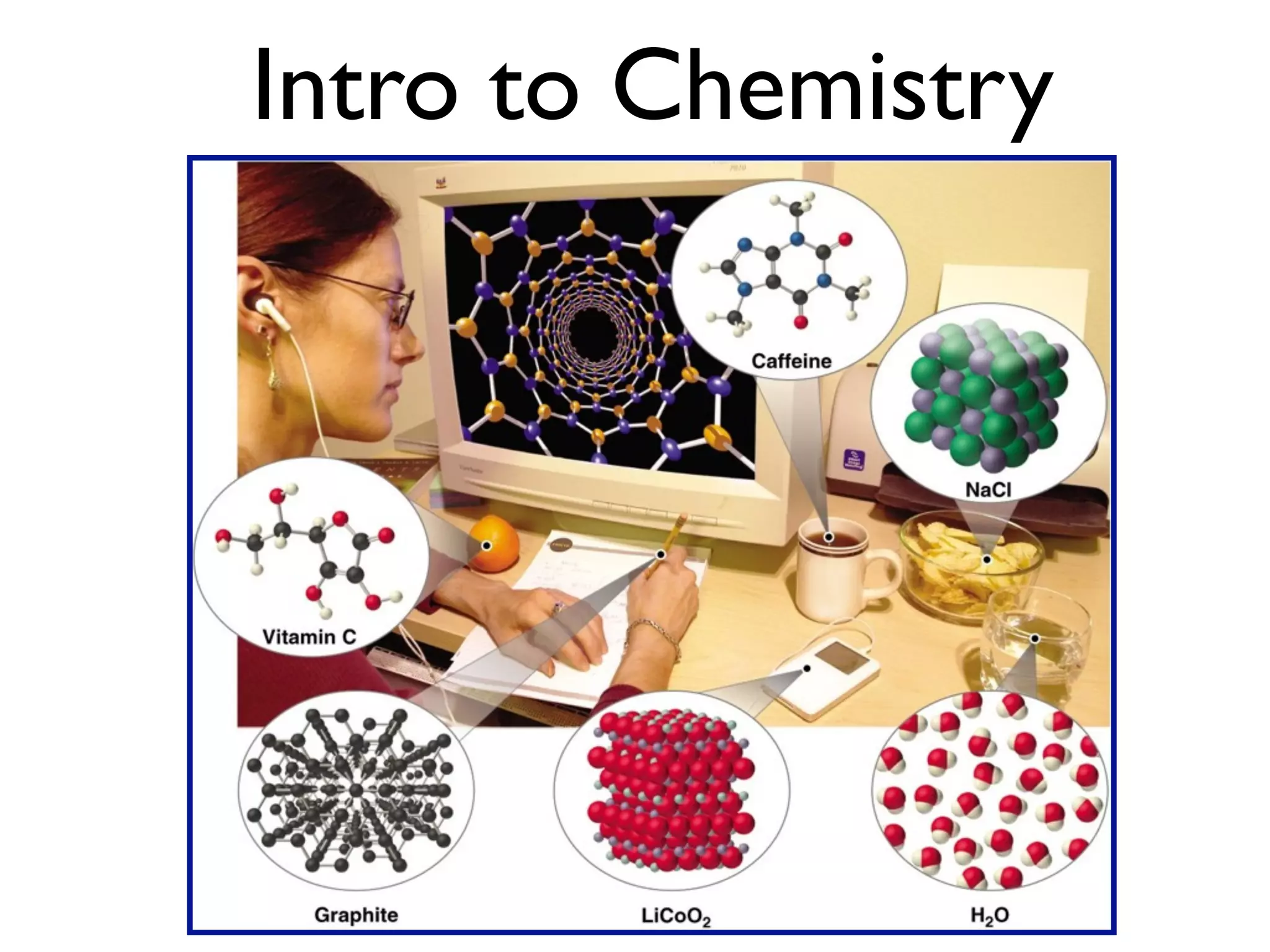
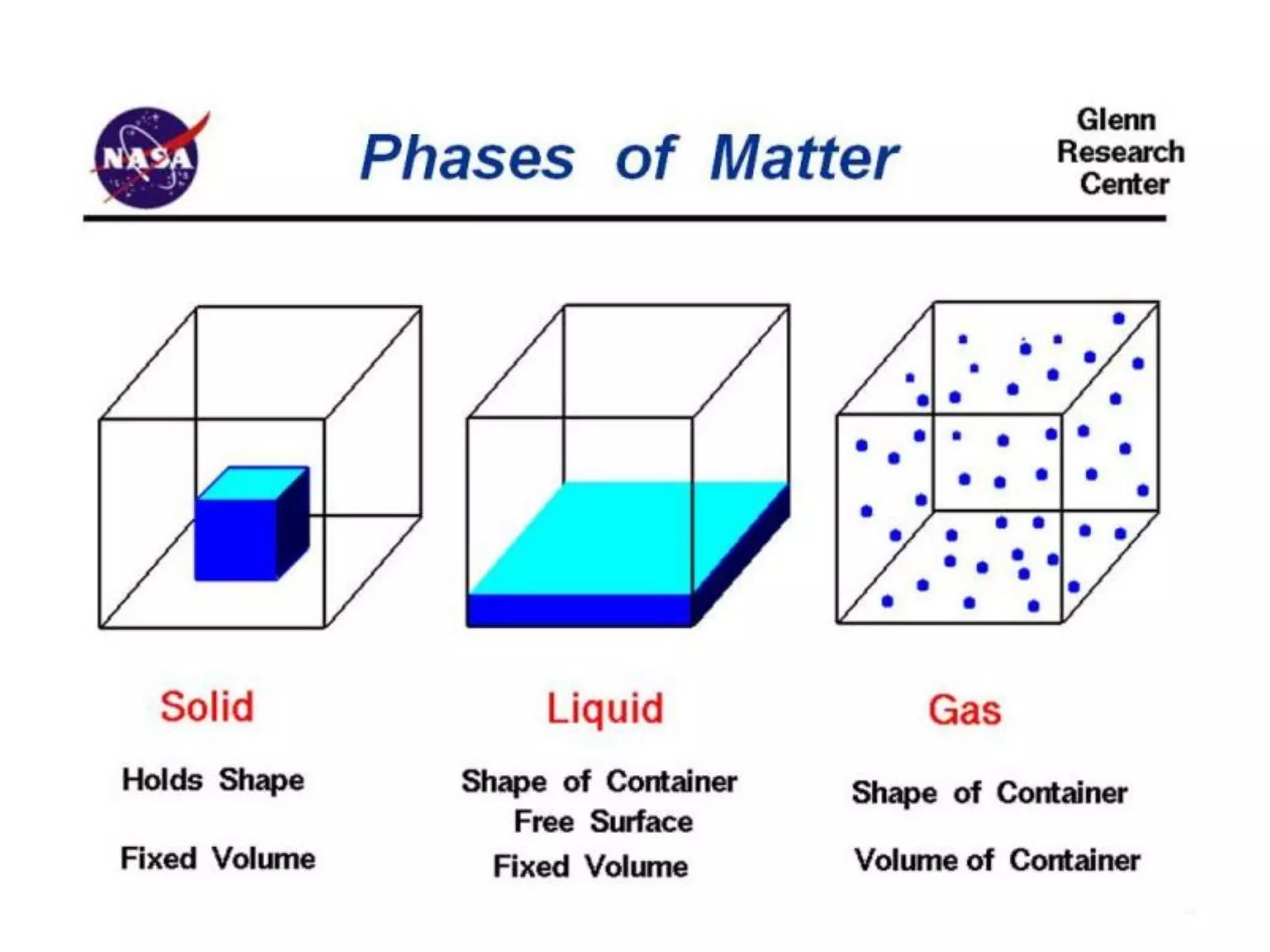
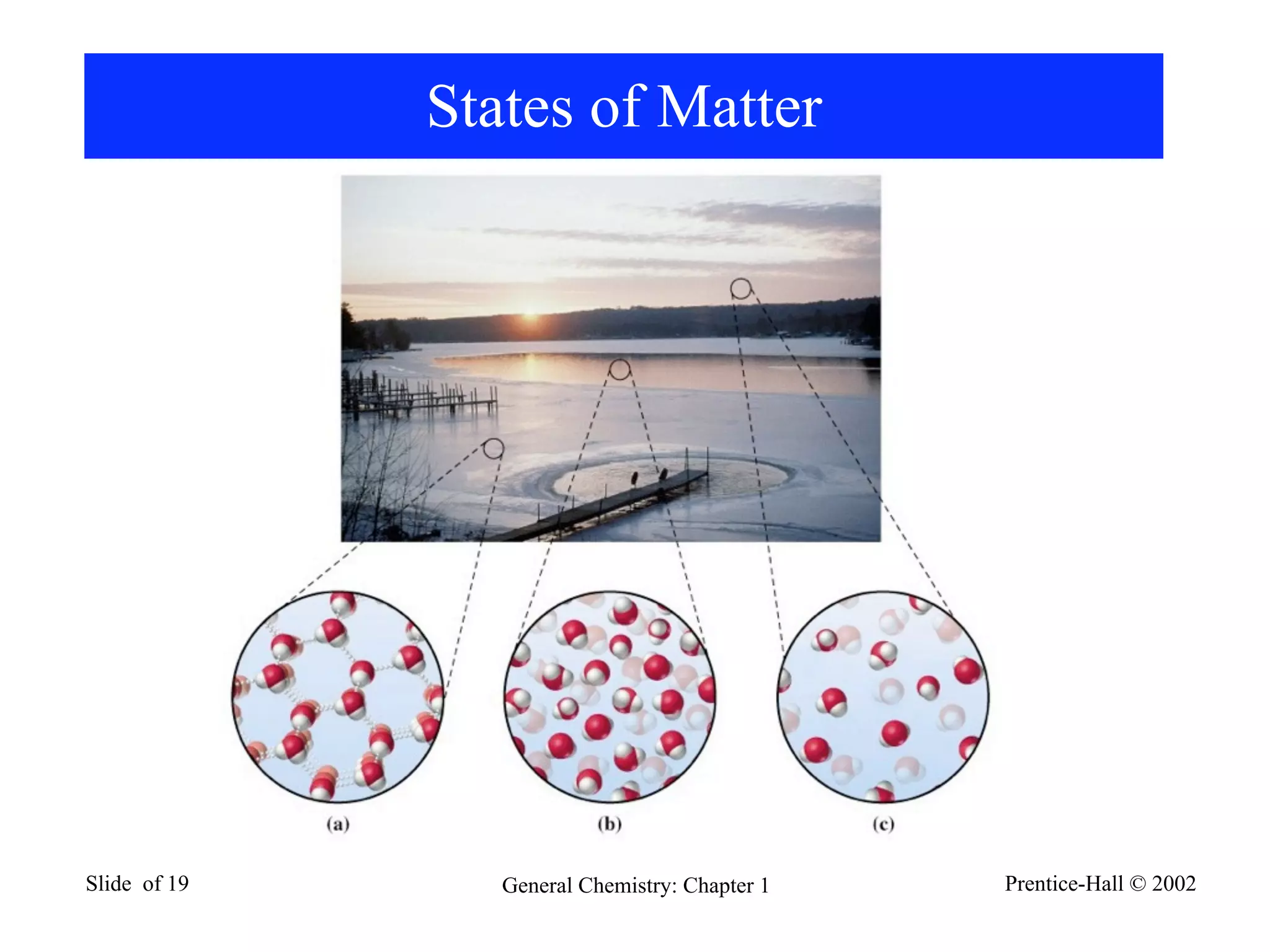
