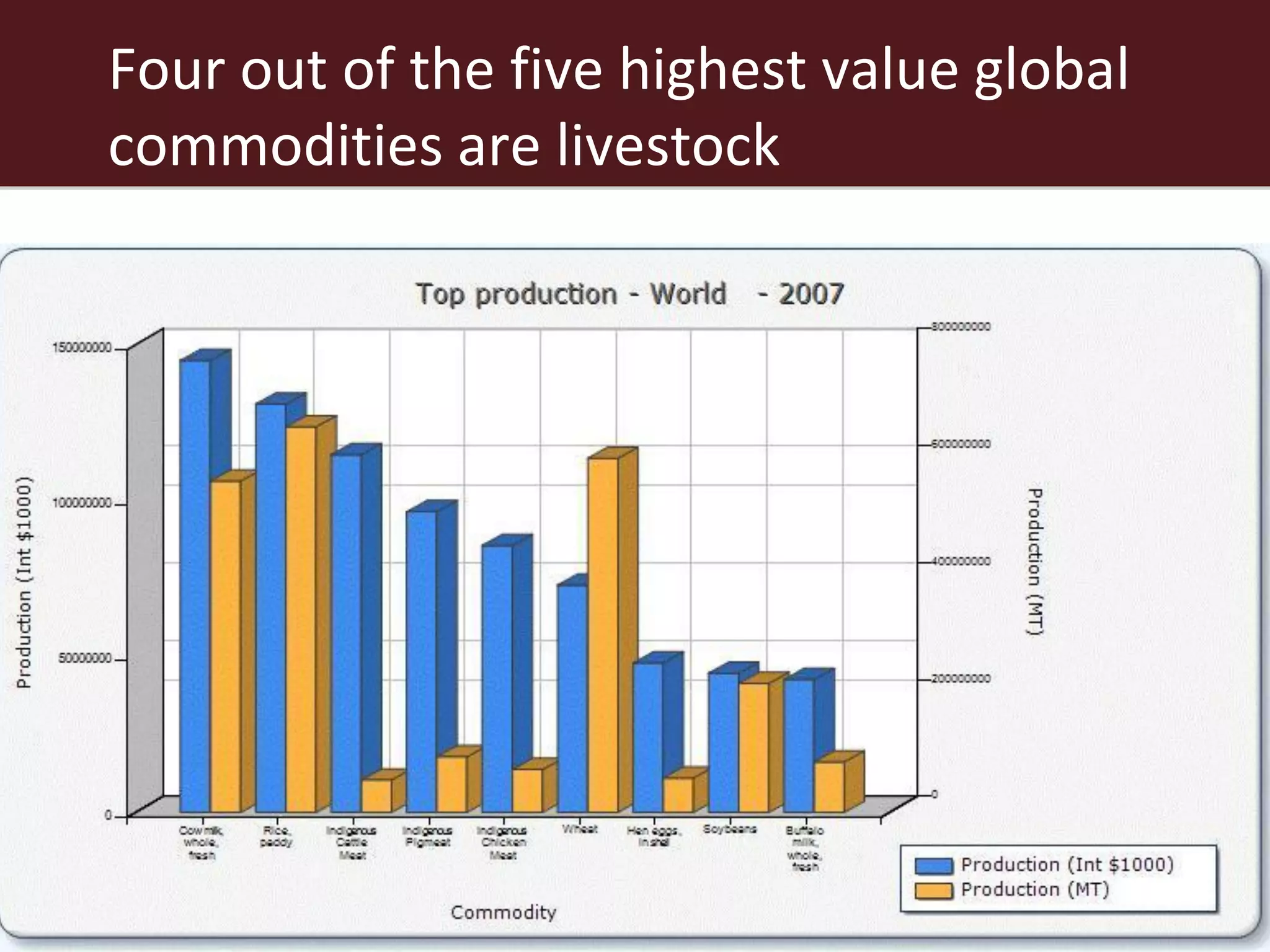
