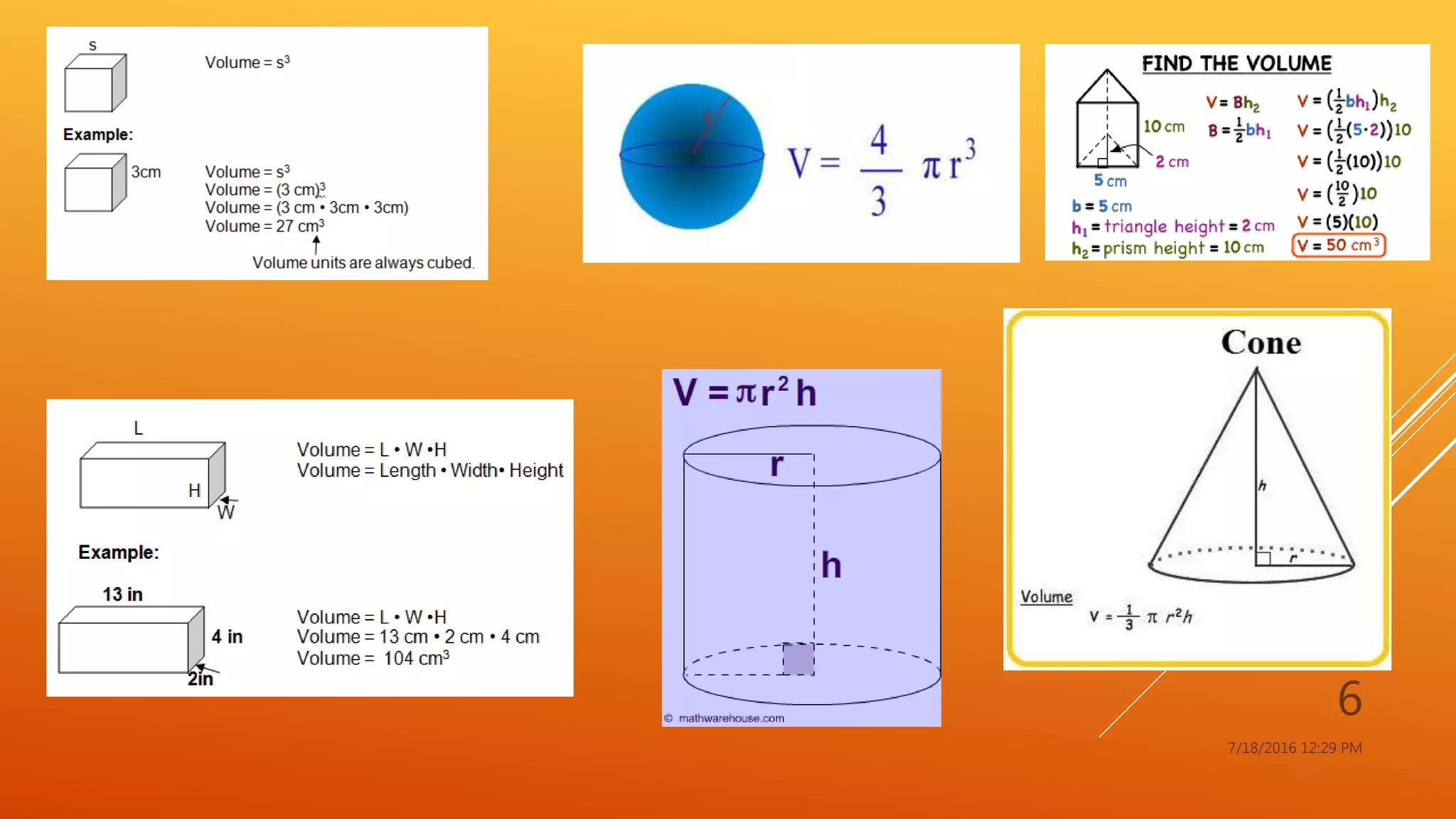
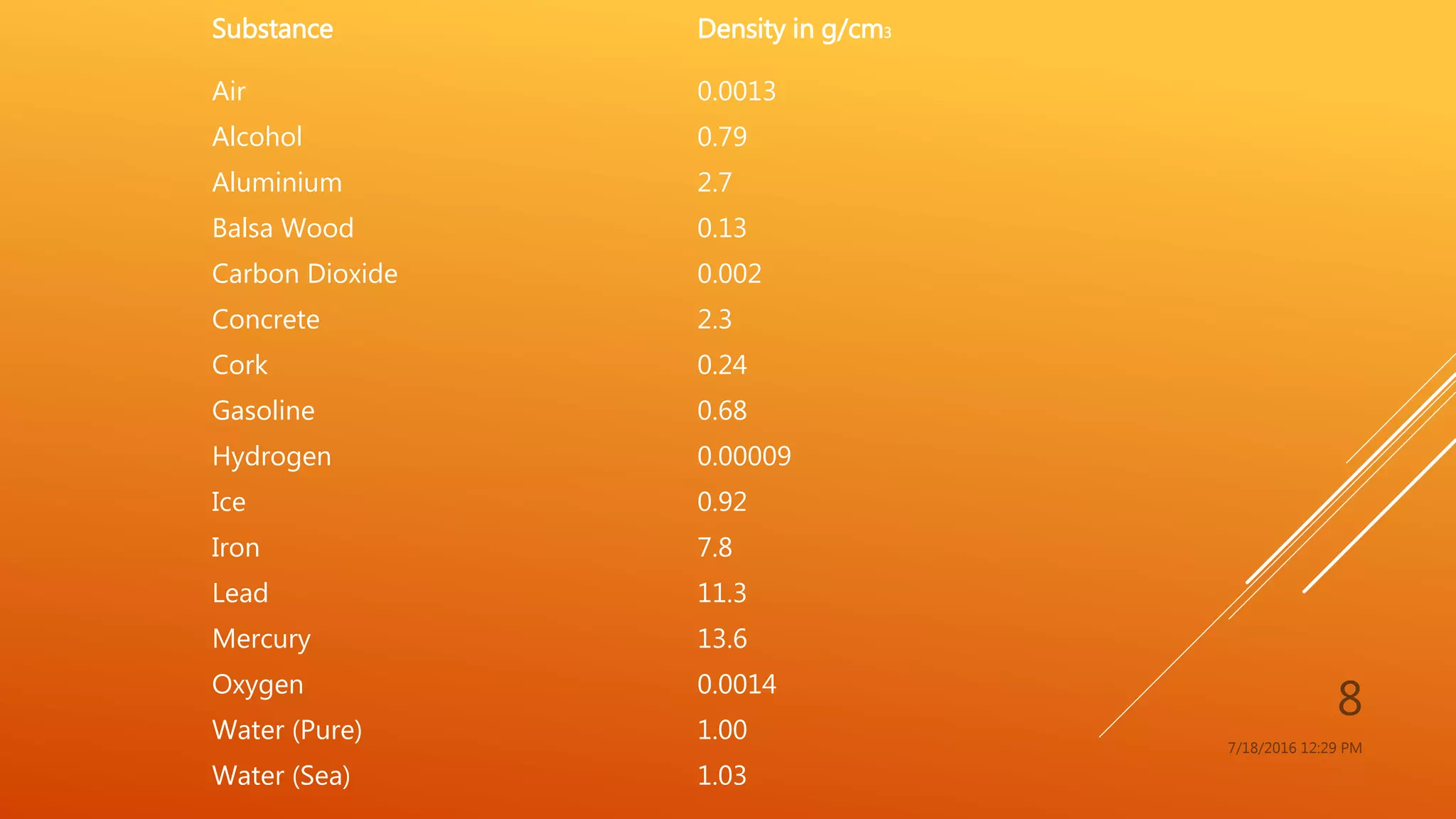
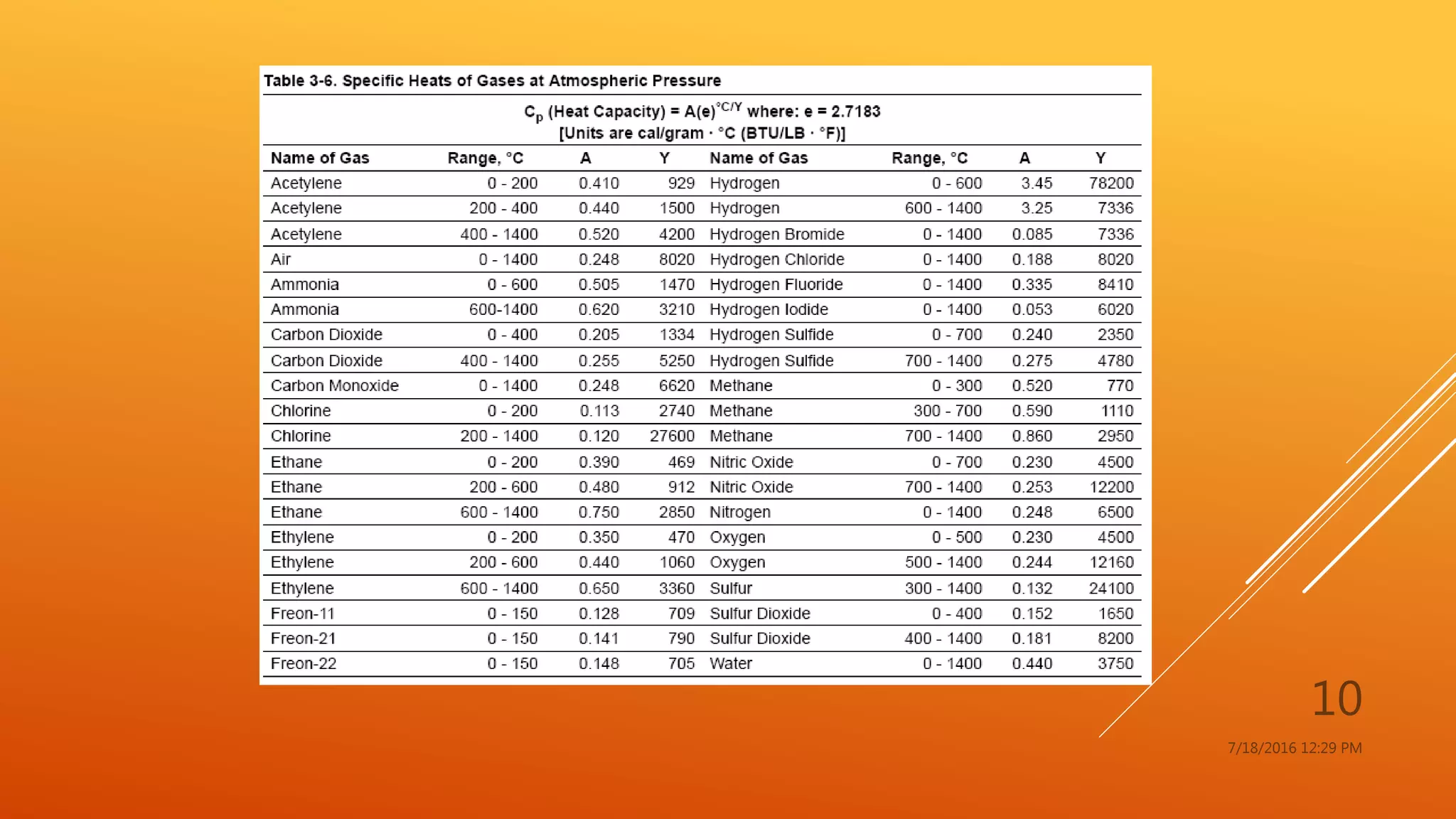