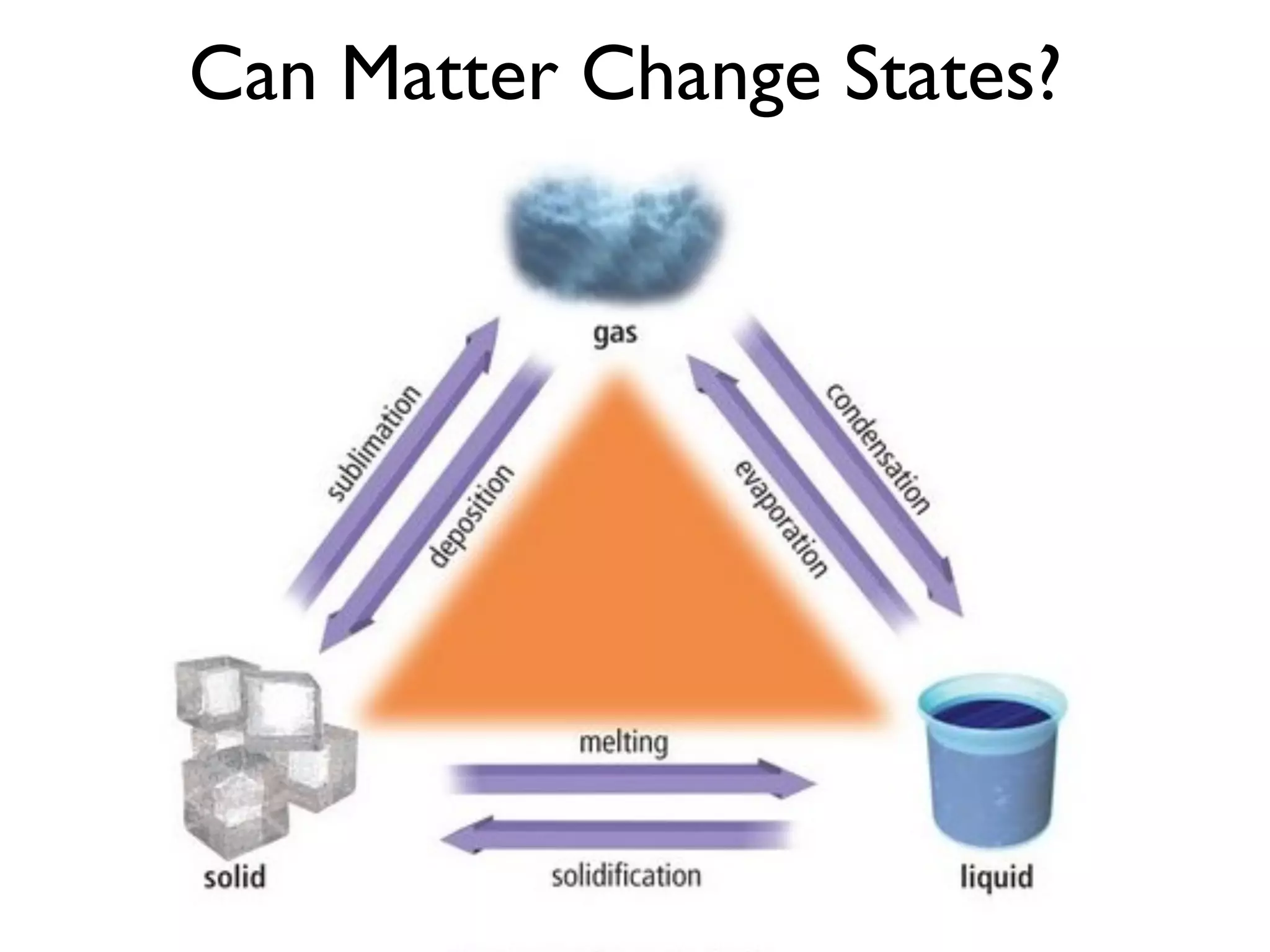
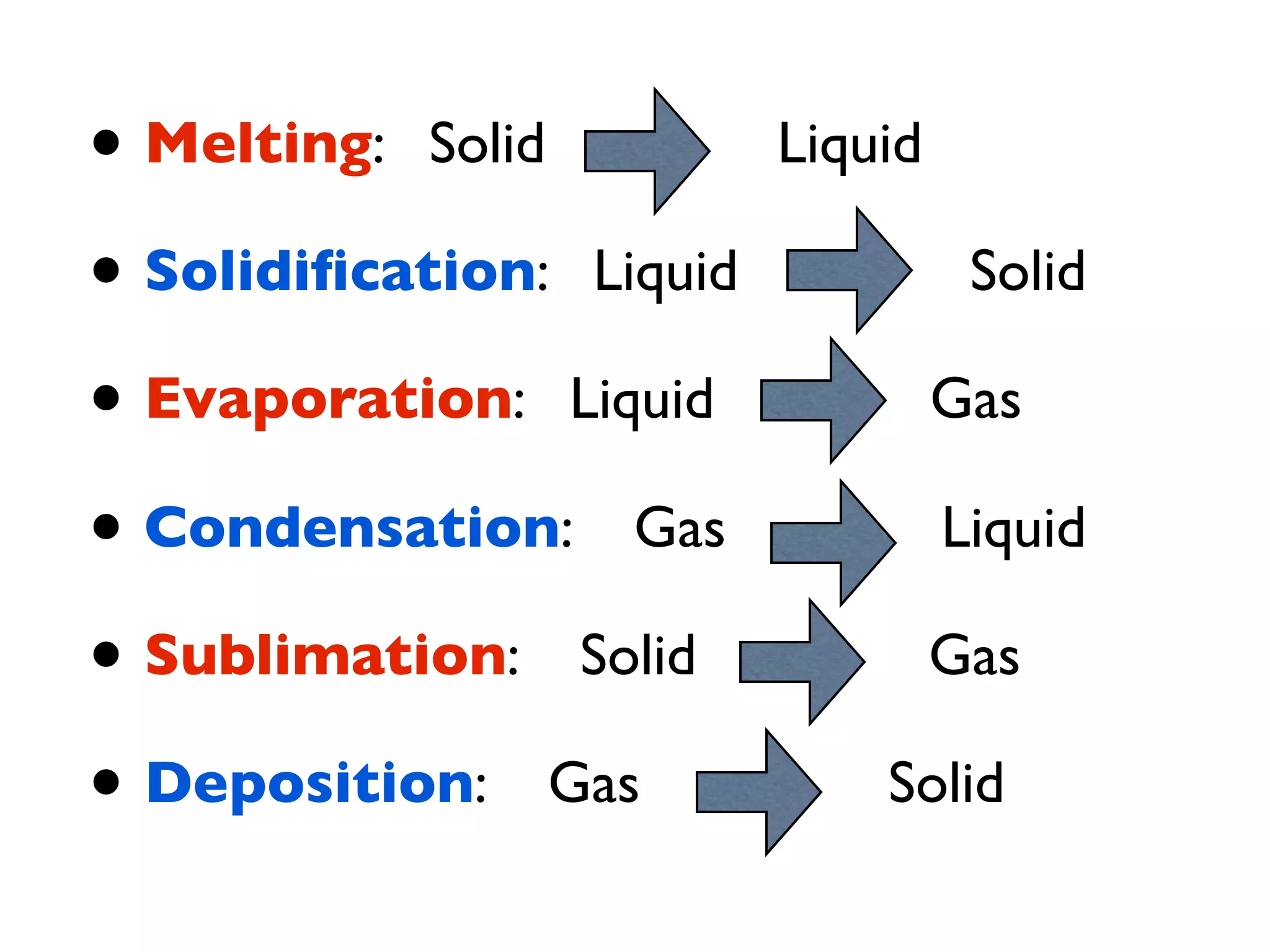
The document provides an overview