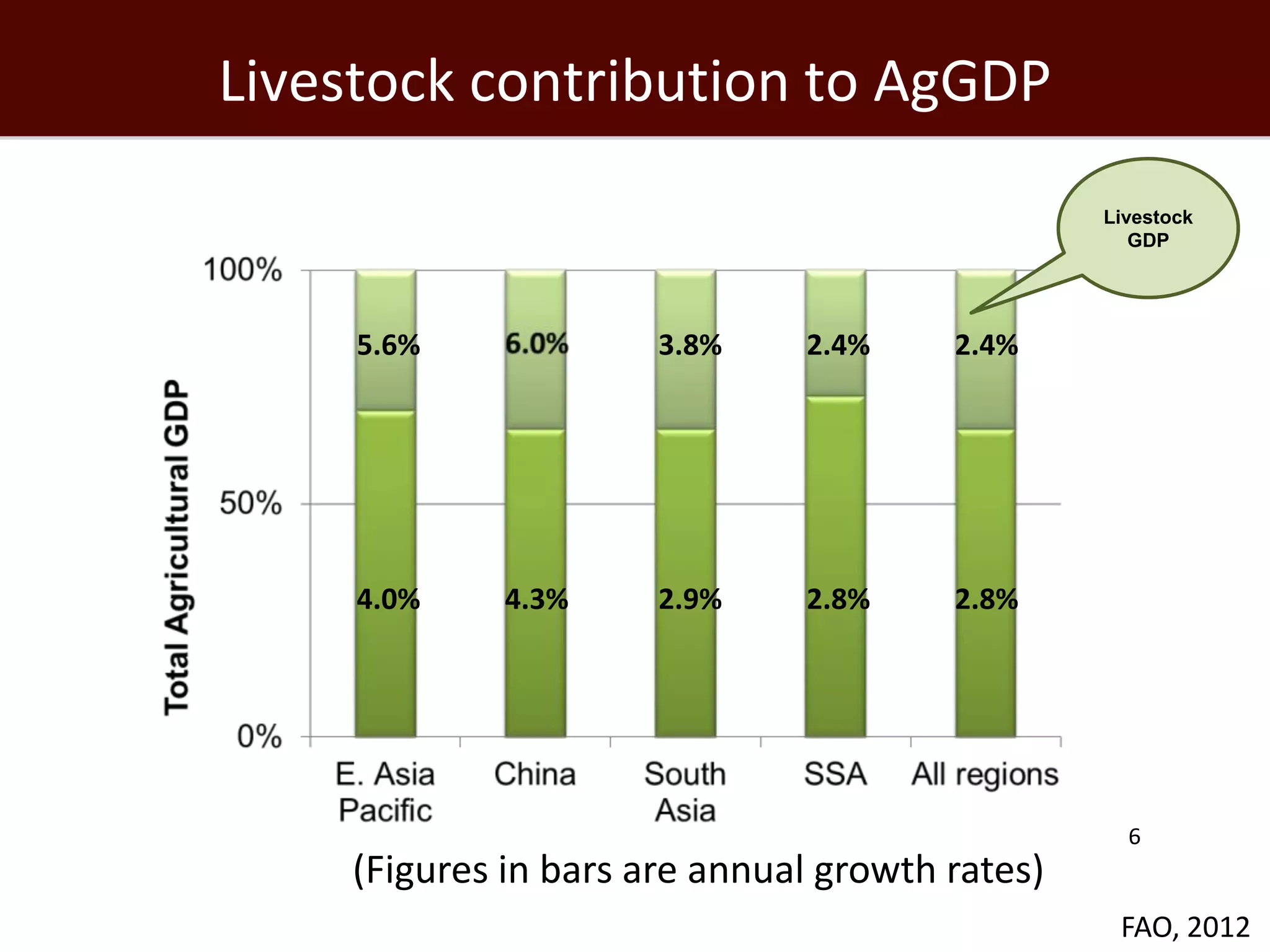
