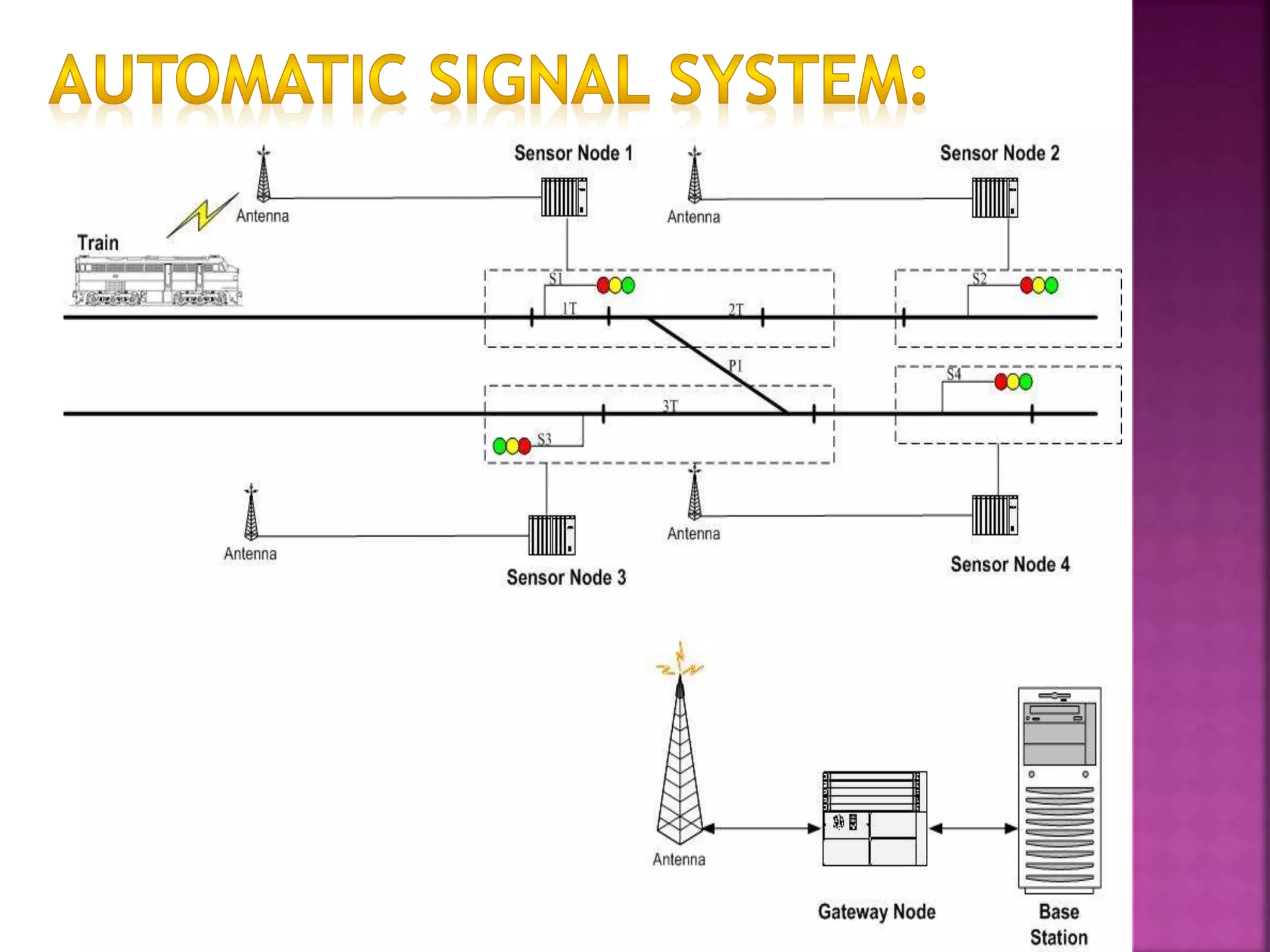
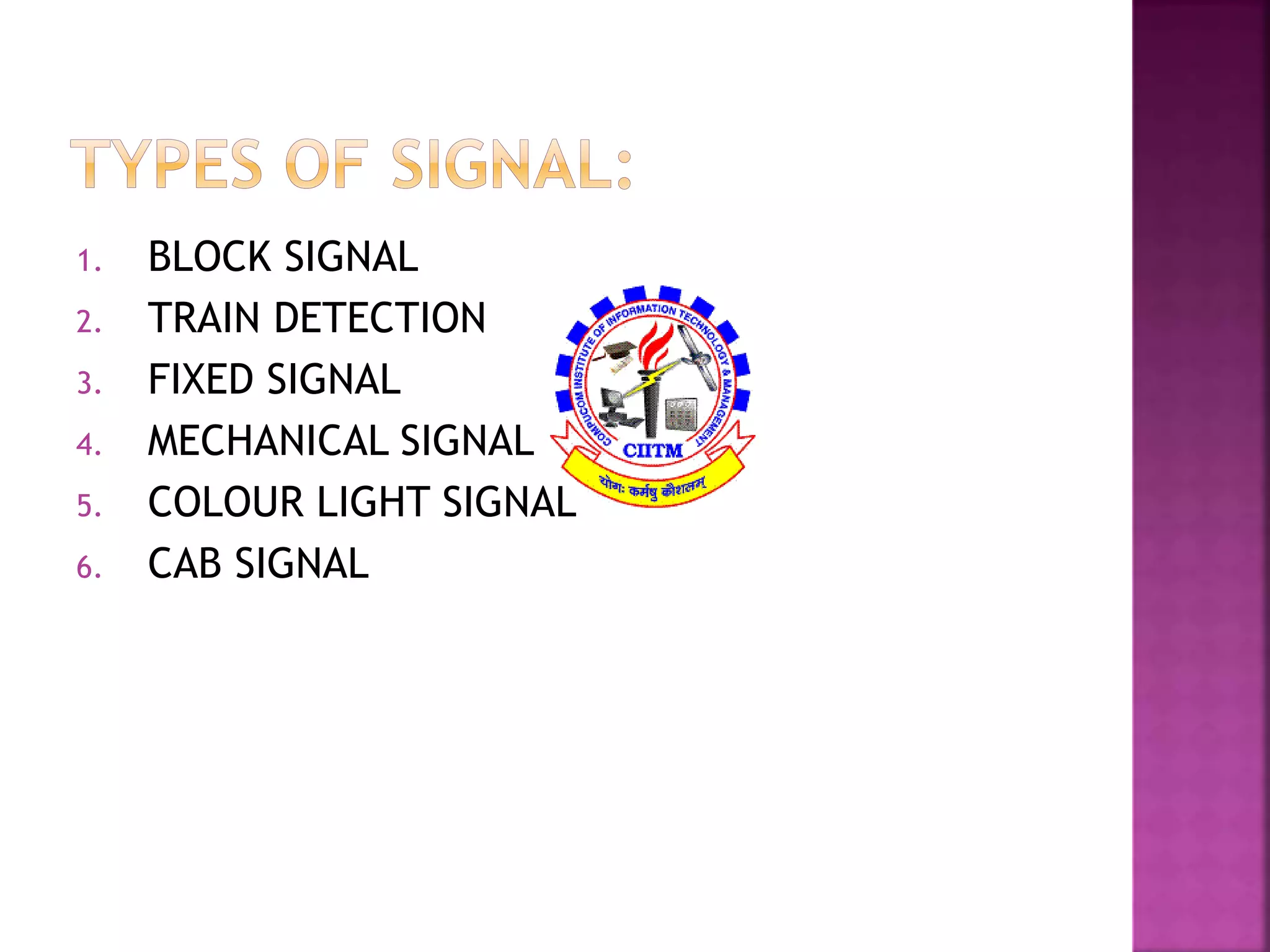
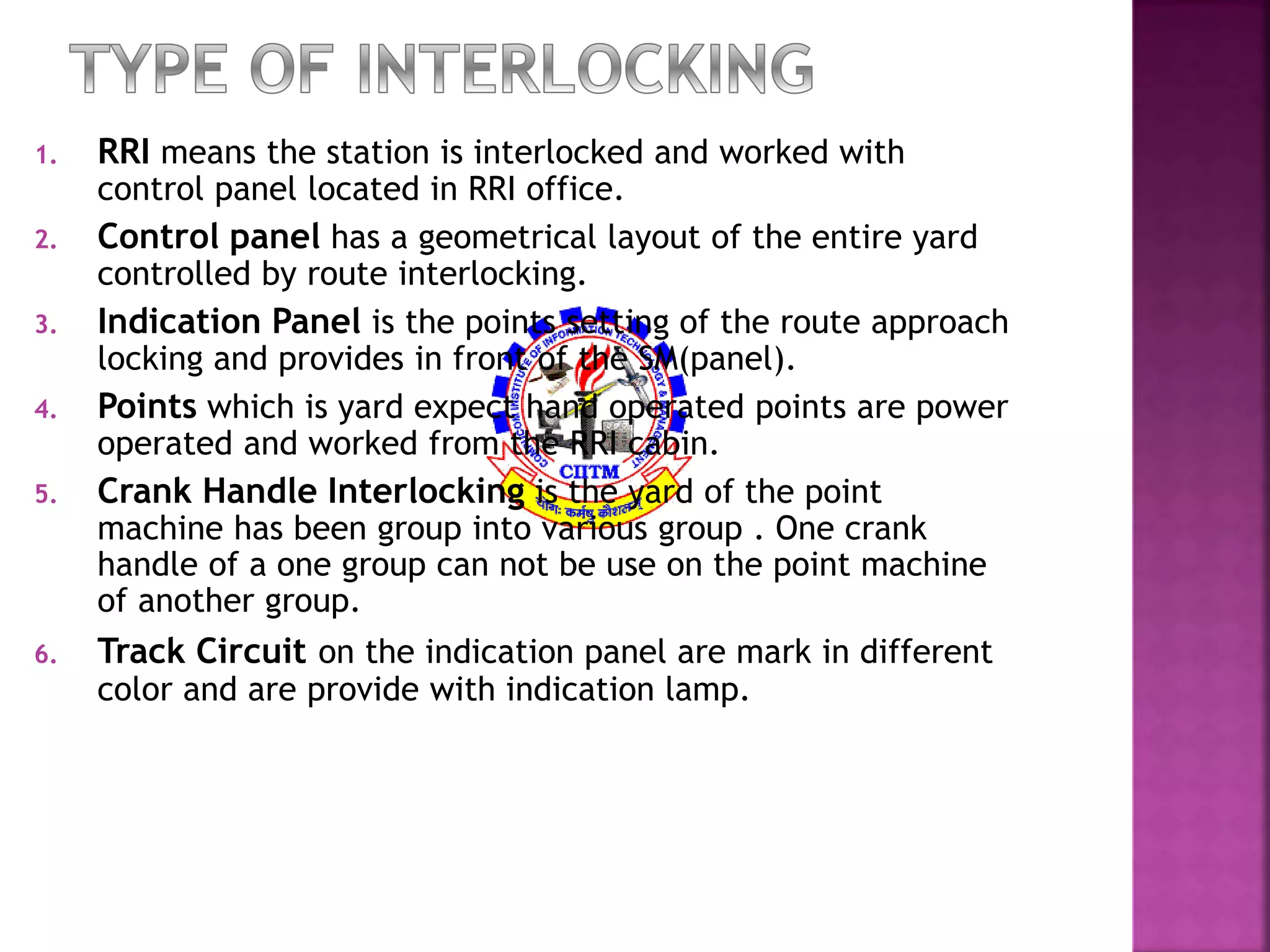
