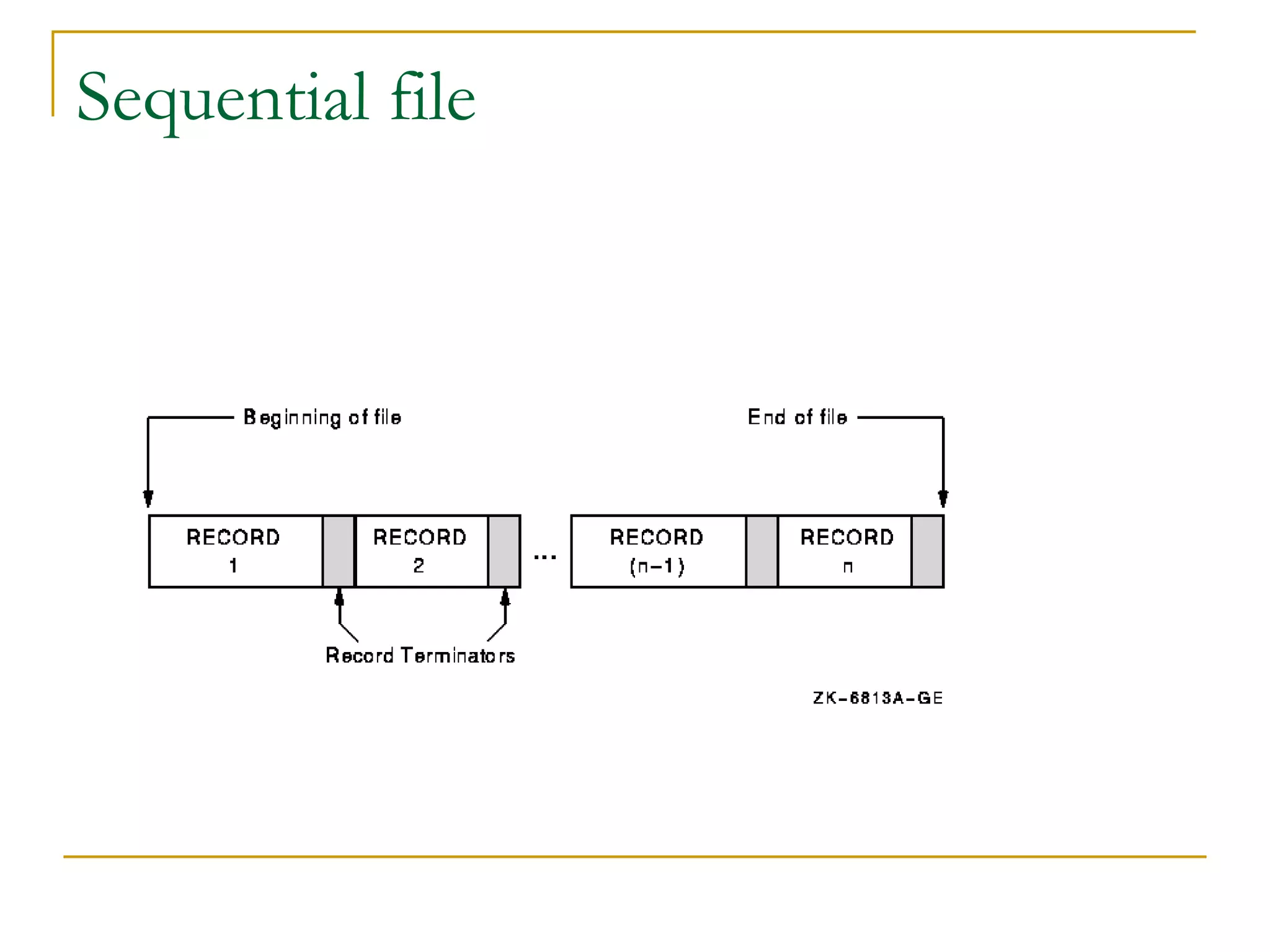
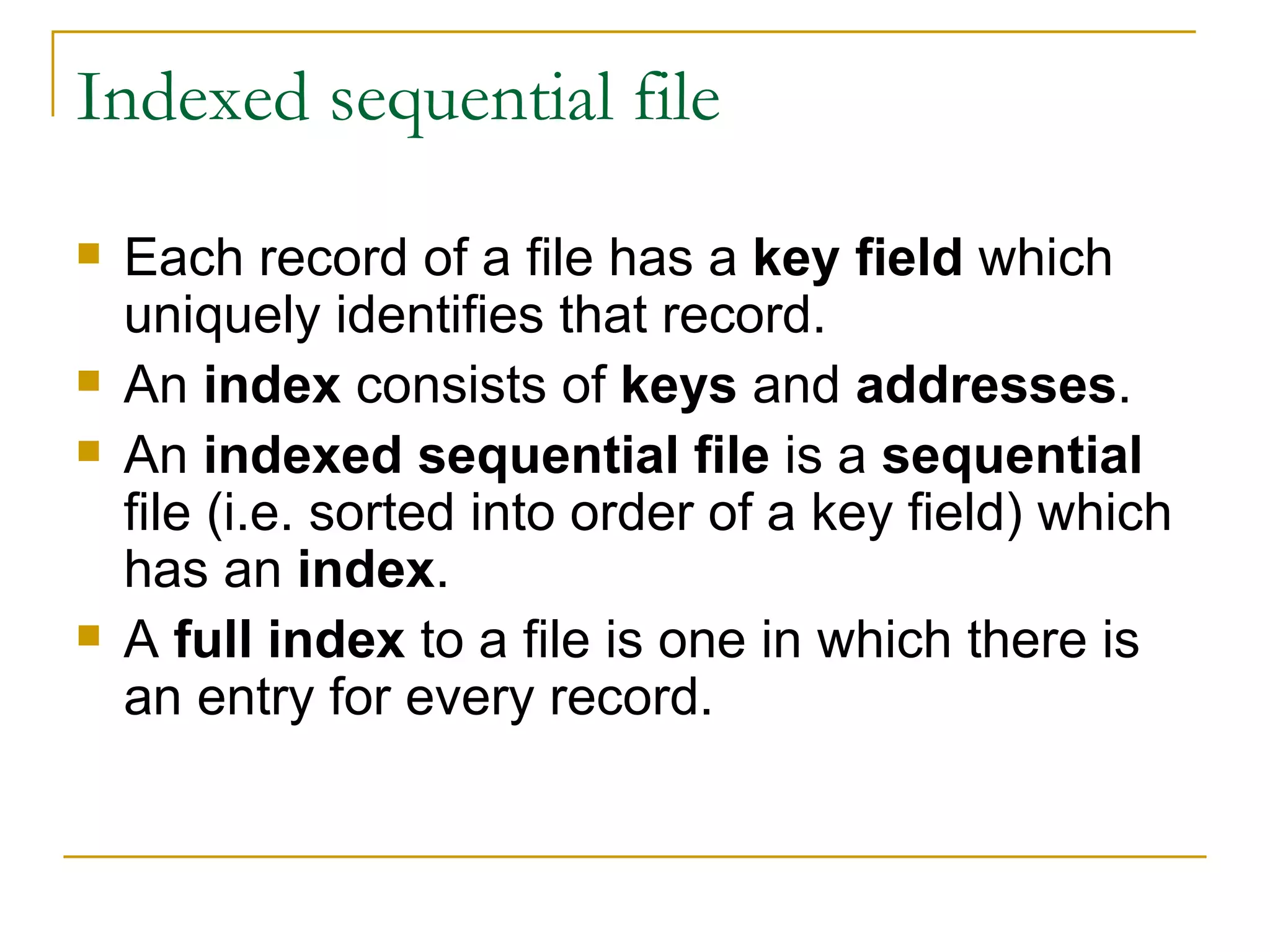
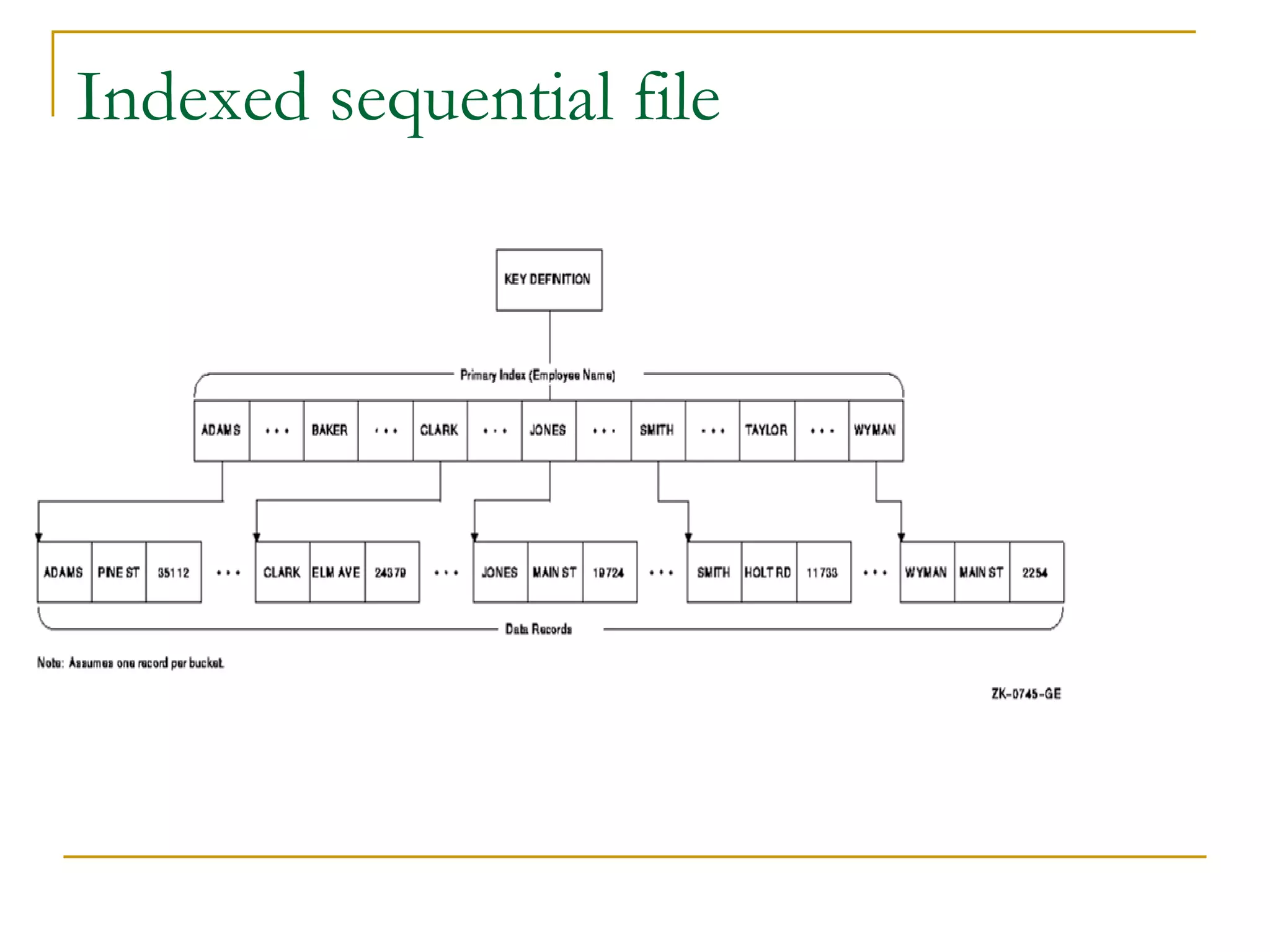