of introductory chemistry concepts including:
1) Lab safety rules such as using common sense and no horseplay.
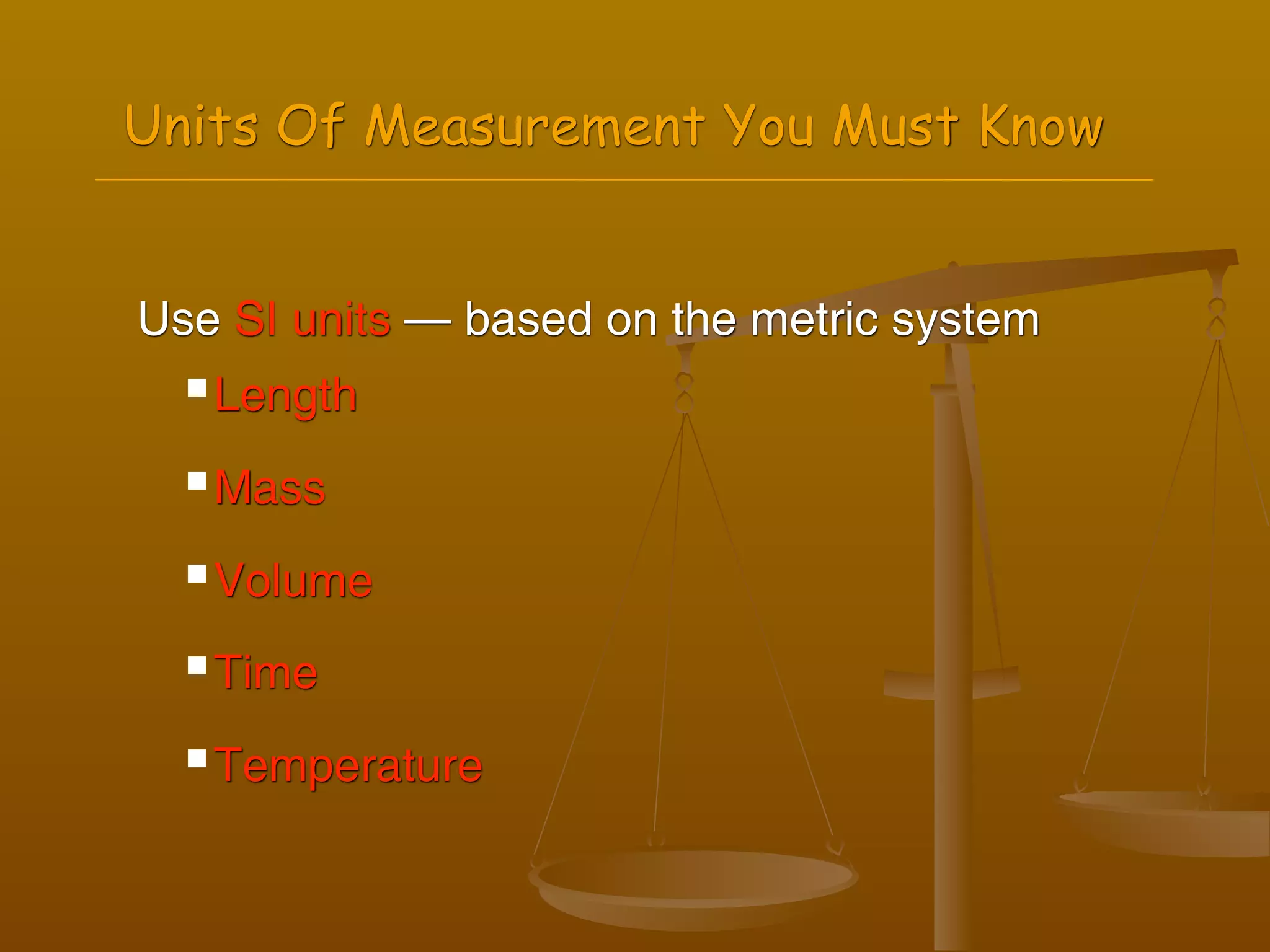
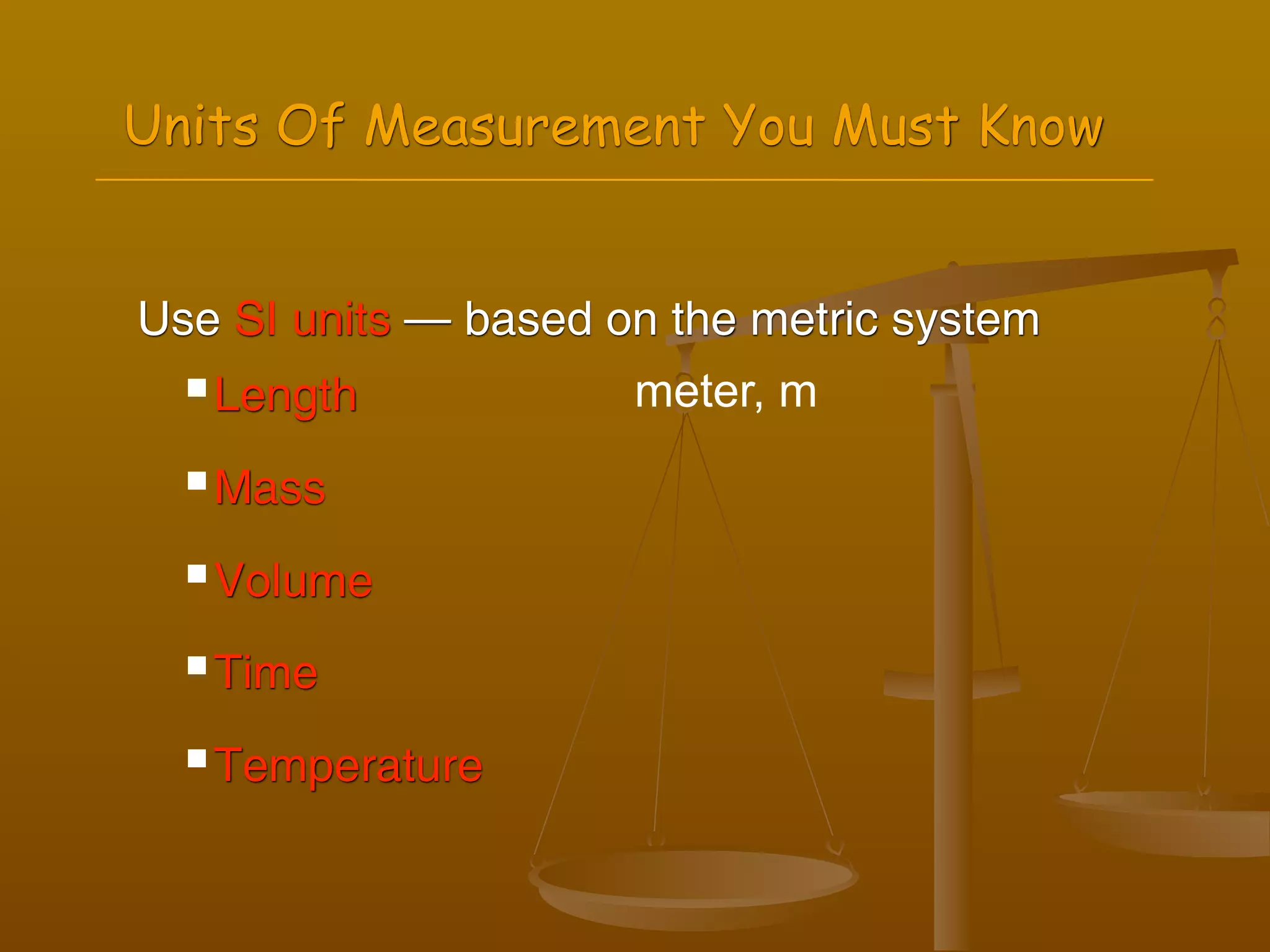
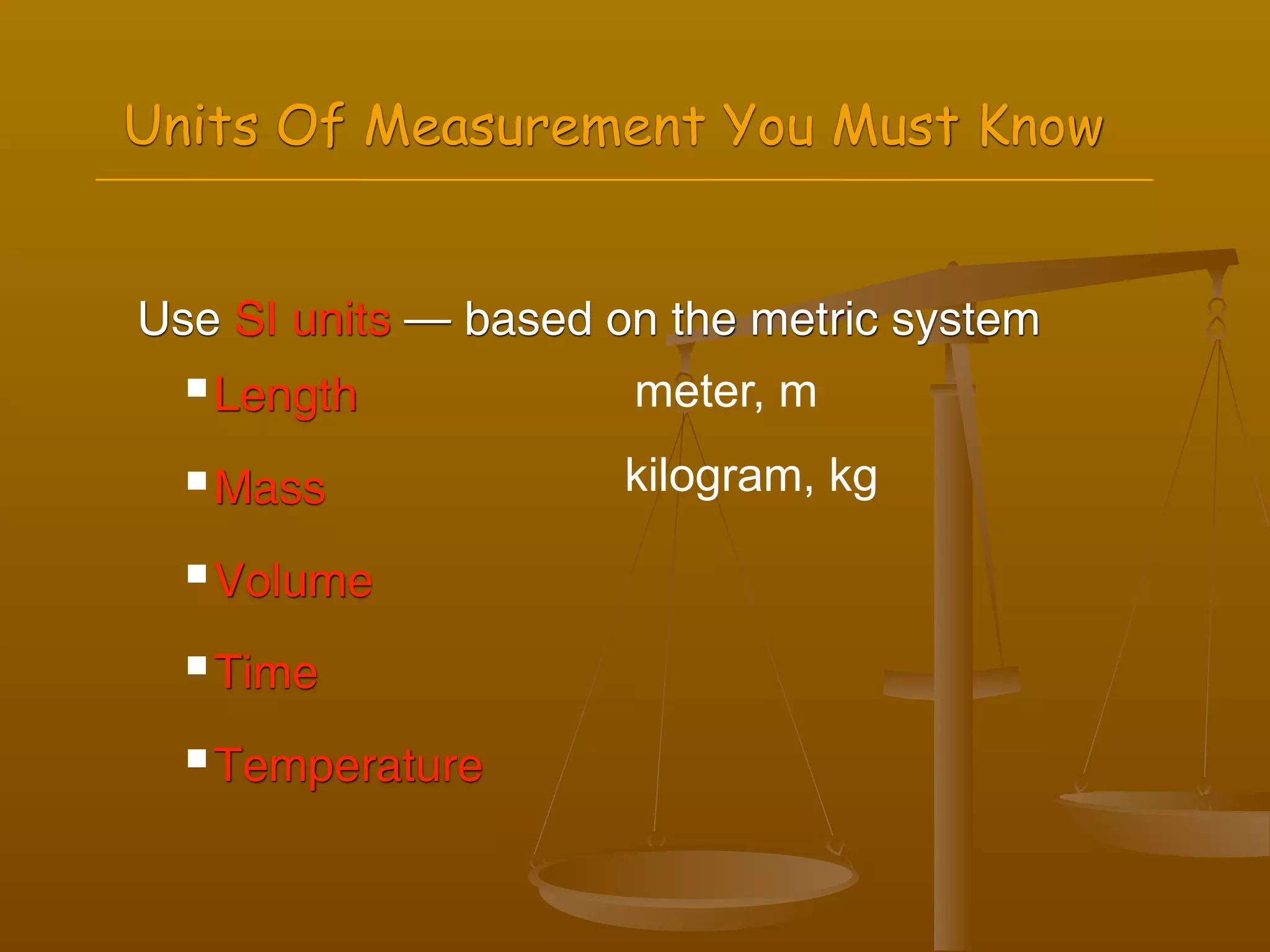
