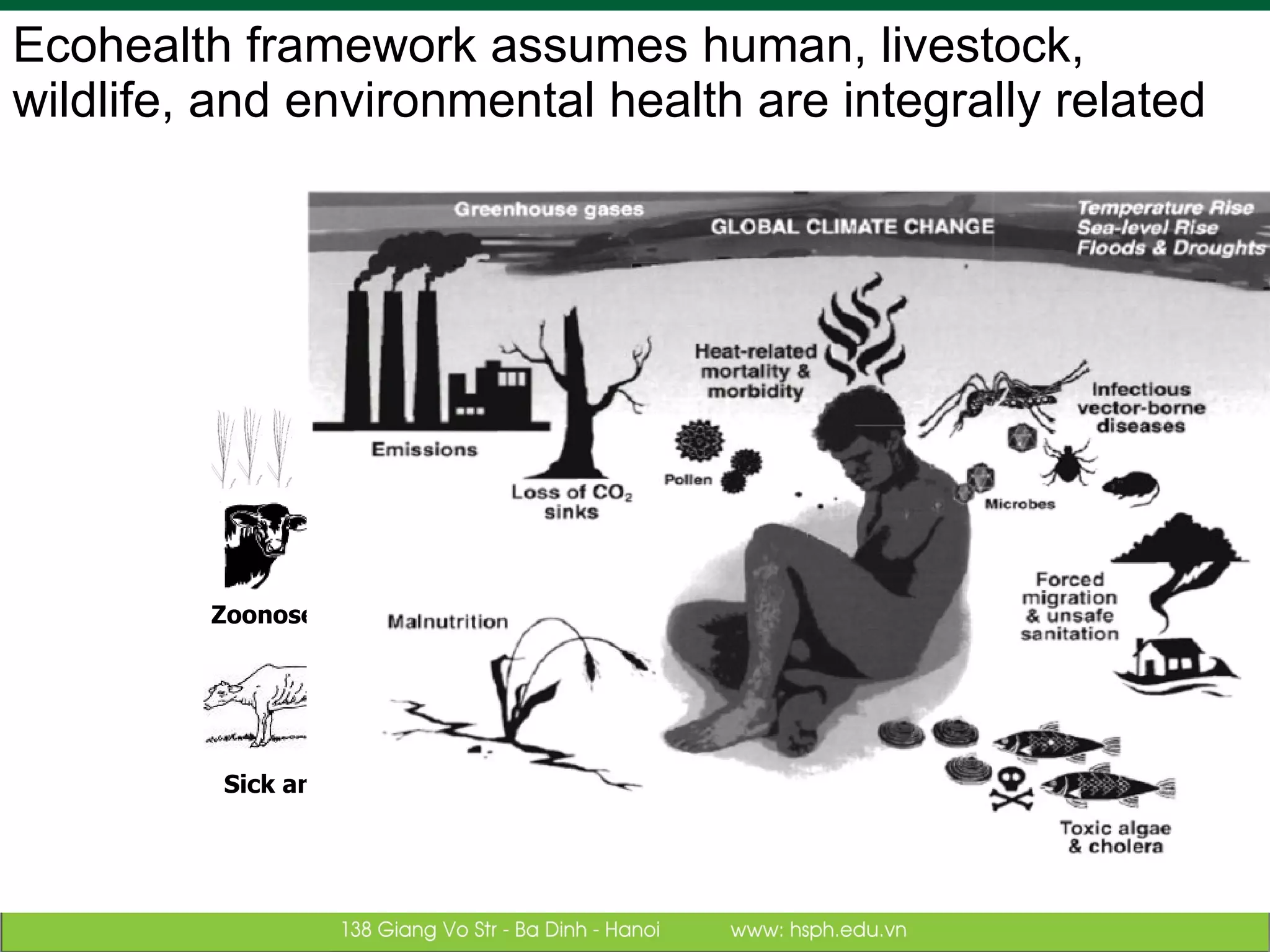
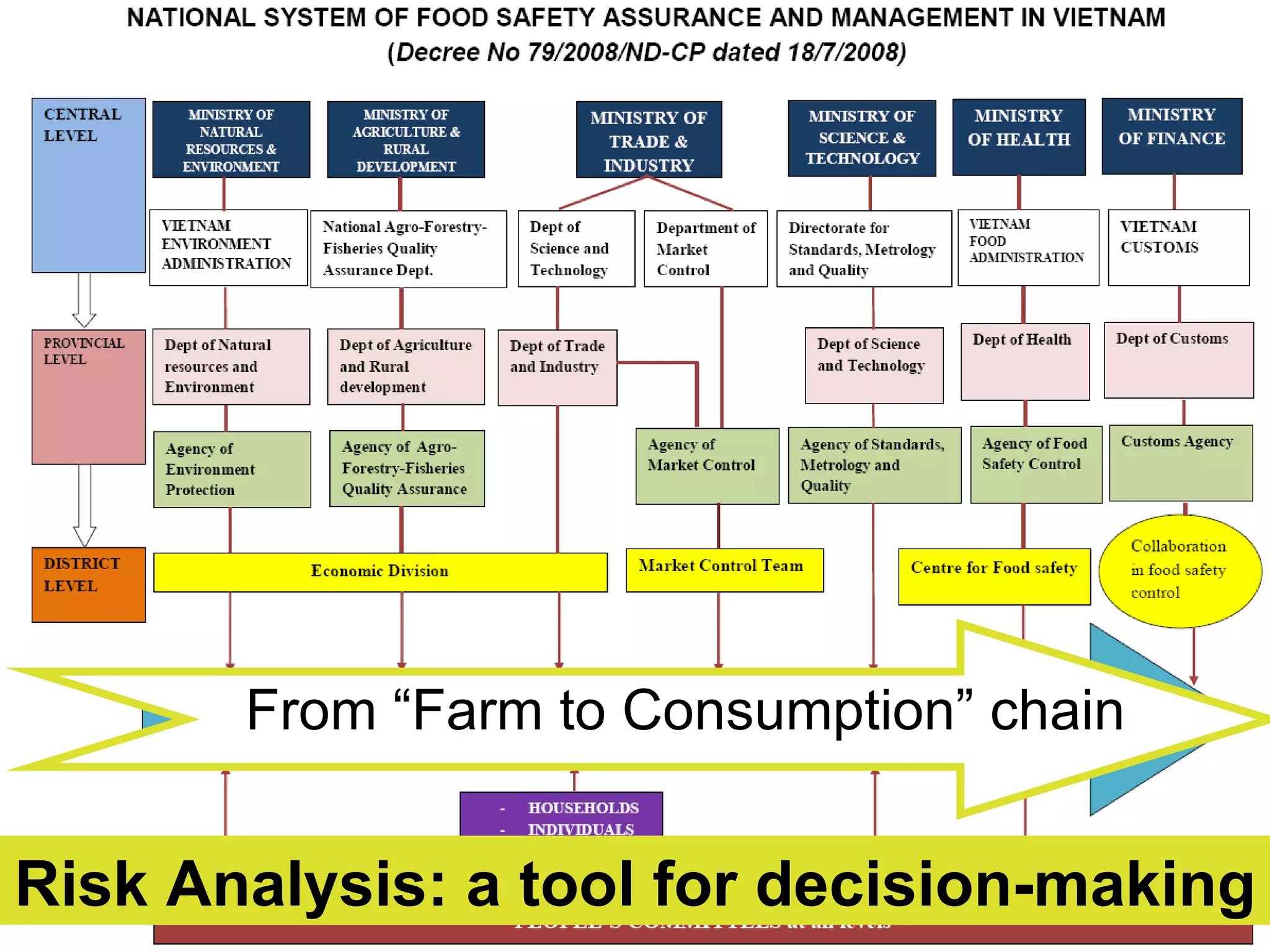
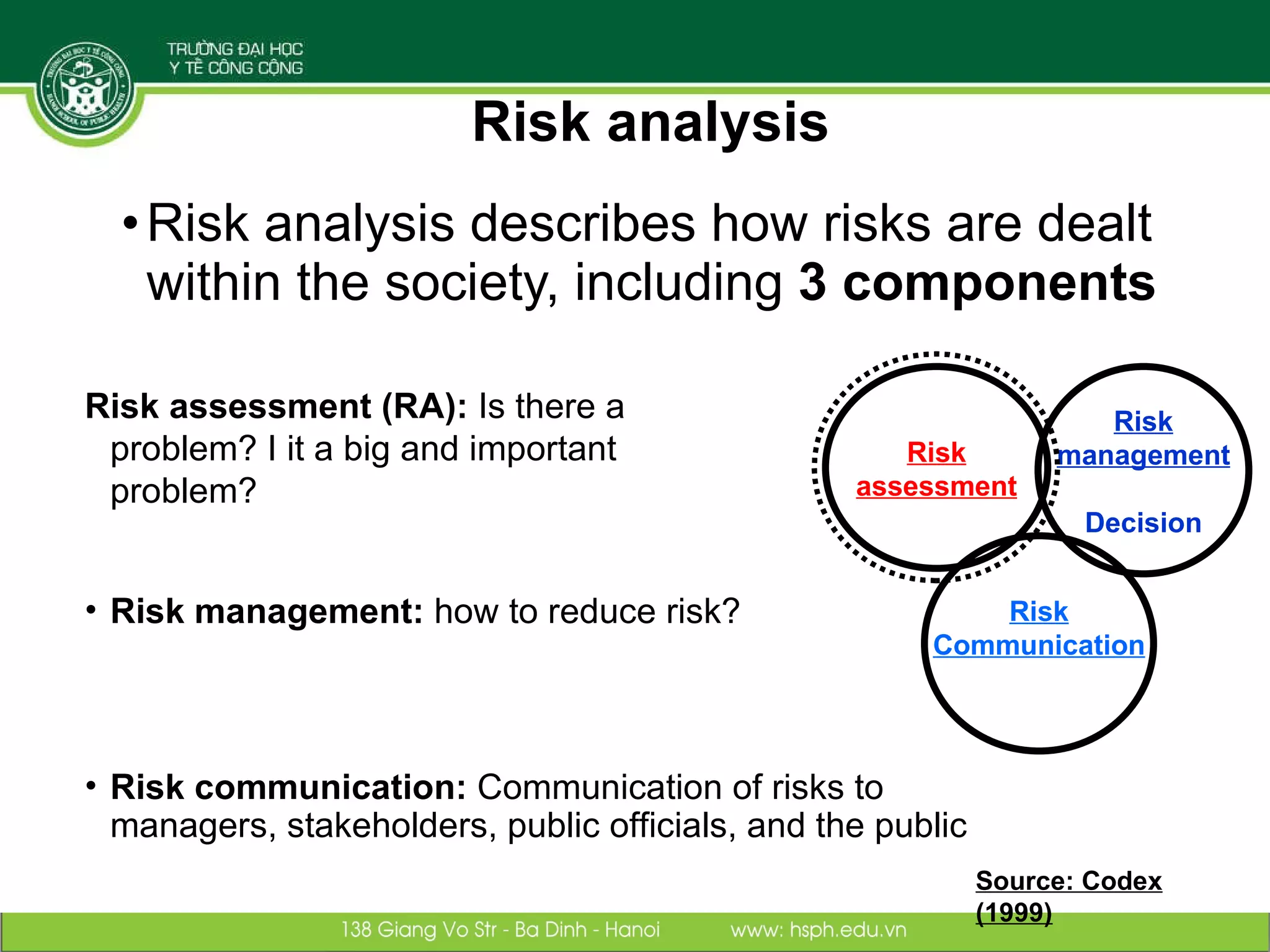