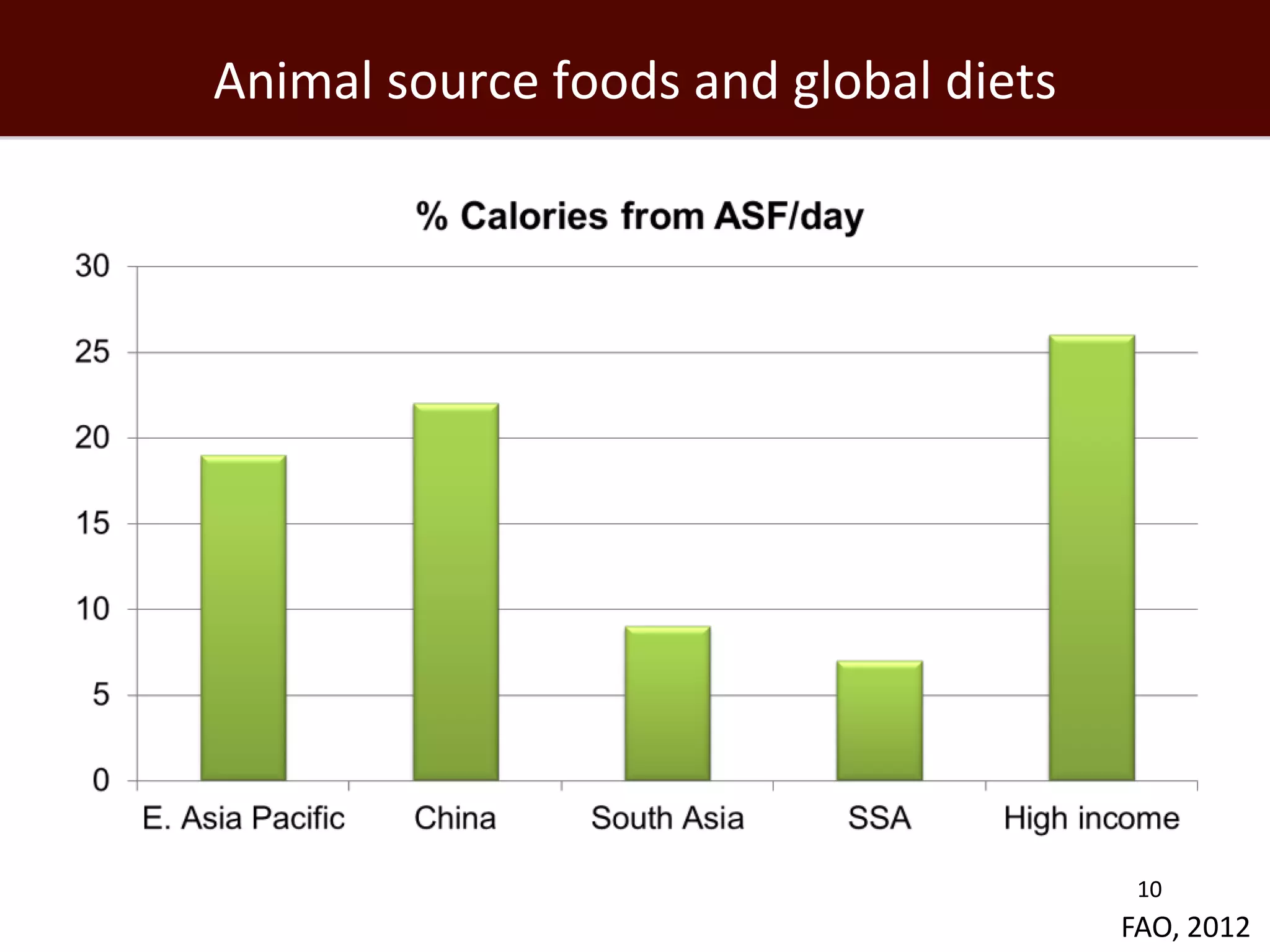
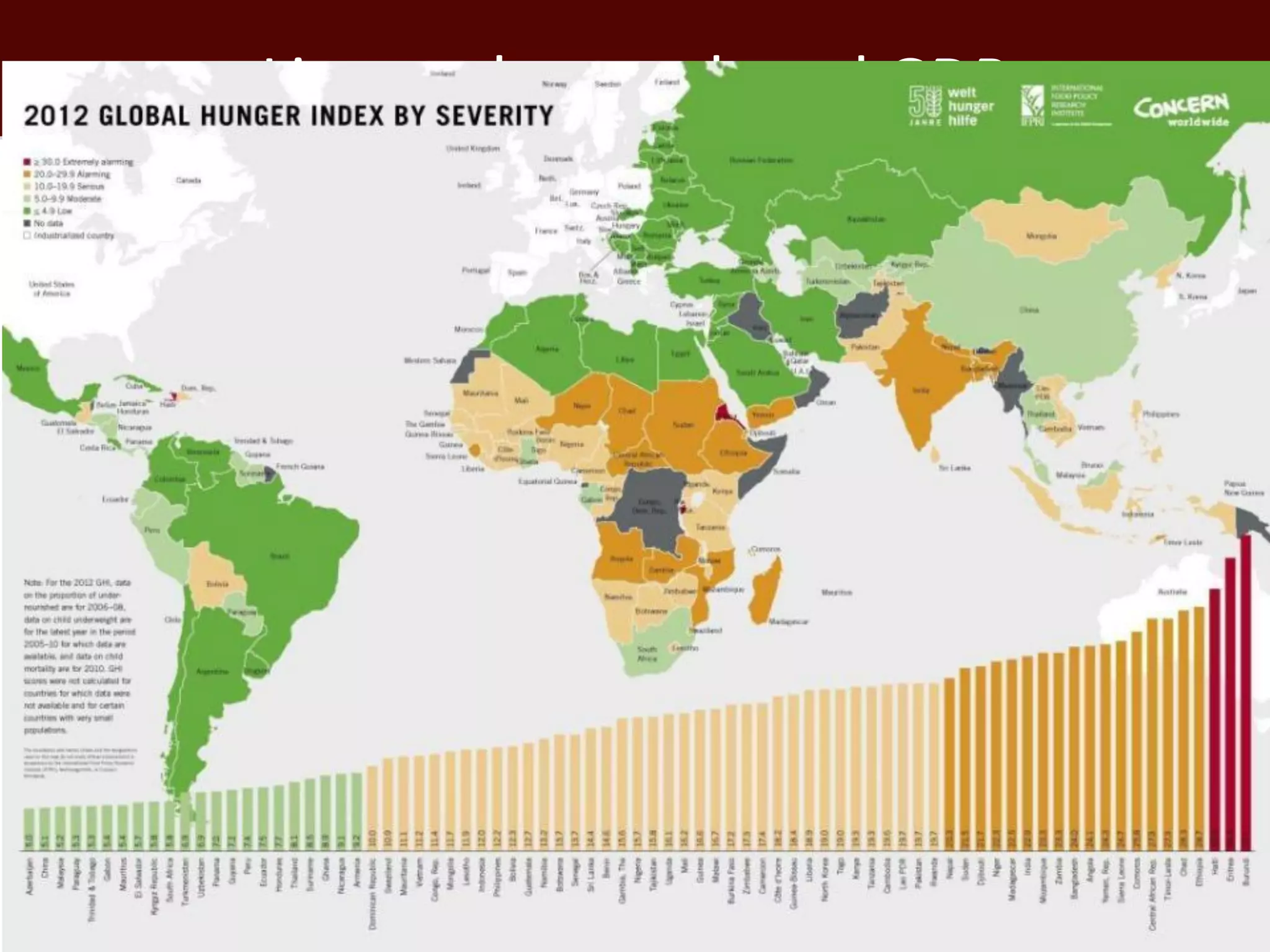
