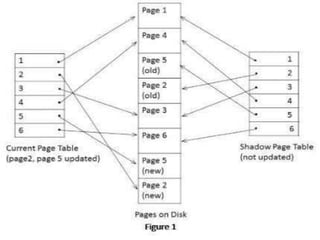
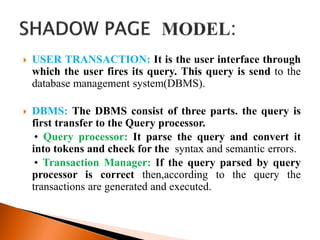
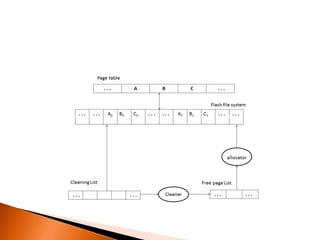
The document describes shadow paging, an alternative to log-based recovery for databases. It maintains two page tables during transactions: a current page table and a shadow page table stored in non-volatile storage. This allows recovery of the pre-transaction state if needed. Shadow paging has advantages over logging like no log overhead and trivial recovery, but has higher commit overhead as many pages must be flushed. It also risks data fragmentation and requires garbage collection of old data versions after transactions.