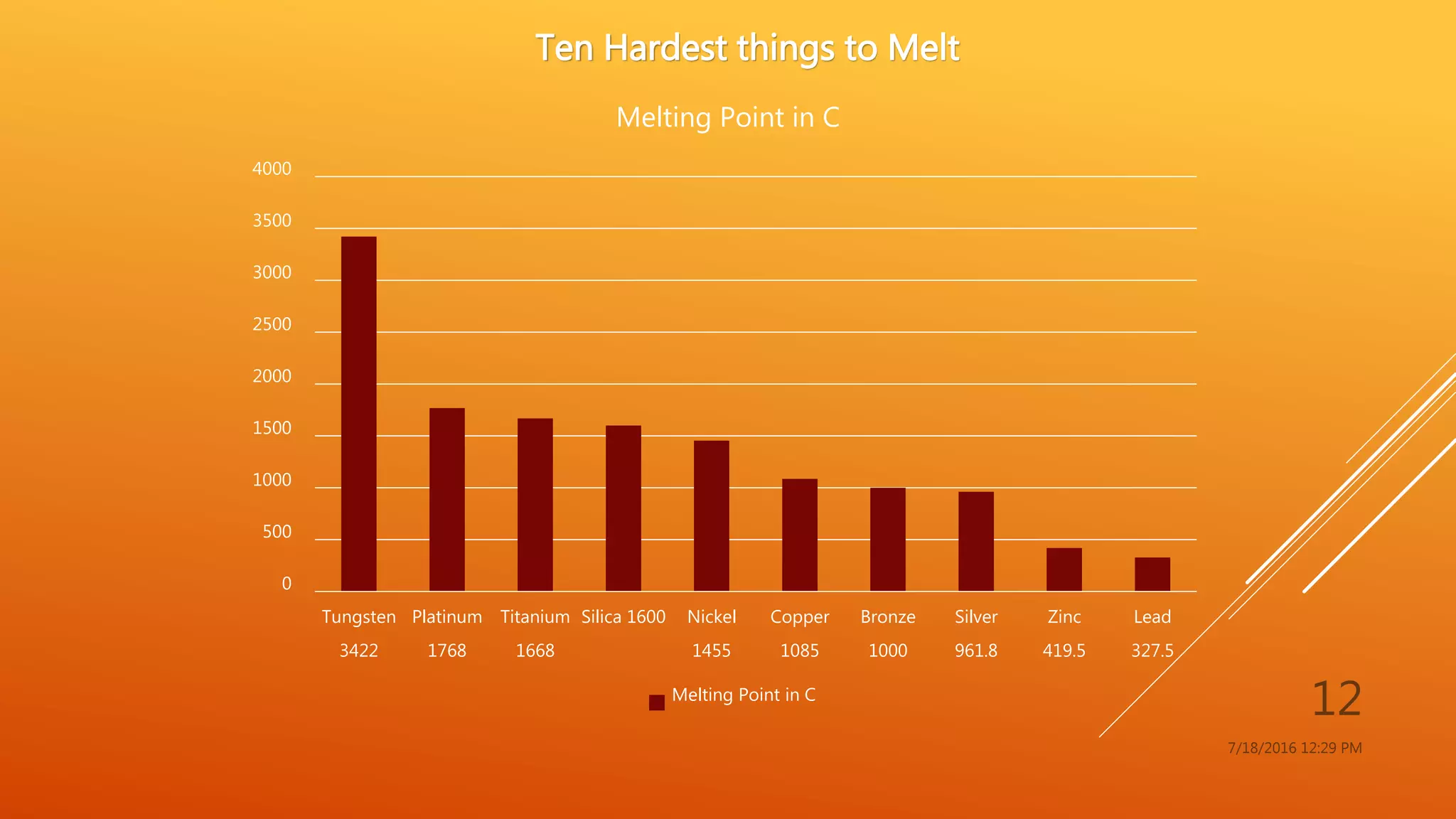
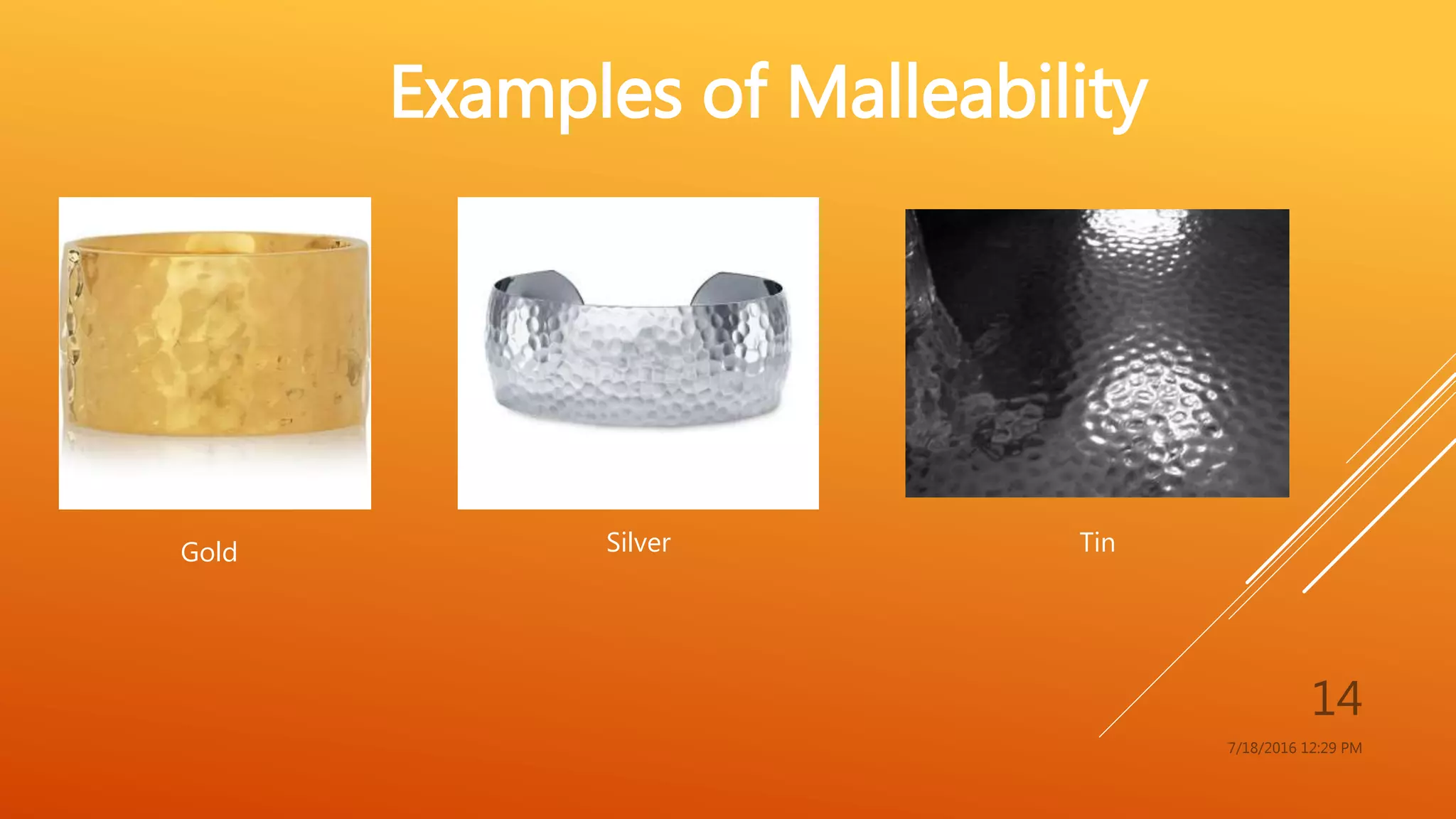
The document provides an overview of physical and chemical properties of matter, defining key concepts such as volume, density, boiling point, melting point, and various metallic properties like malleability and ductility. It includes specific examples and measurements of these properties for different substances, as well as characteristics of chemical properties that can be observed during reactions. The content concludes with a Q&A section that reinforces the information presented.