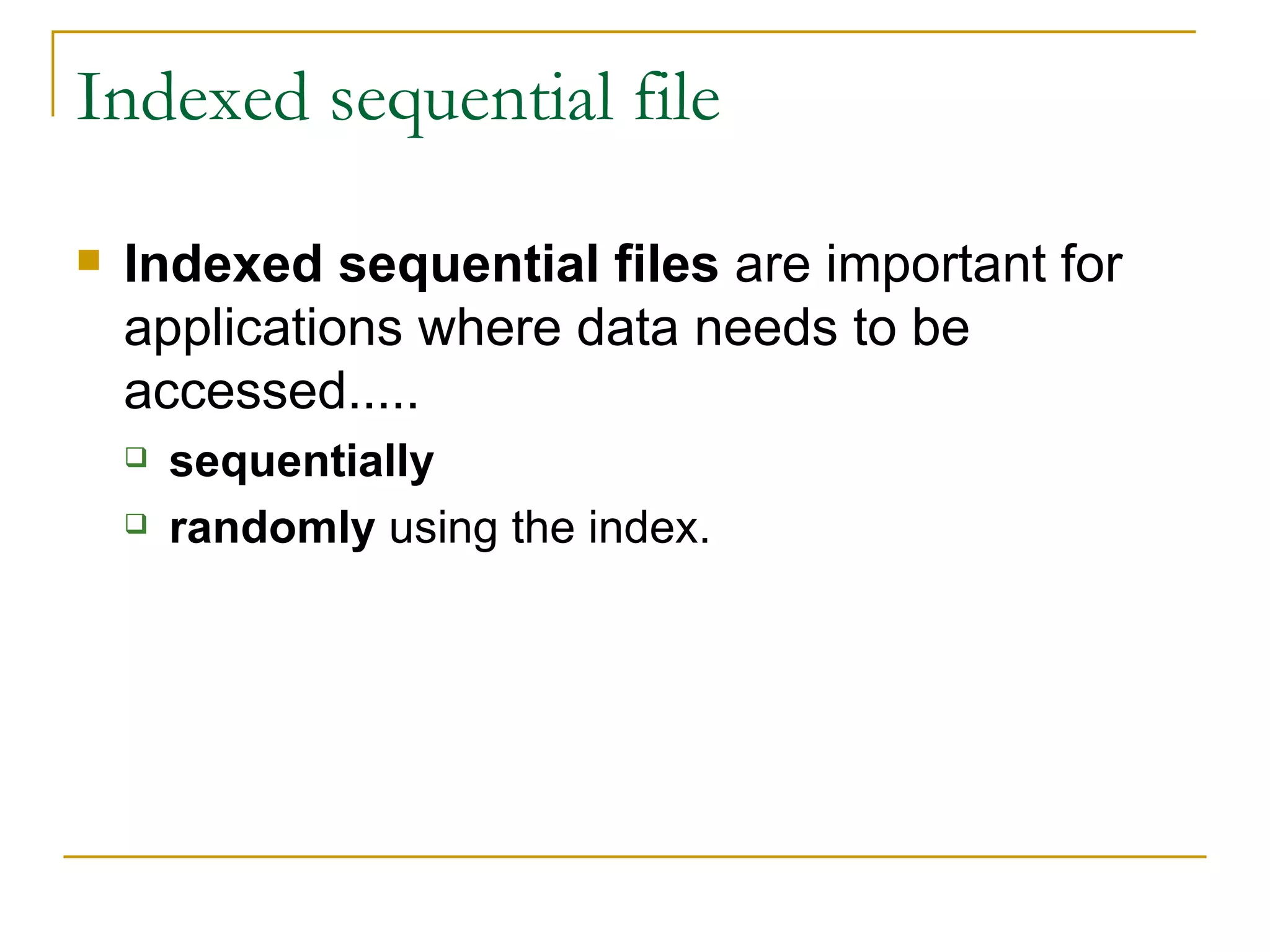
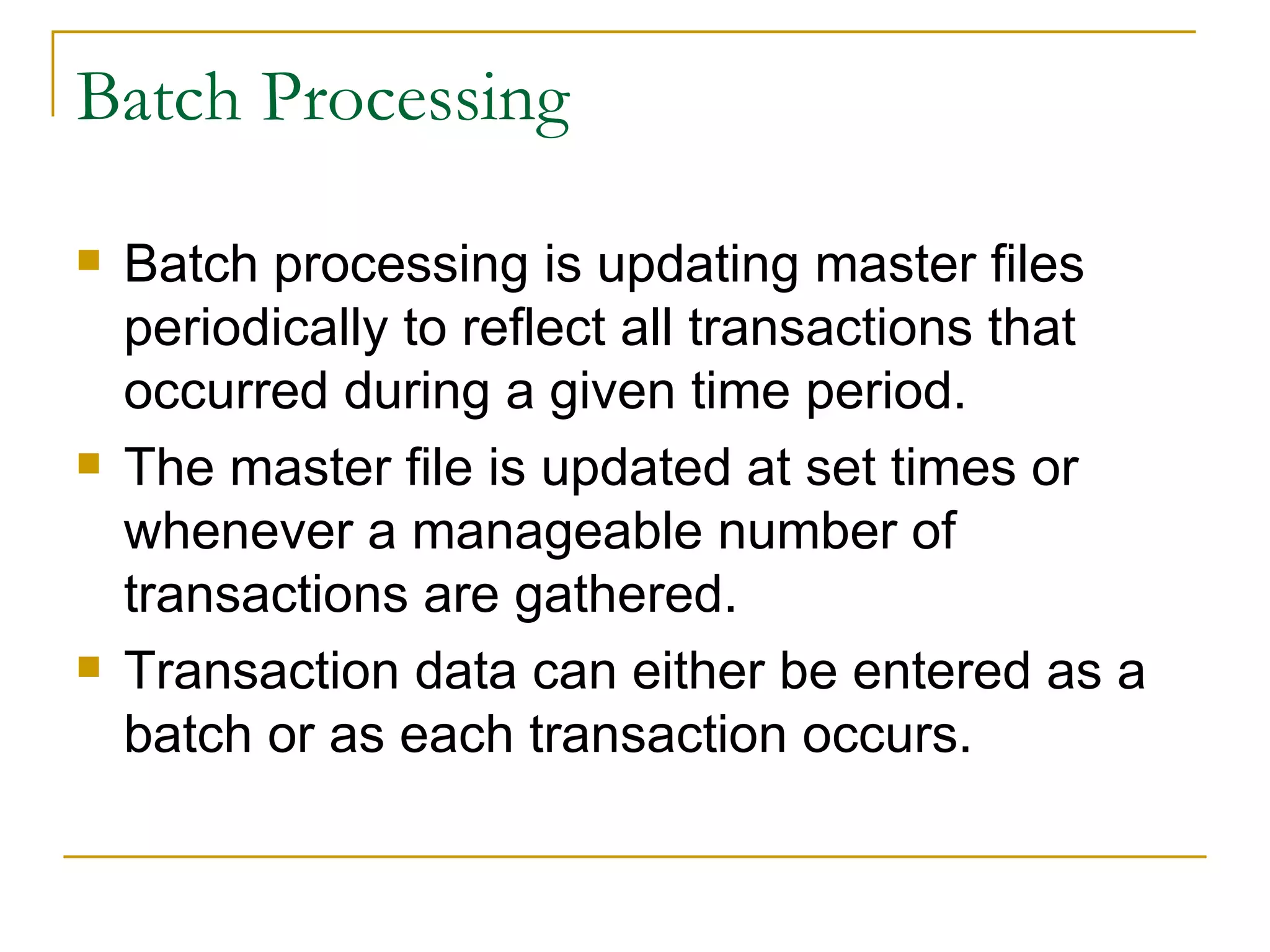
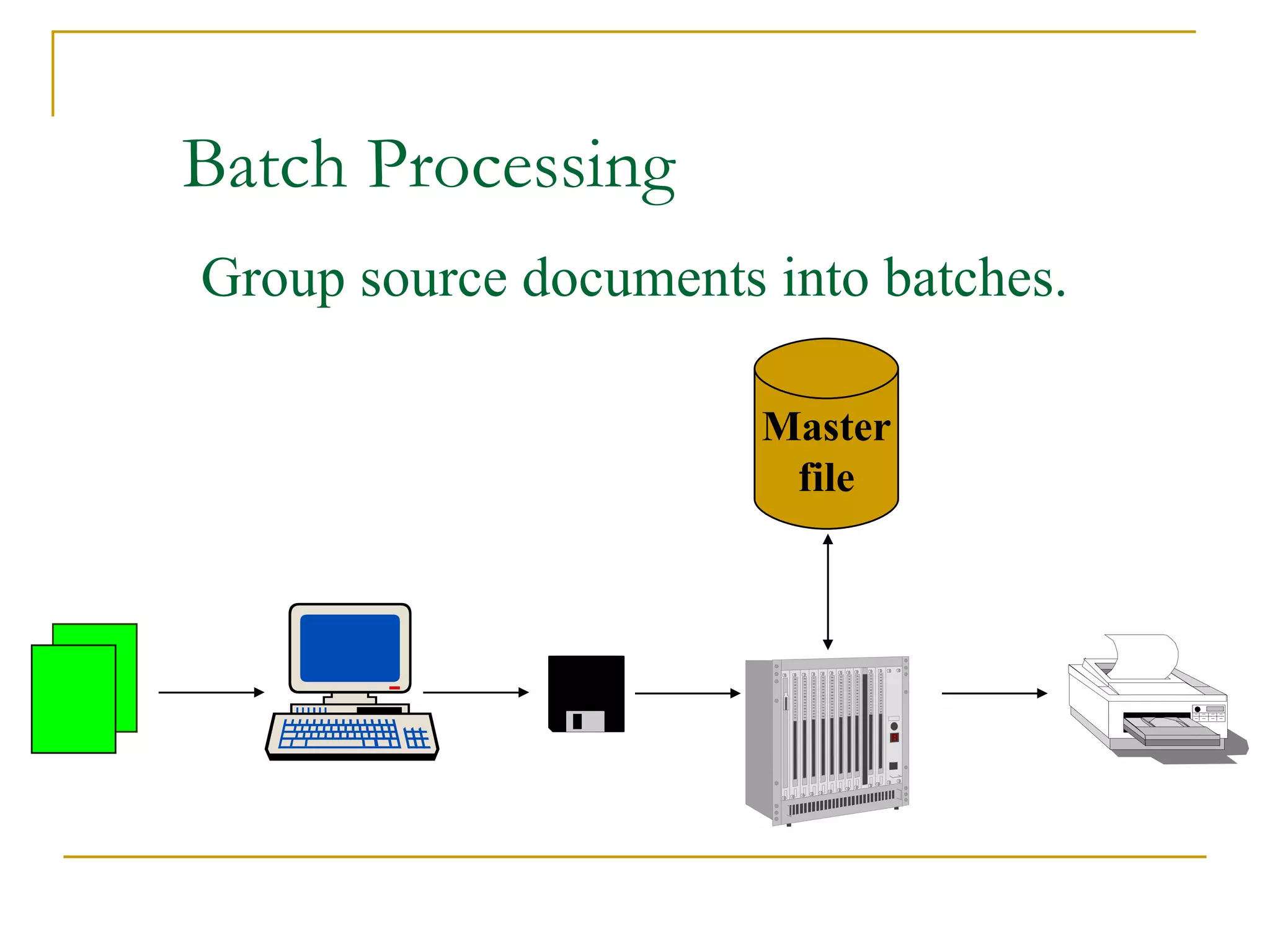
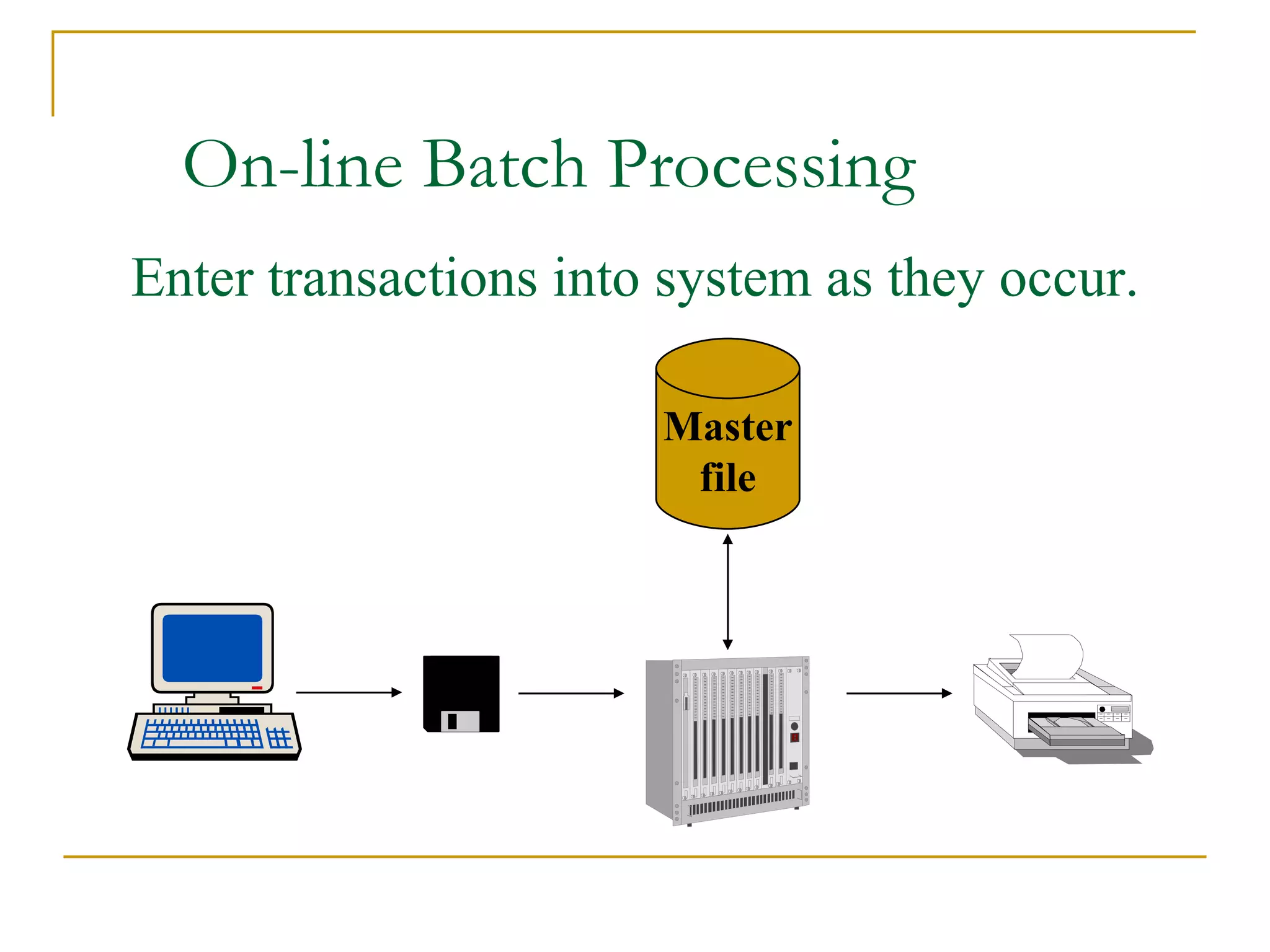
