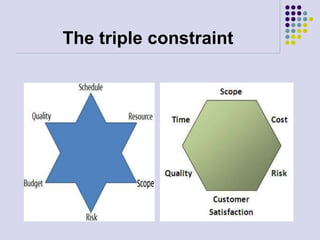
This document provides an overview of key topics from Lesson 2 of the PMBOK Guide, including: the purpose of the PMBOK Guide is to promote good practices in project management; a project is a temporary endeavor with a definite start and end undertaken to create a unique product or service; project management involves applying knowledge, skills, and tools to balance scope, time, cost, quality, risks, and resources; and the project manager is responsible for leading the project team to satisfy task, team, and individual needs.