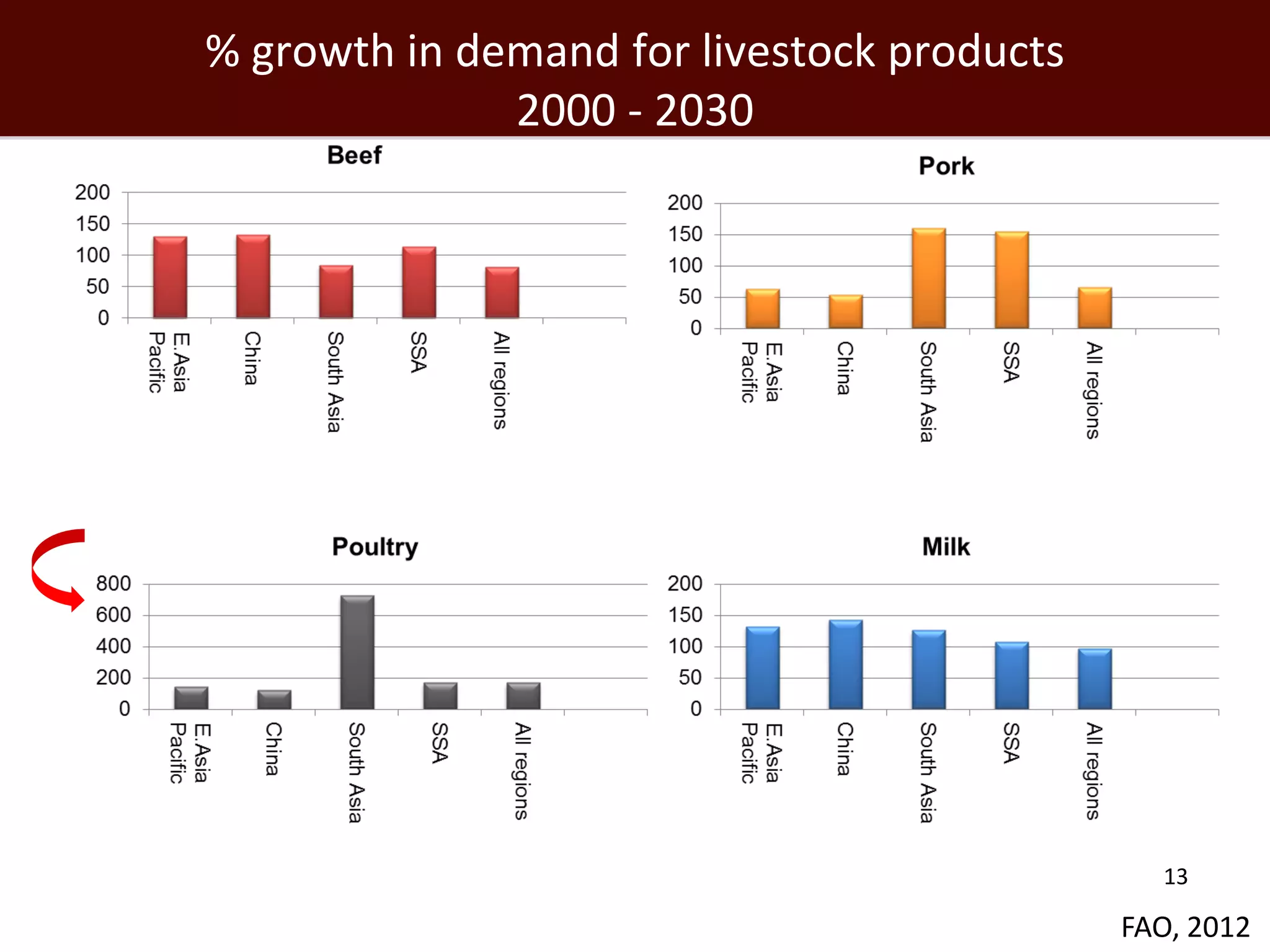