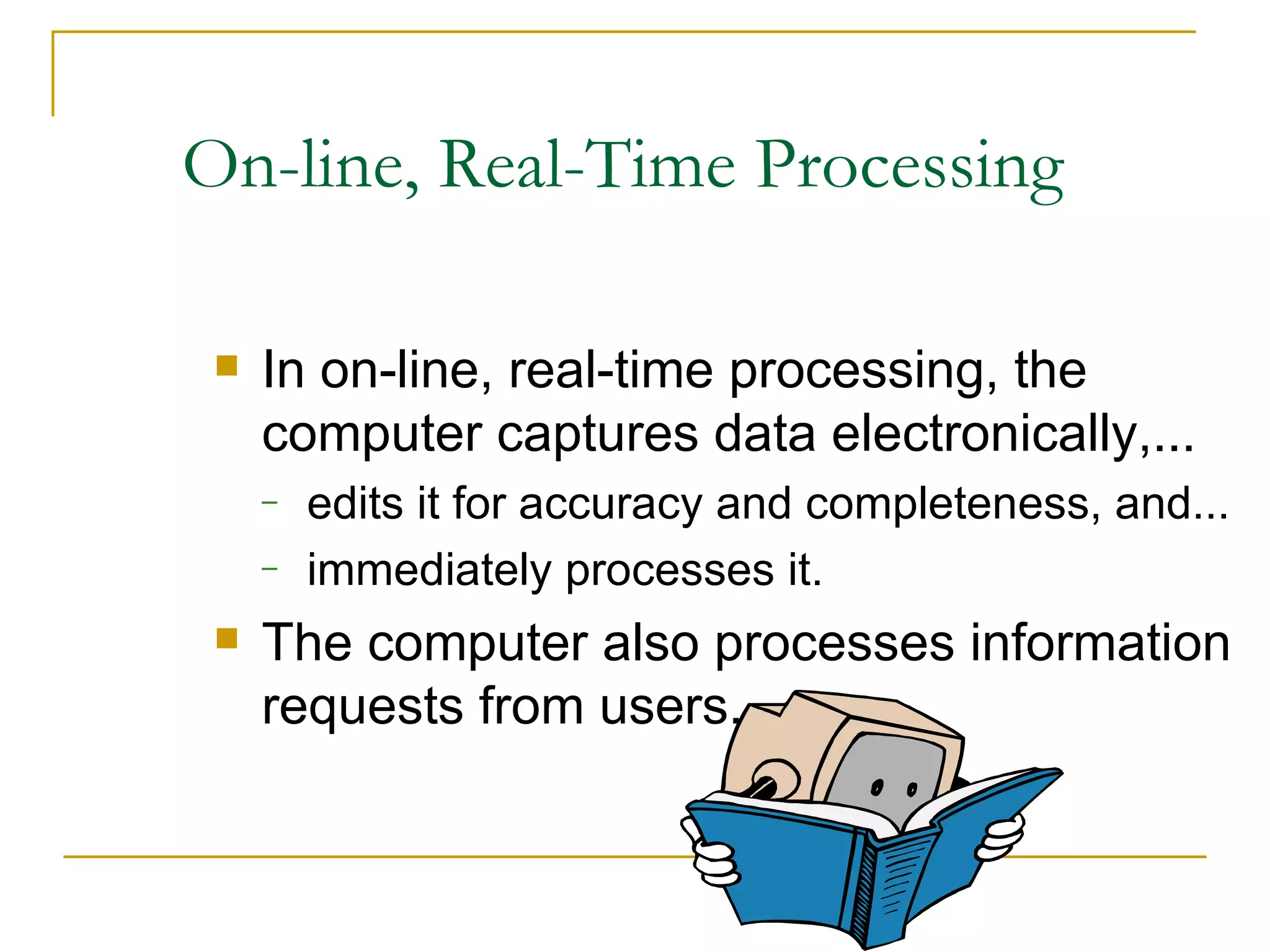
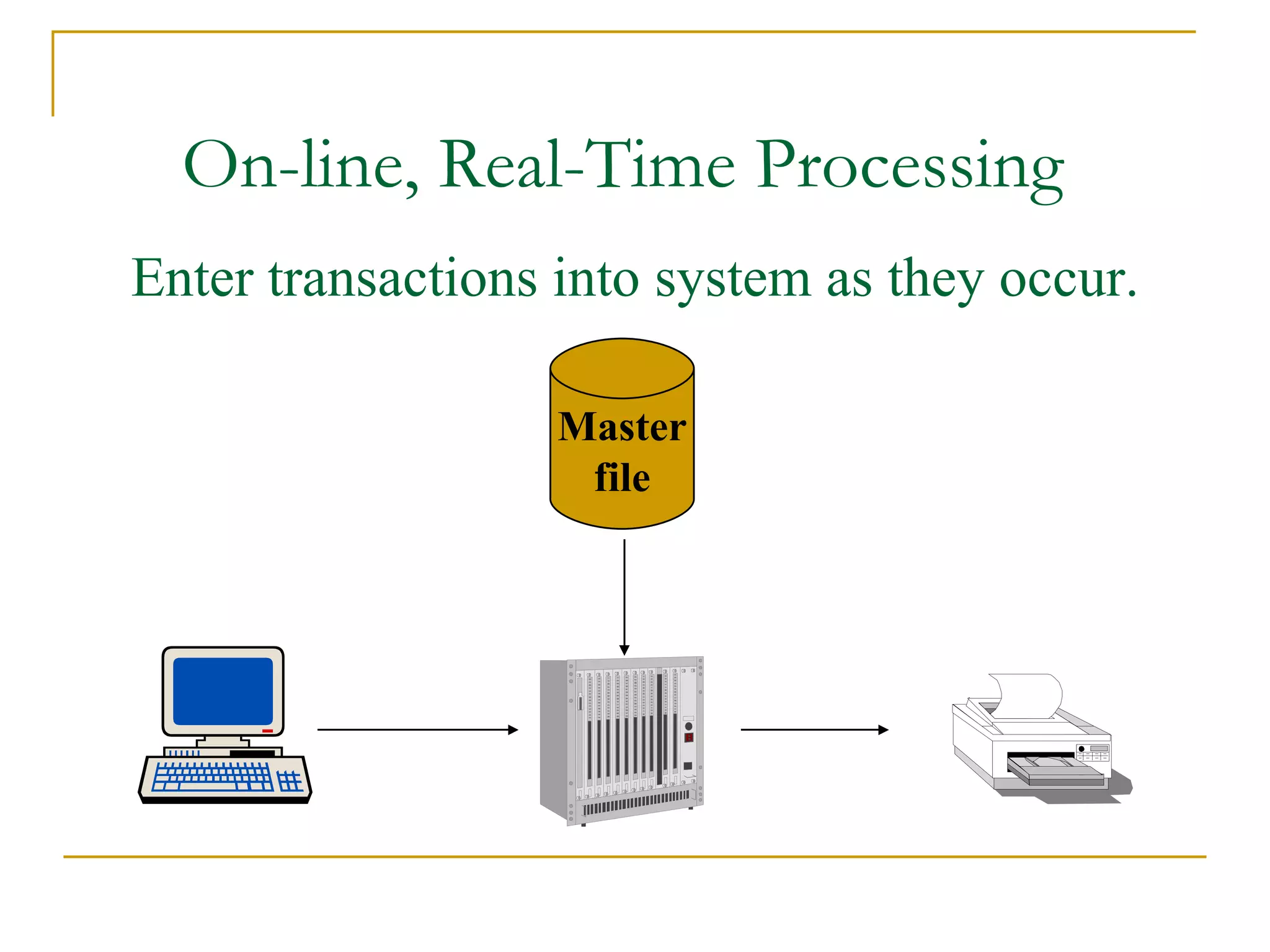
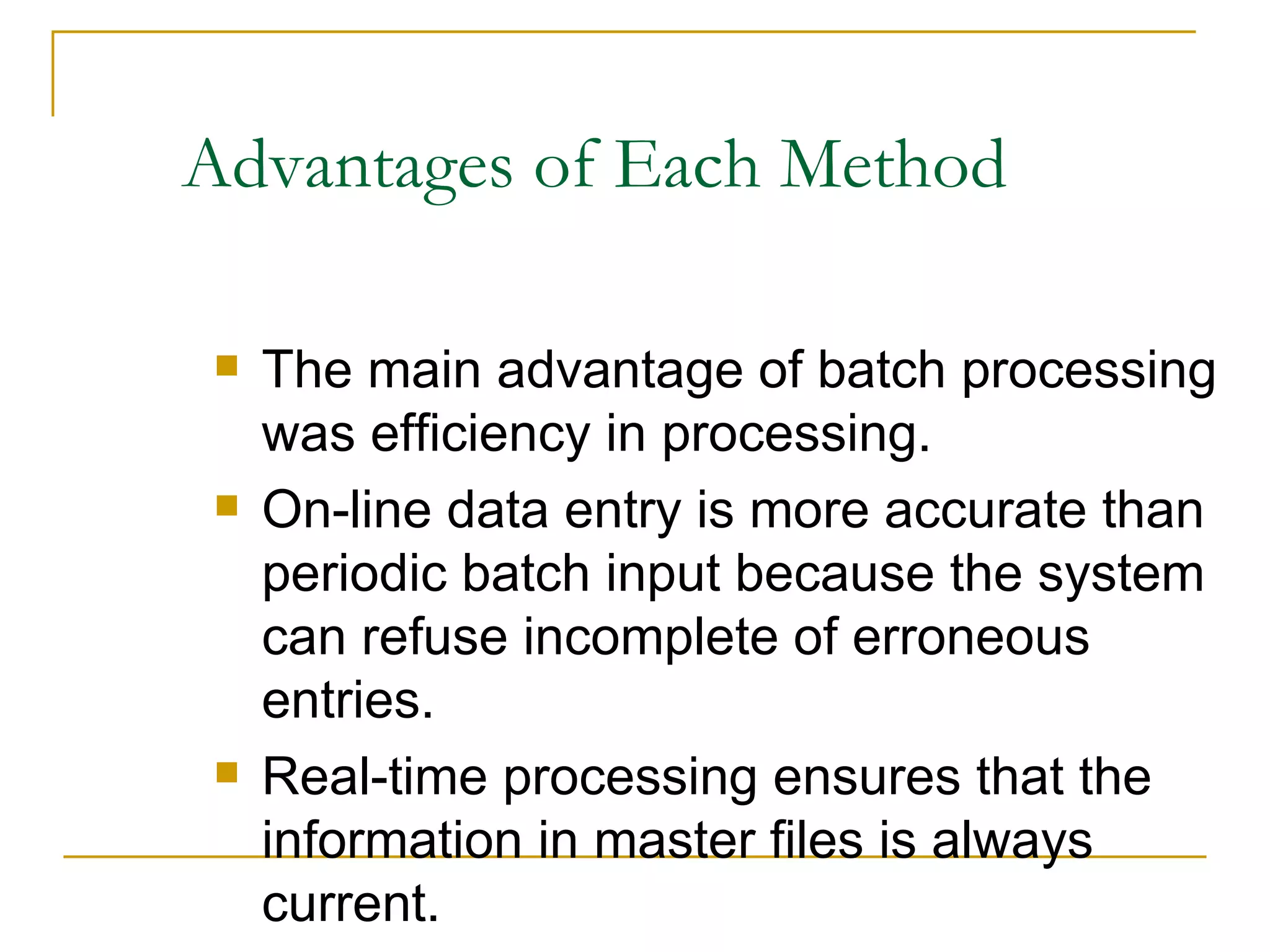
There are four main types of file organization: serial, sequential, indexed sequential, and direct access/random access. Sequential files store records in a specific key-based order and require rewriting the entire file to add or delete records. Direct access files allow directly reading or writing records based on their address, allowing quick random access but being more complex. Indexed sequential files combine the sequential ordering of records with an index to allow both sequential and random access via the index. Batch processing periodically updates master files in batches while online and real-time processing allow immediate updating as transactions occur.