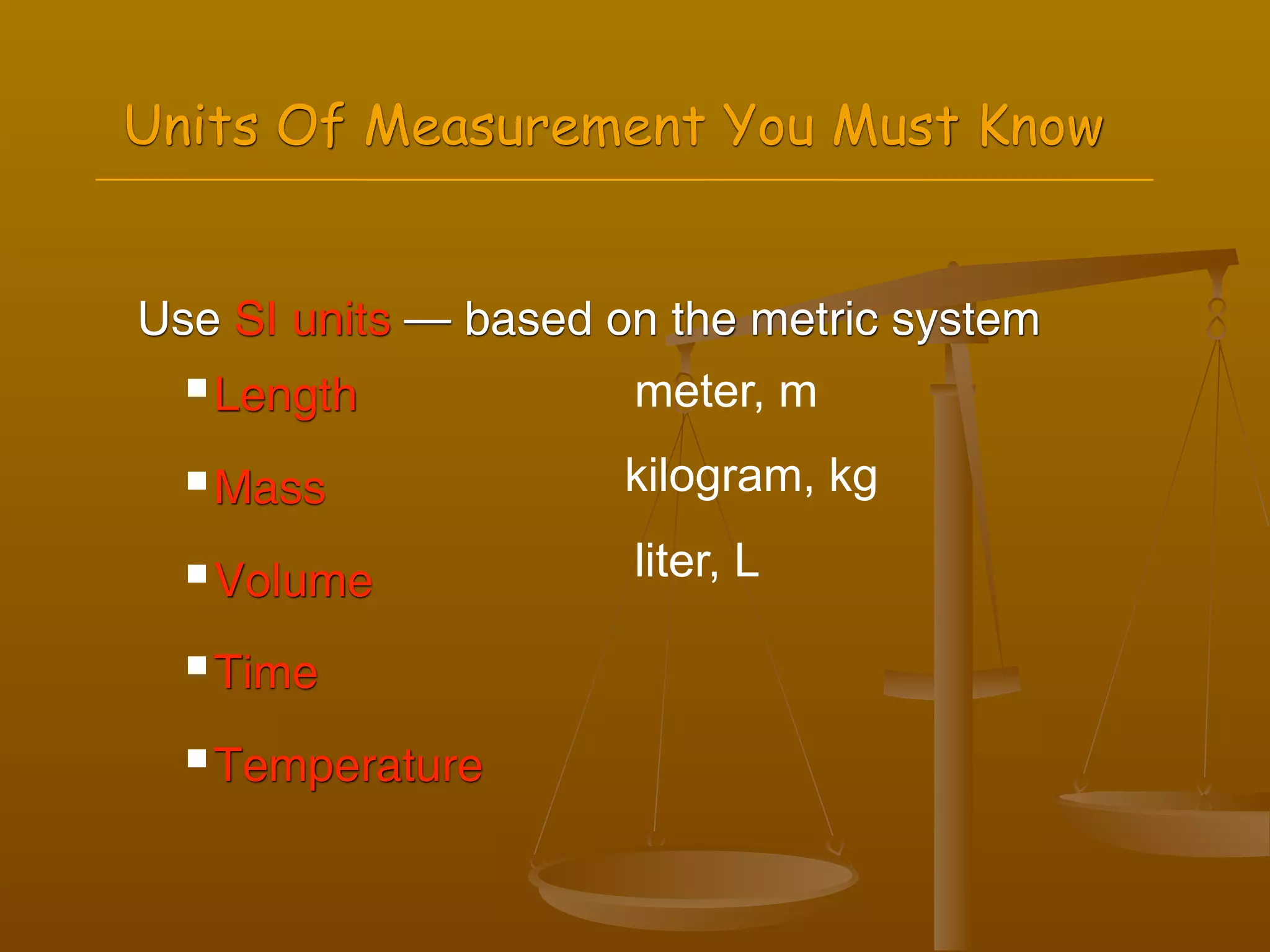
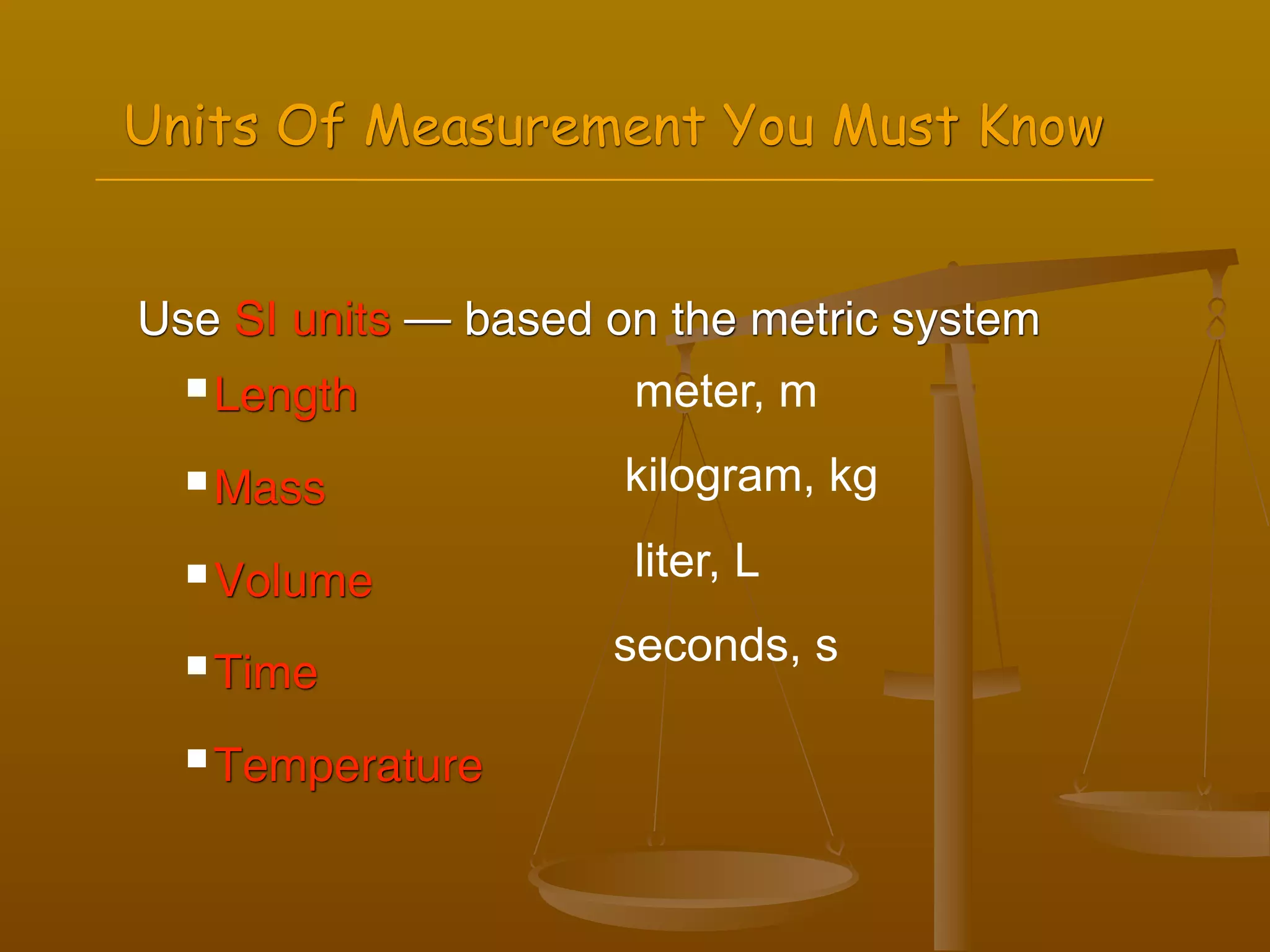
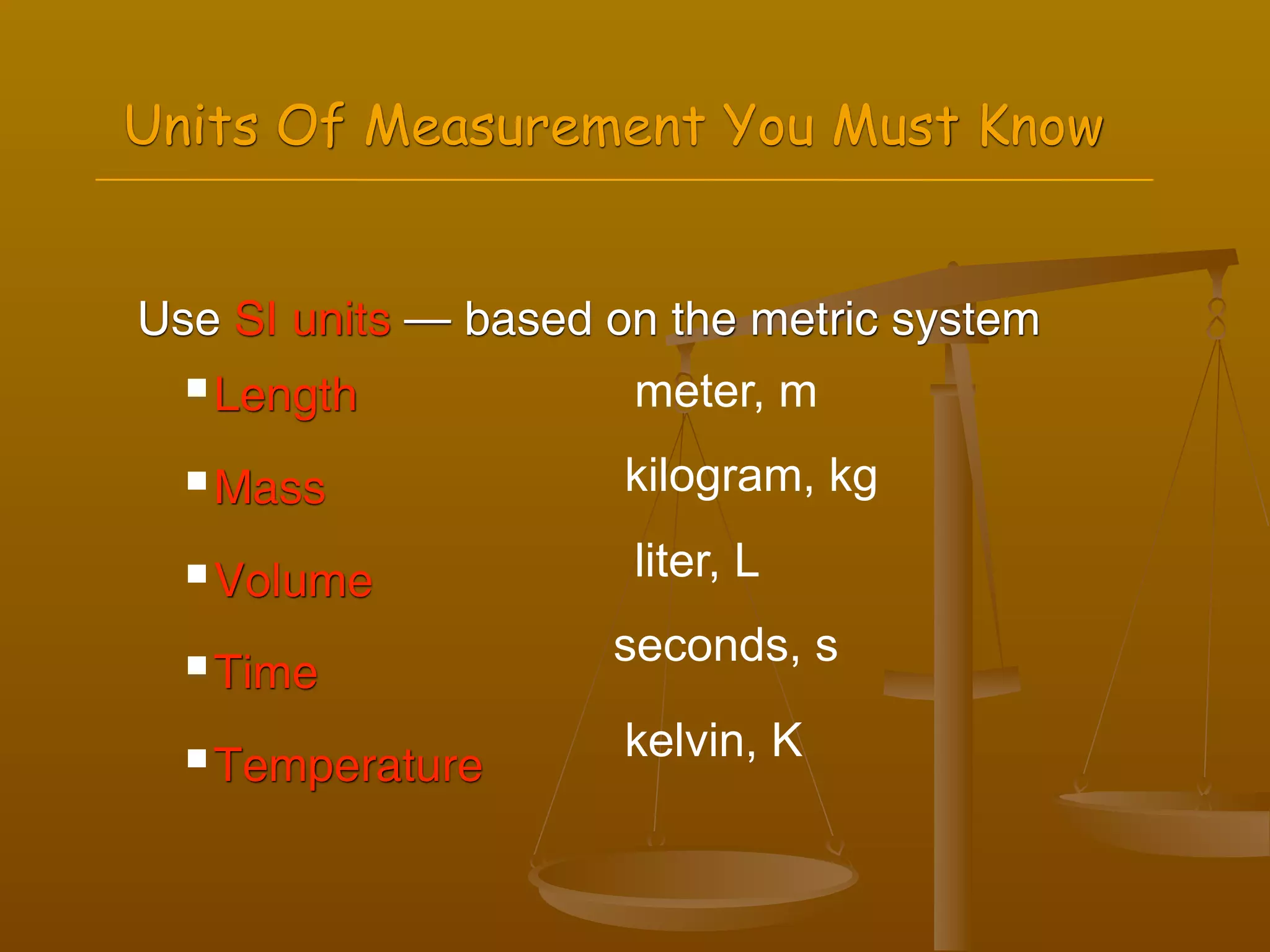