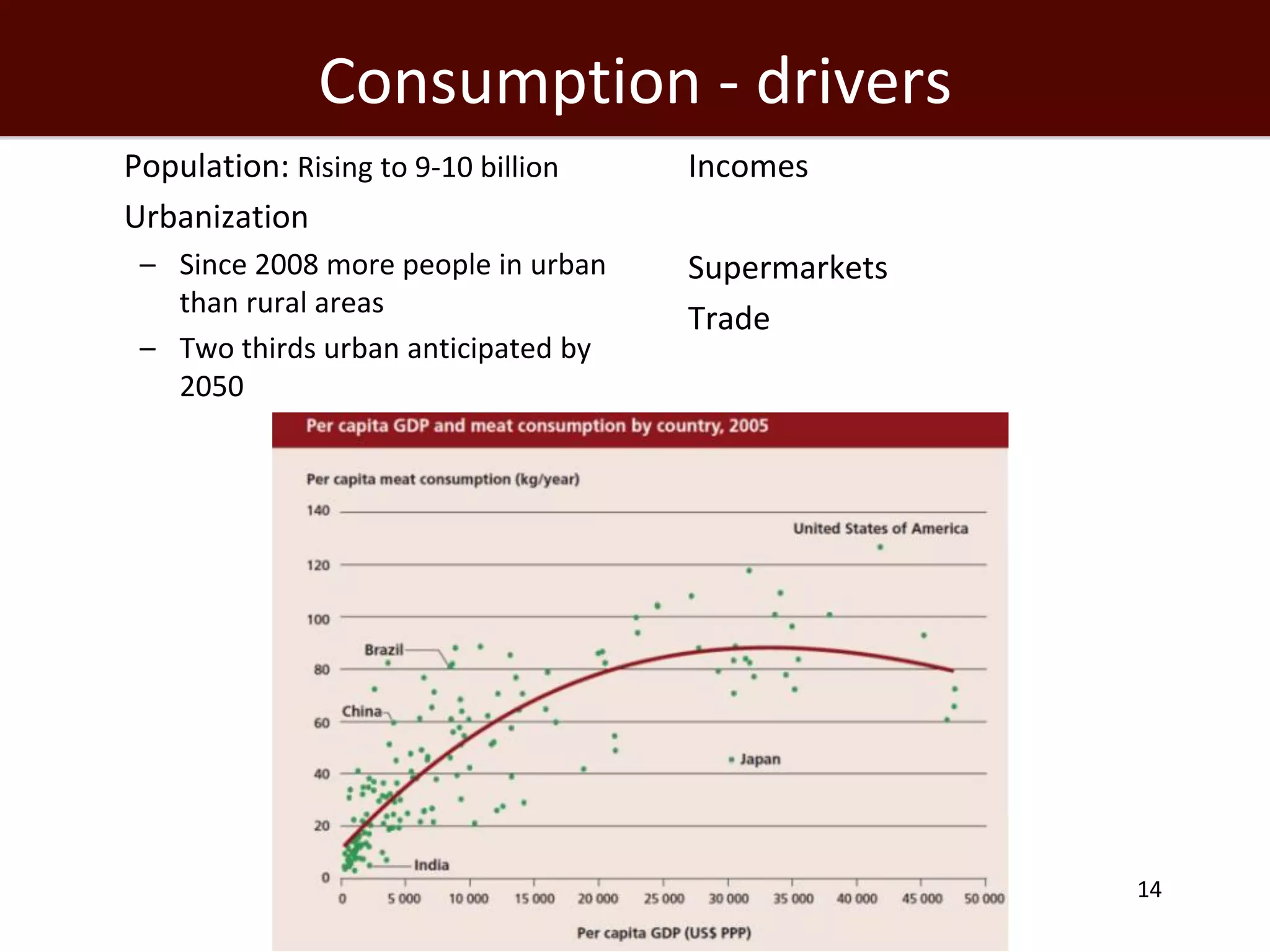
