Embed presentation
Download to read offline



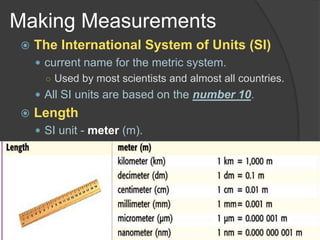
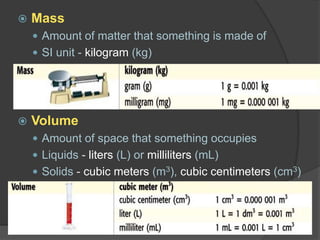





The document discusses the International System of Units (SI) which is the standard global system of measurements. It provides examples of common SI units for length, mass, volume, density, temperature, and area. The SI units are based on multiples of ten to make conversions between units easier. The document also mentions that density is a derived quantity and provides the formulas for calculating density and area. Finally, it emphasizes the importance of following safety procedures and being aware of safety symbols when conducting experiments.