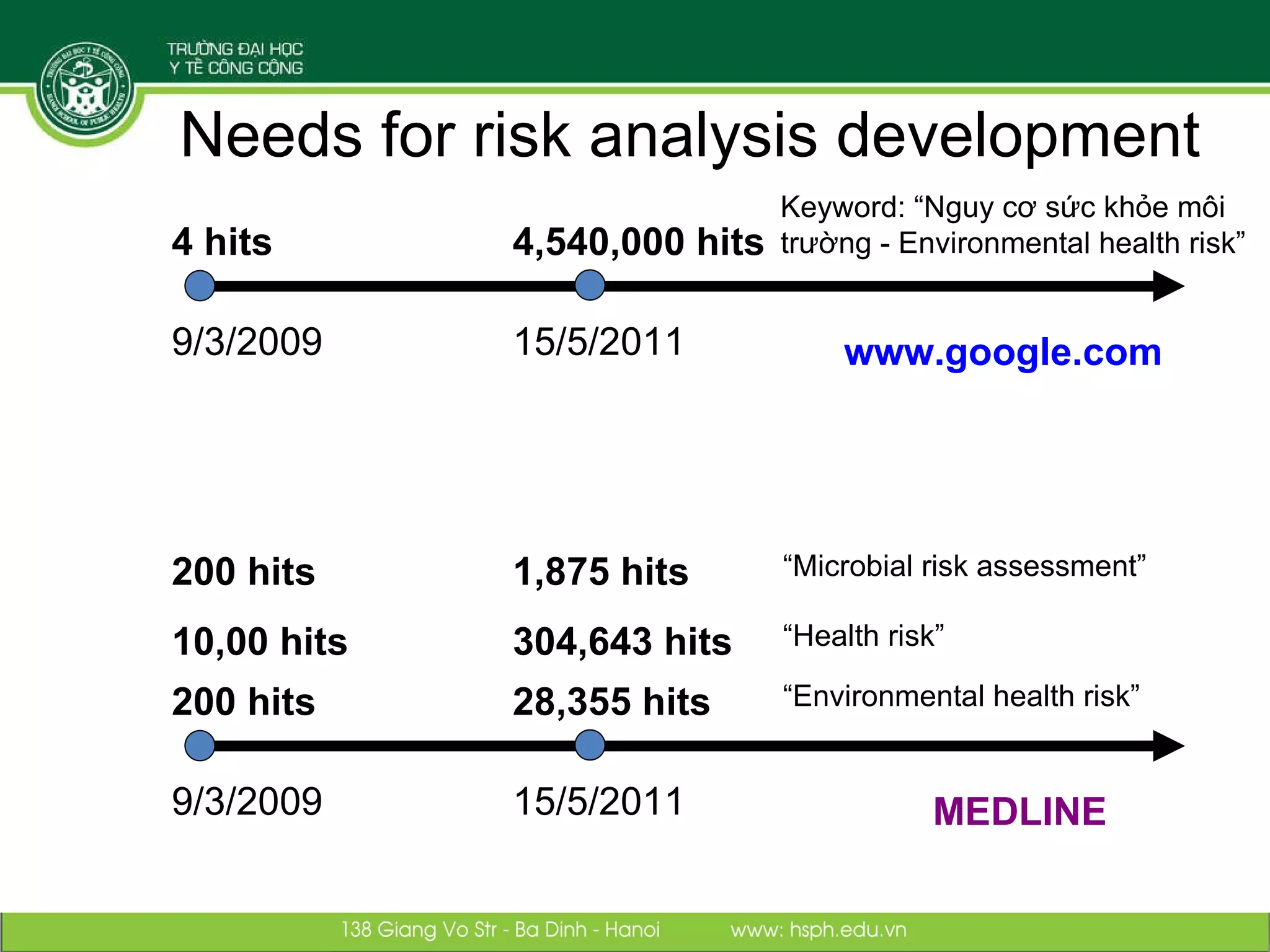
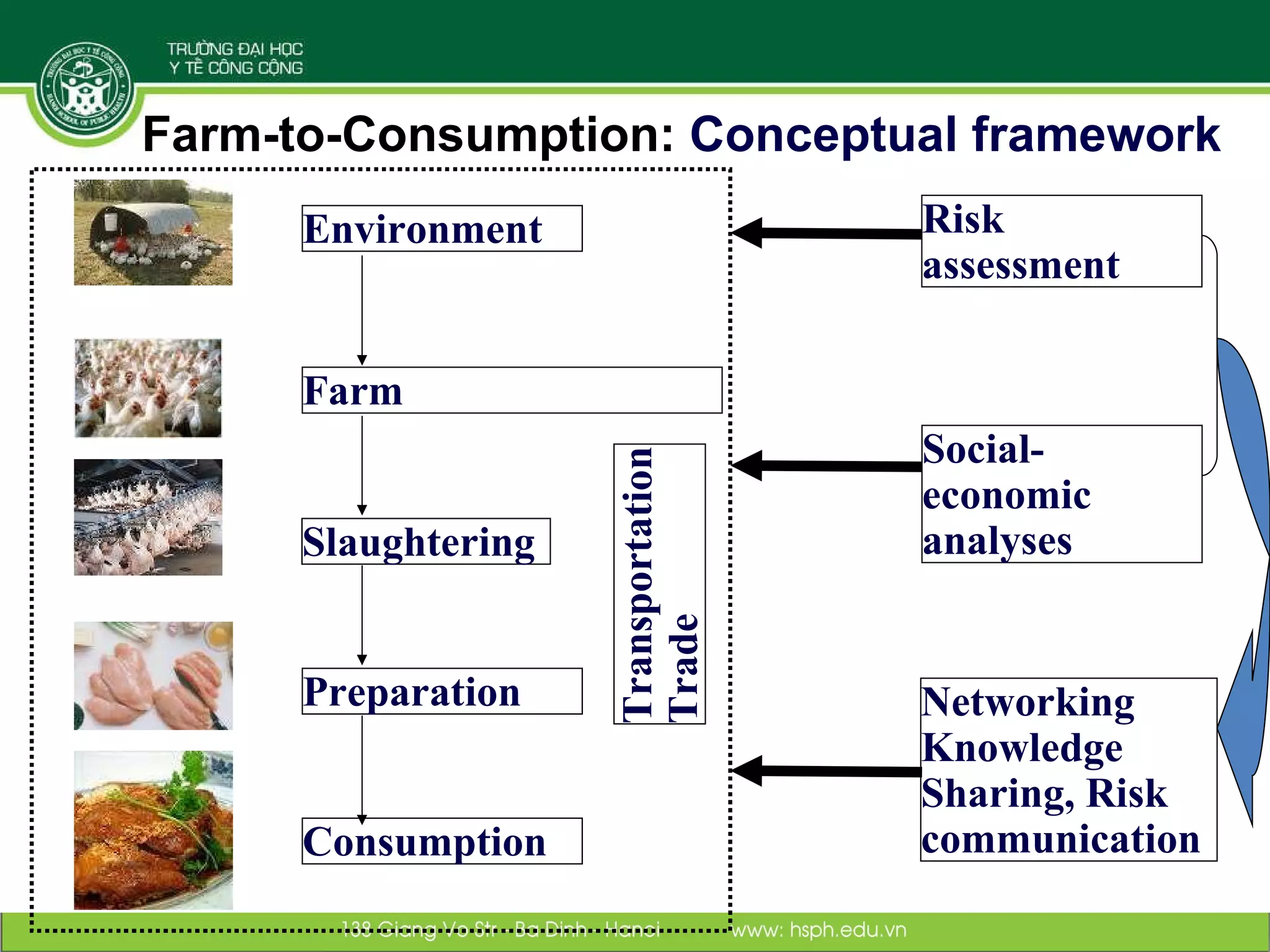