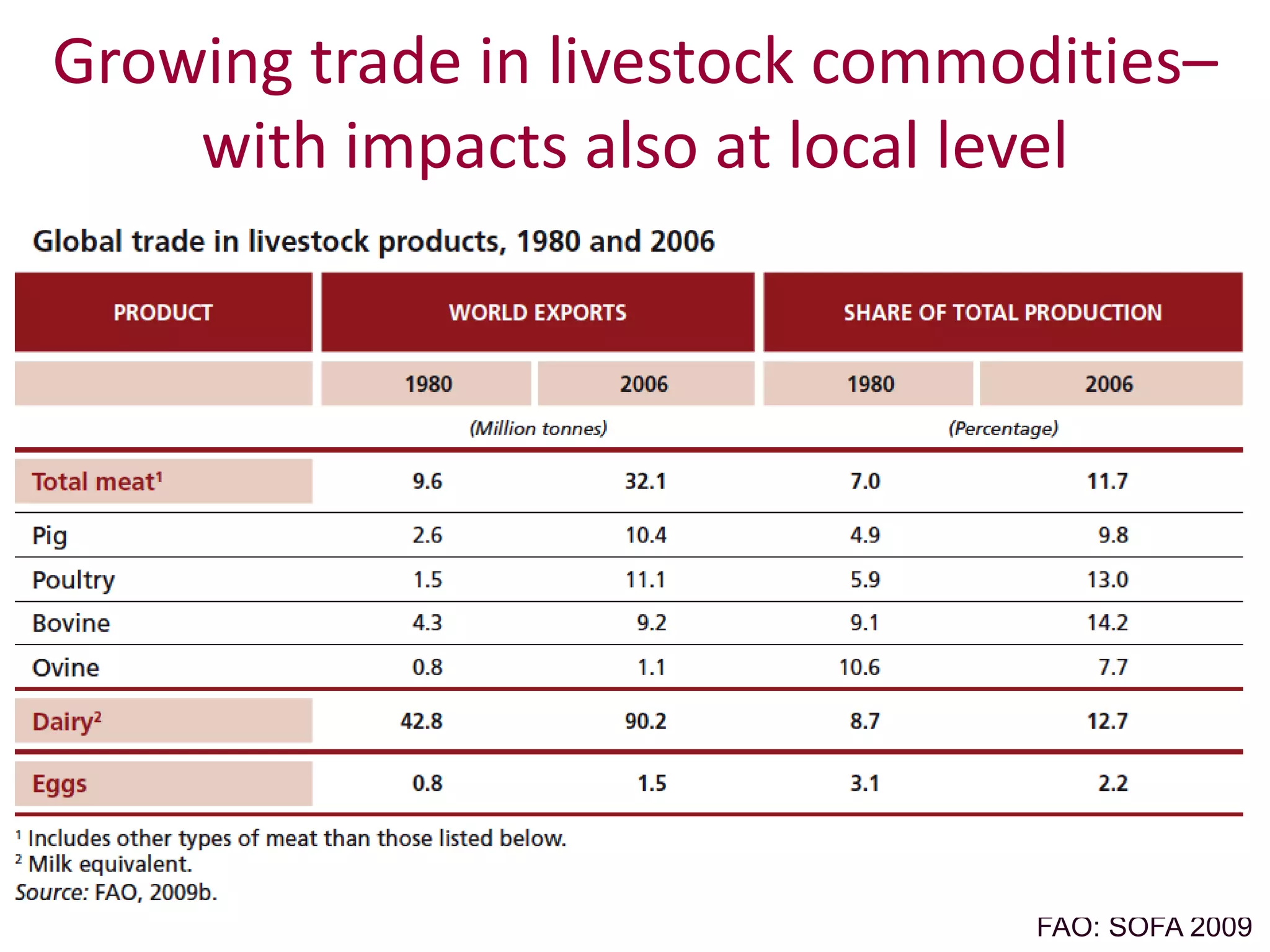
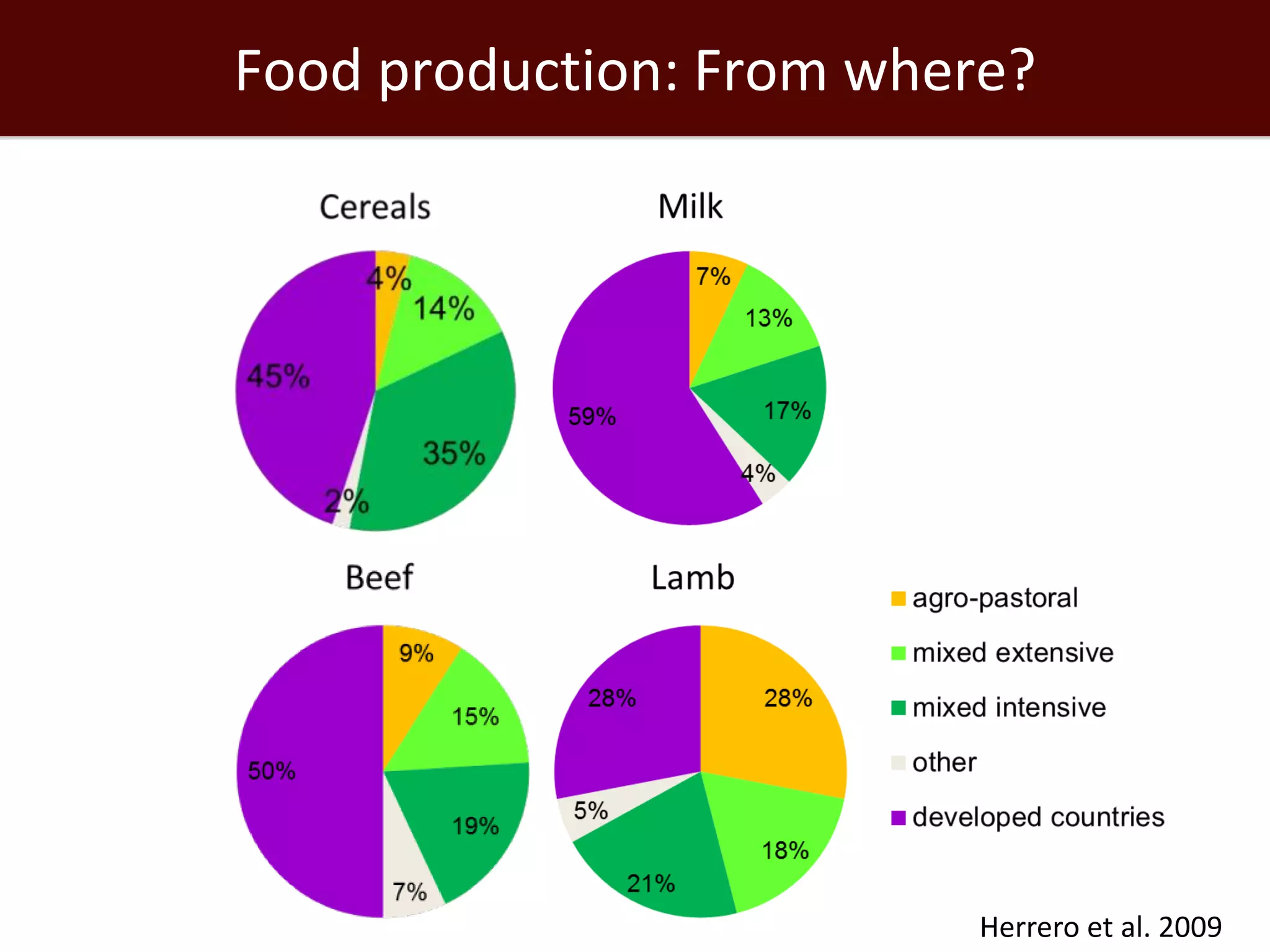