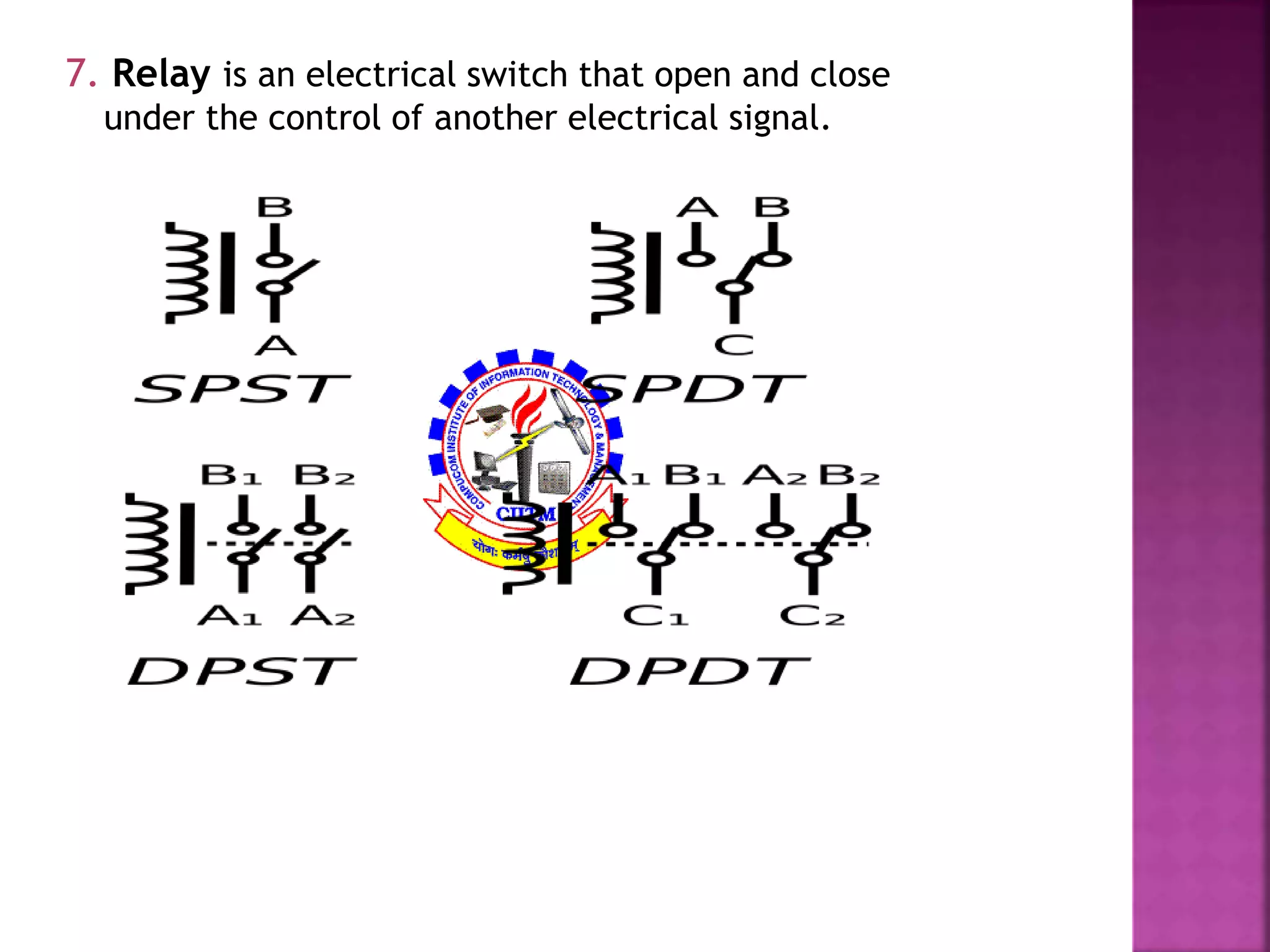
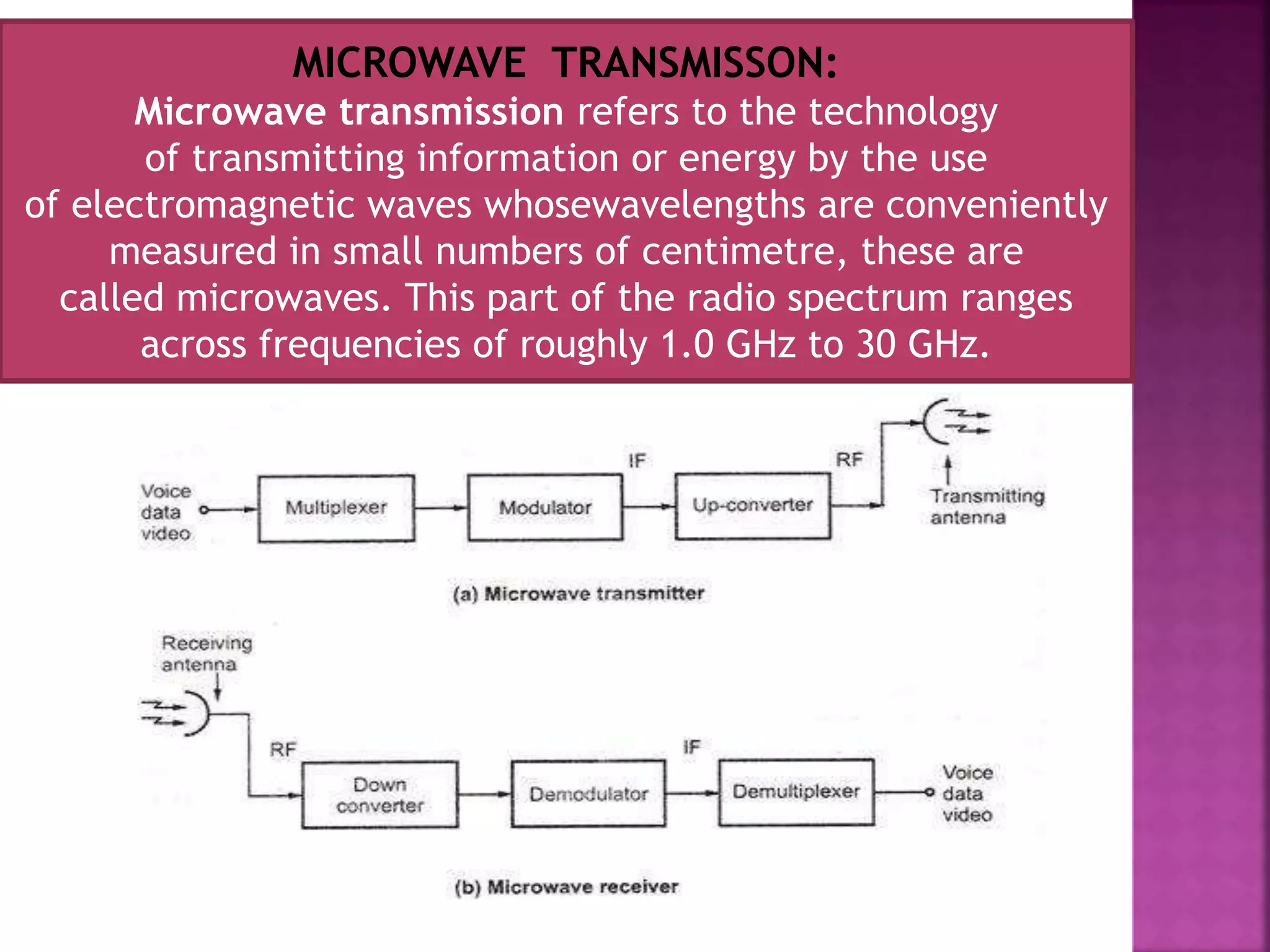
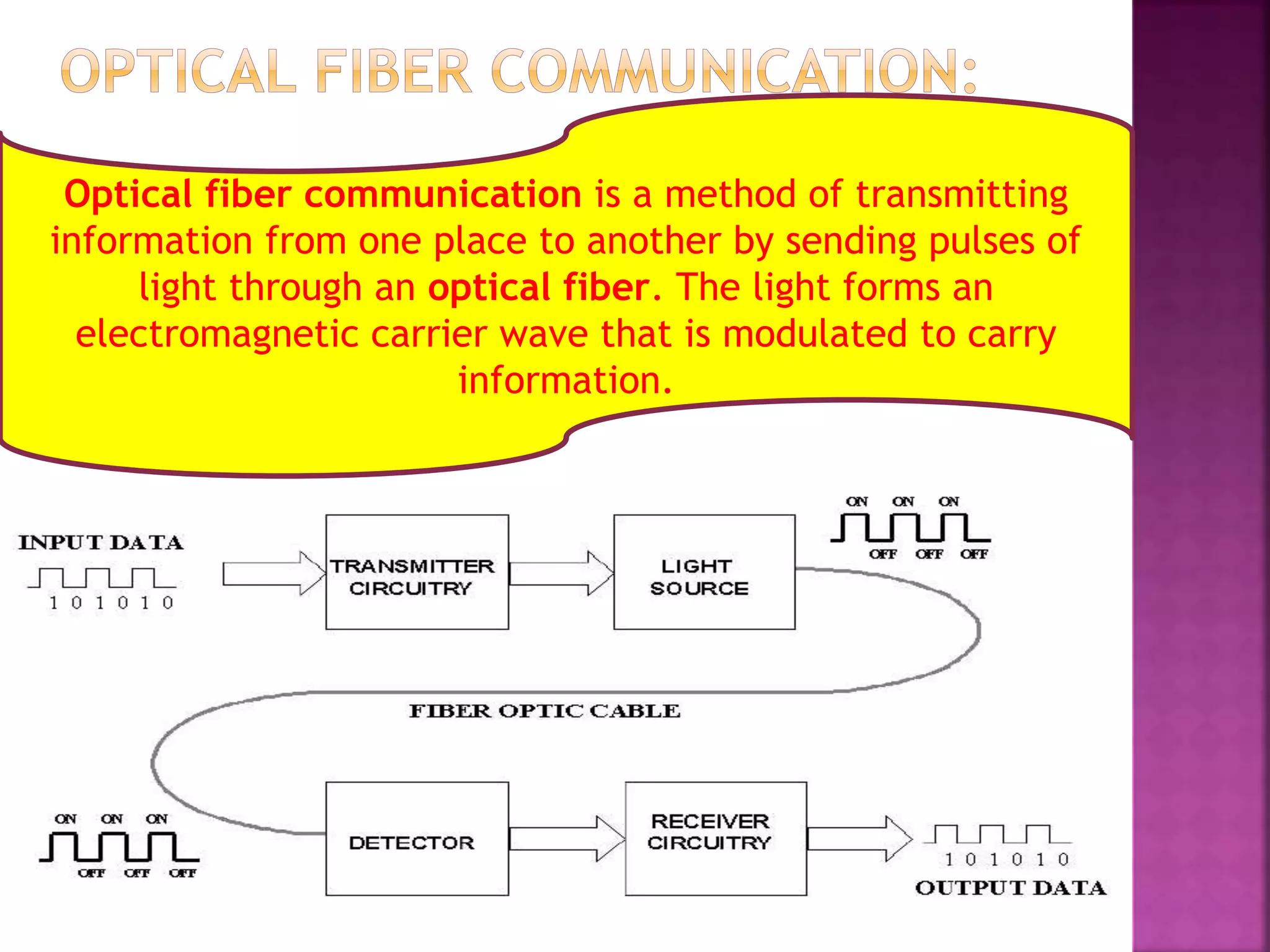
This document discusses railway signaling and communication systems in India. It provides background on Indian Railways, the largest commercial employer in the world. It then describes different types of railway signaling such as block signaling and color light signaling used to safely direct train traffic. Interlocking systems using mechanical and electrical devices are also discussed to prevent conflicting train movements. The document concludes by covering various wired and wireless communication systems used by Indian Railways including microwave transmission, overhead lines, and optical fiber networks.