2) Units of measurement used in chemistry including meters, kilograms, liters, seconds, and kelvin.
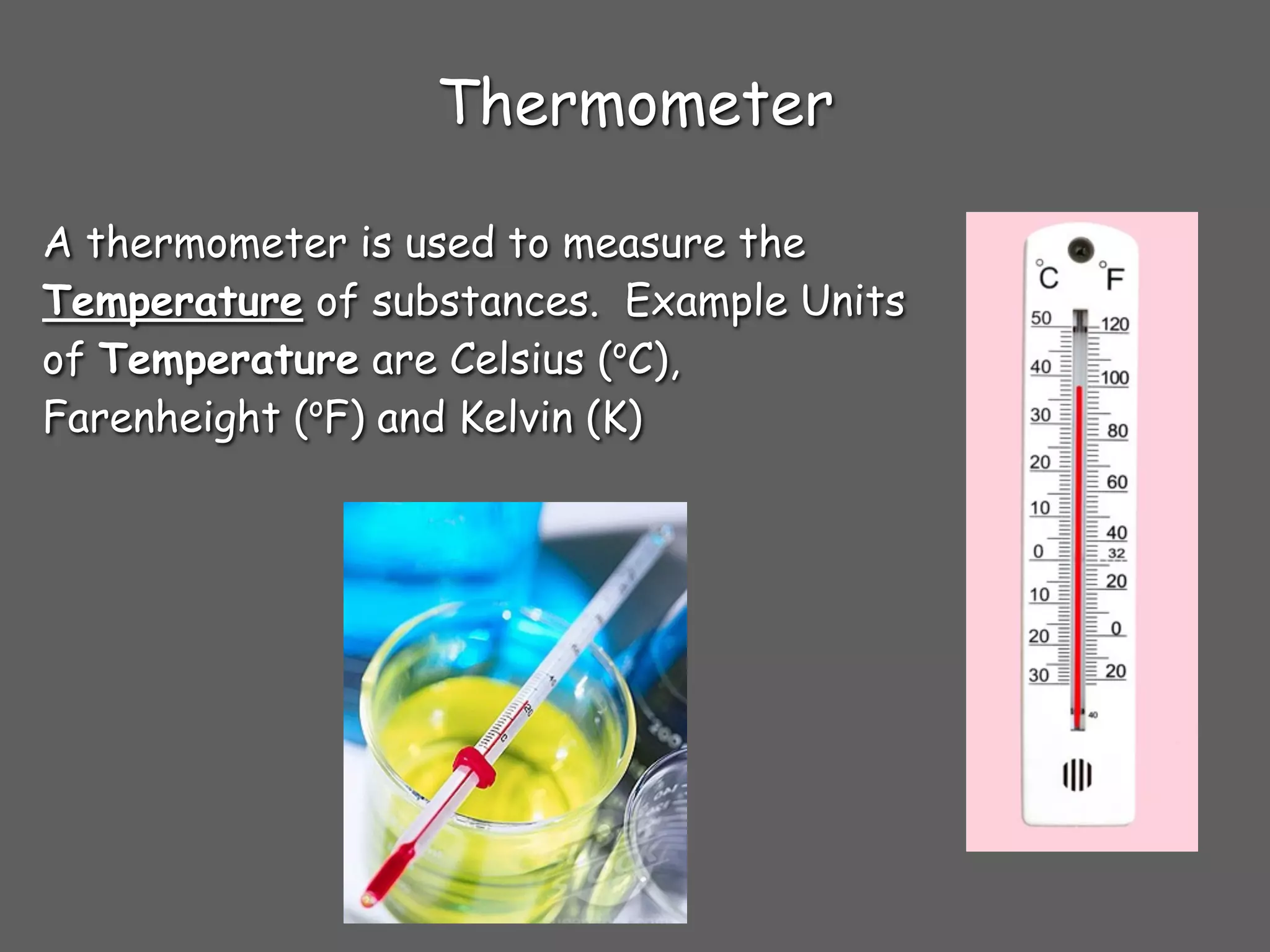
3) Tools used to measure different properties in the lab including graduated cylinders to measure volume, meters sticks to measure length, thermometers to measure temperature, and electronic balances to measure mass.