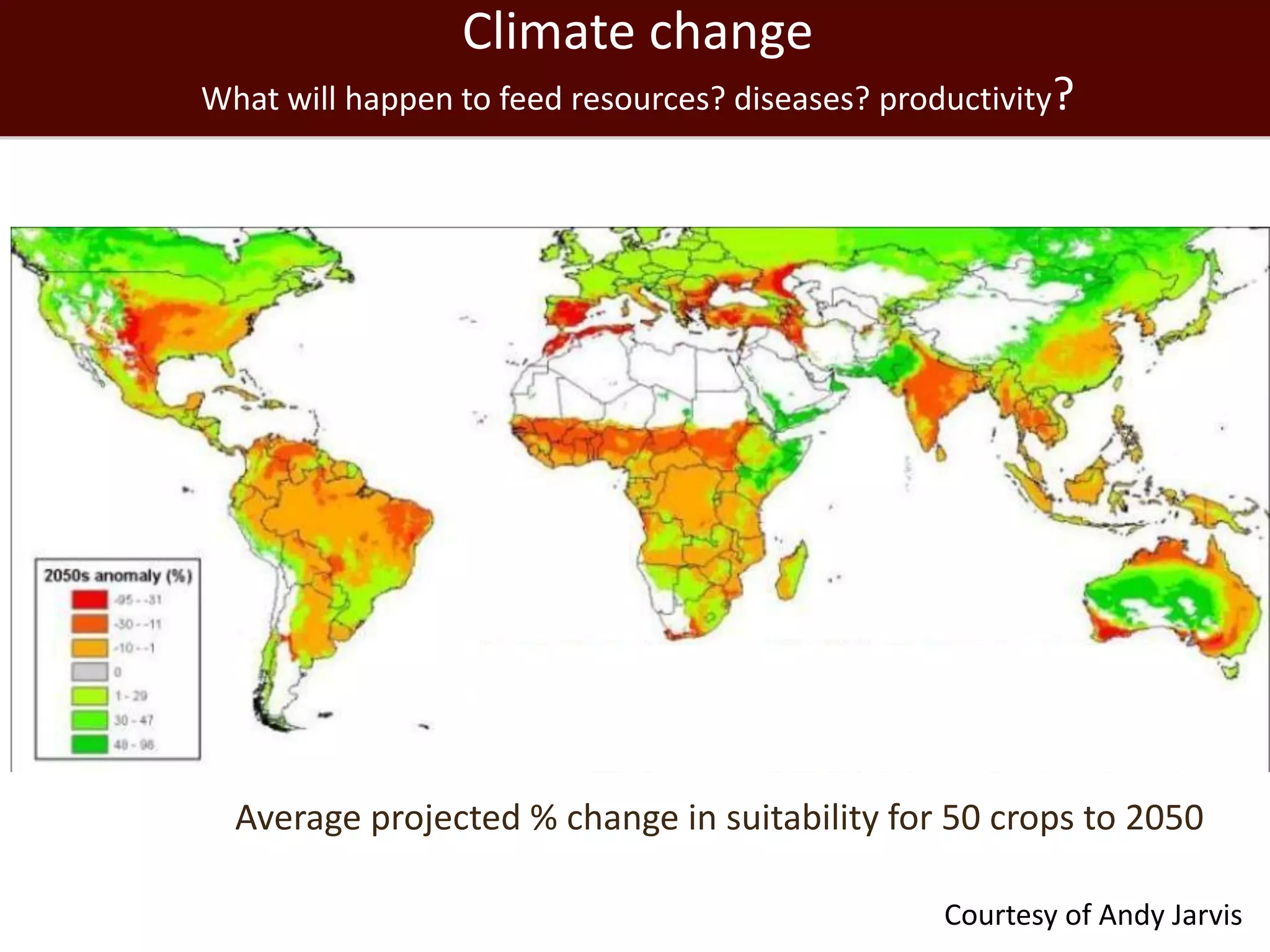