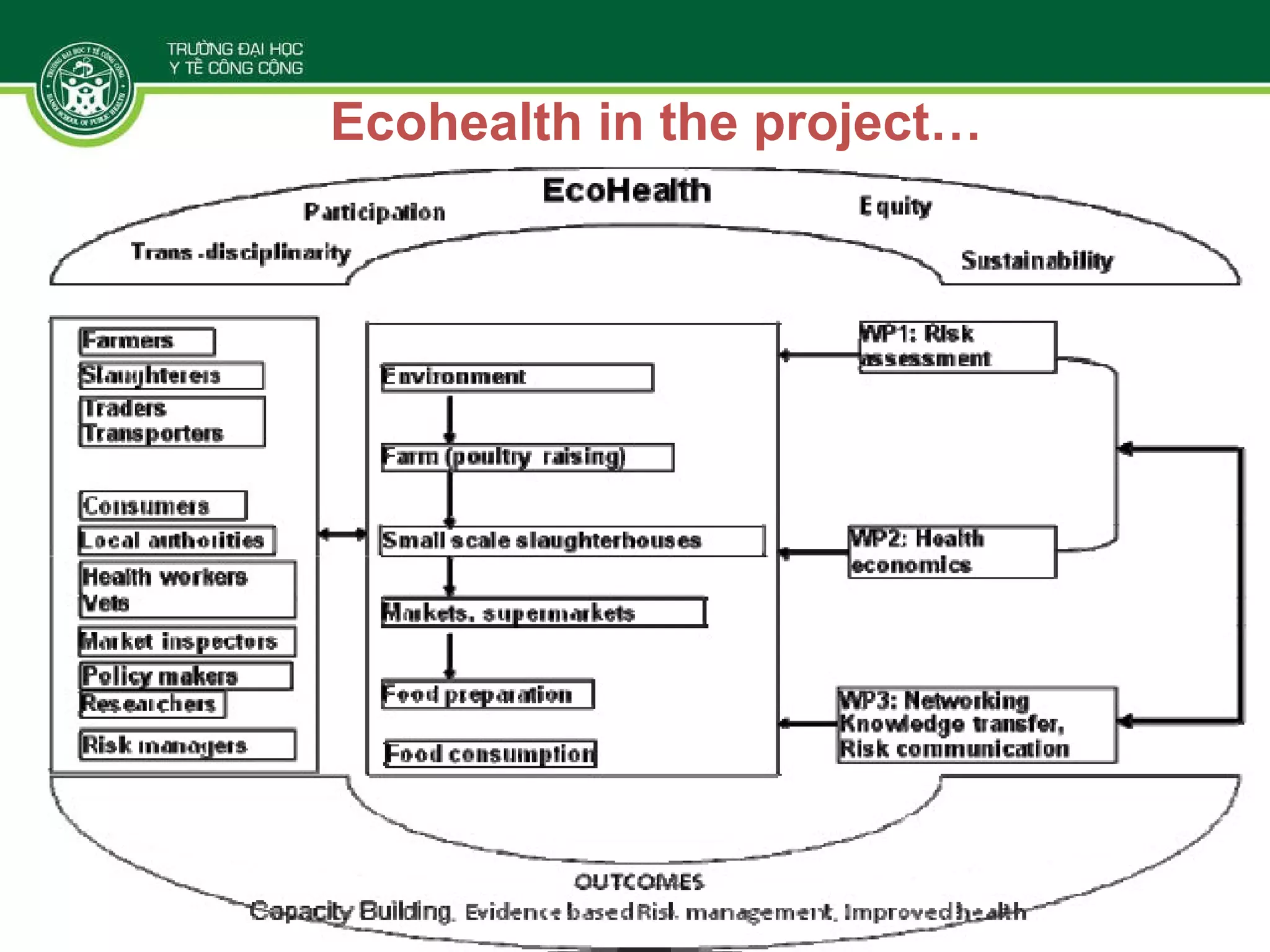
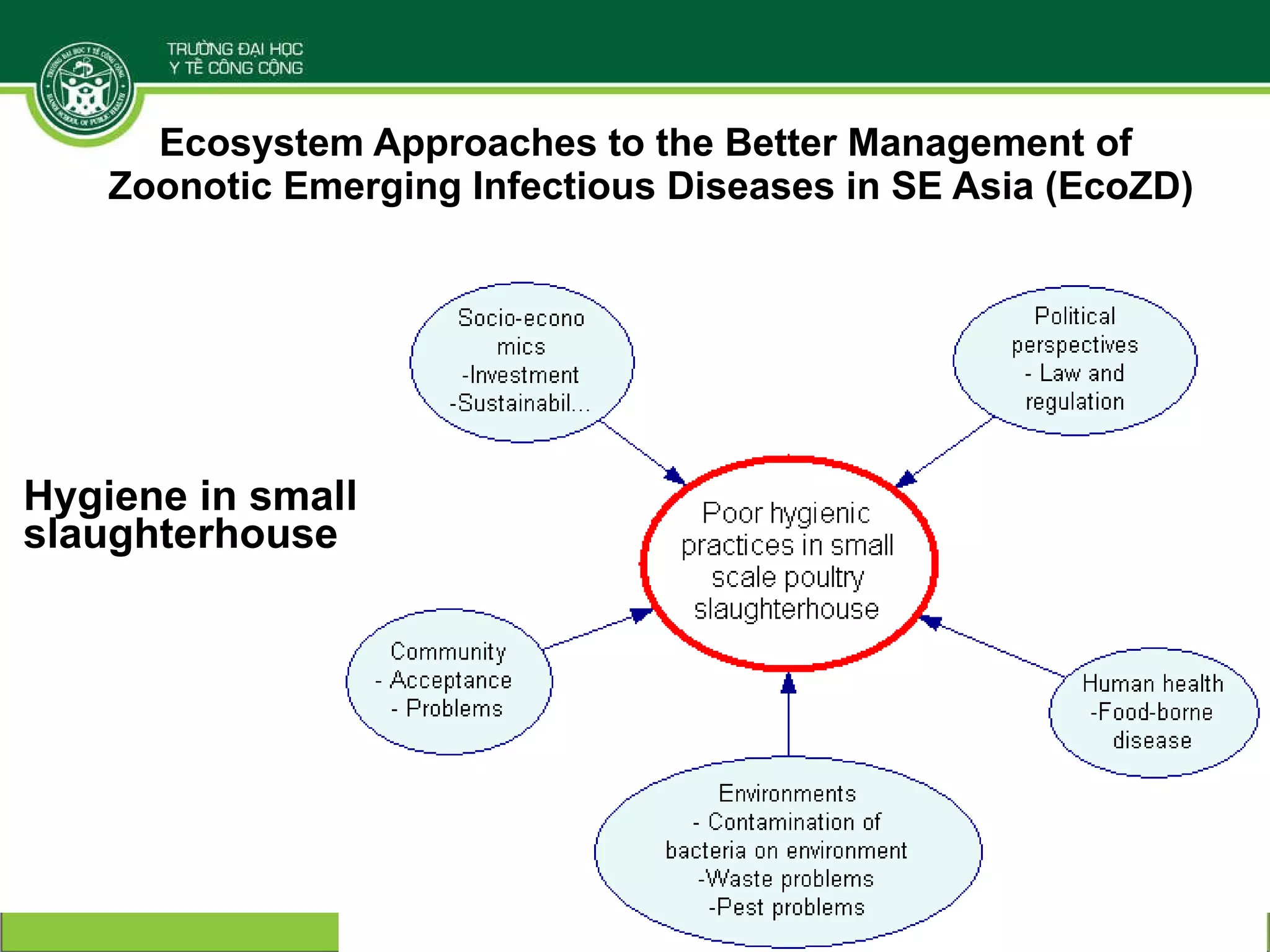
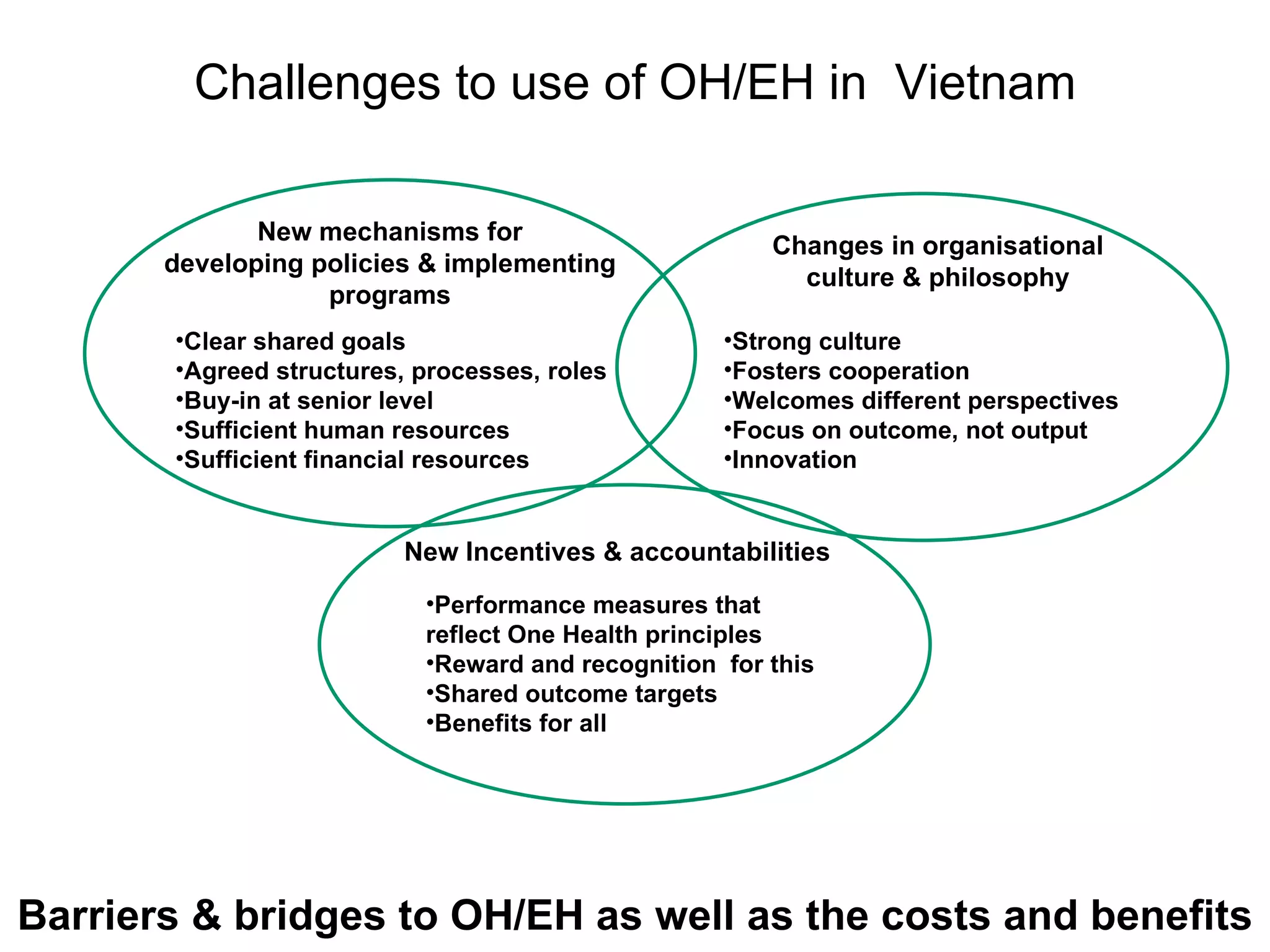
The document discusses the integration of food safety management within the One Health/EcoHealth framework in Vietnam, emphasizing the interconnectedness of human, livestock, wildlife, and environmental health. It highlights significant economic impacts of food-borne diseases and presents a risk analysis approach for improving food safety, including policy implications and training modules for health risk assessment. The document also outlines challenges and opportunities for enhancing One Health/EcoHealth initiatives in Vietnam.