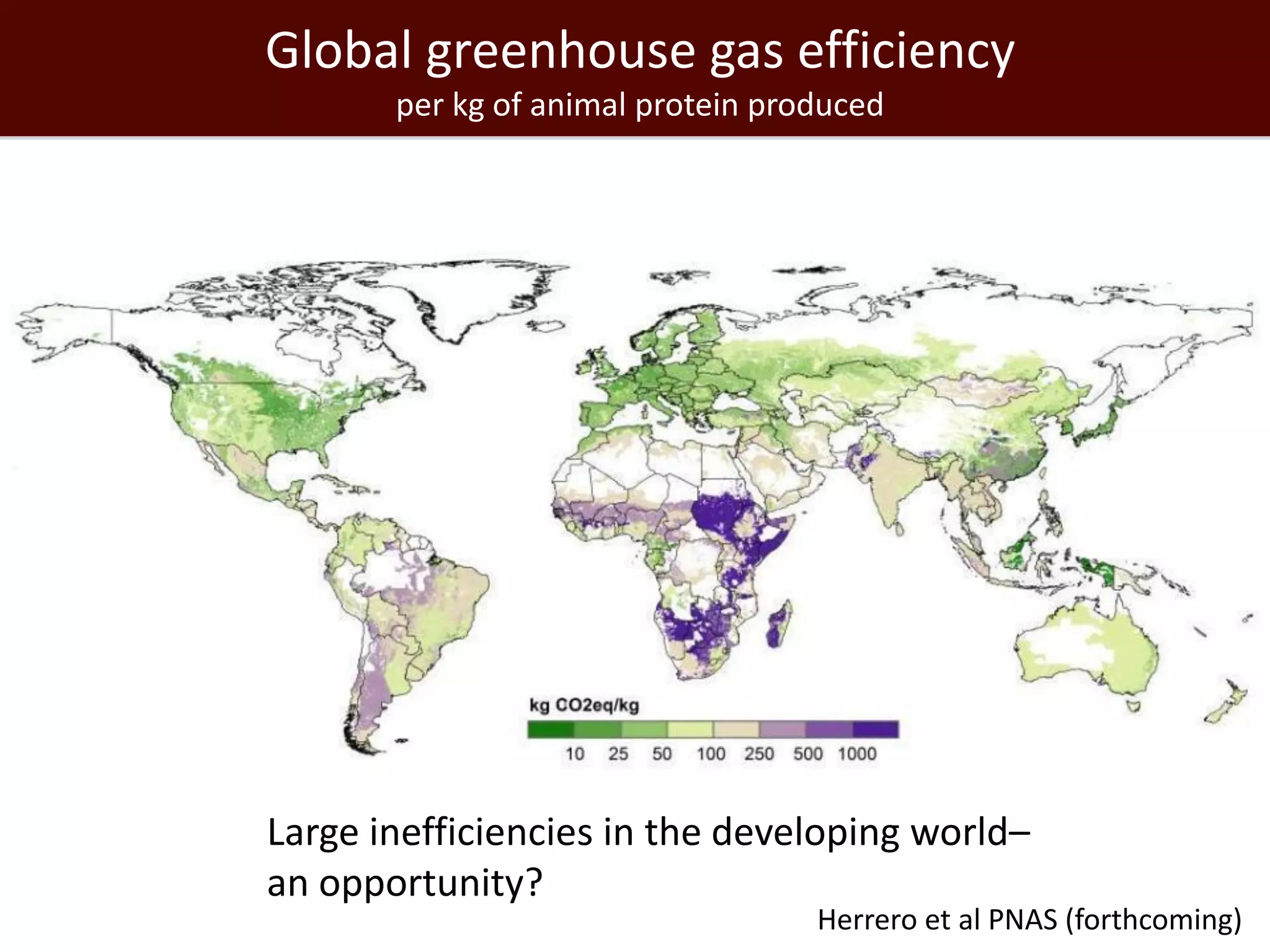
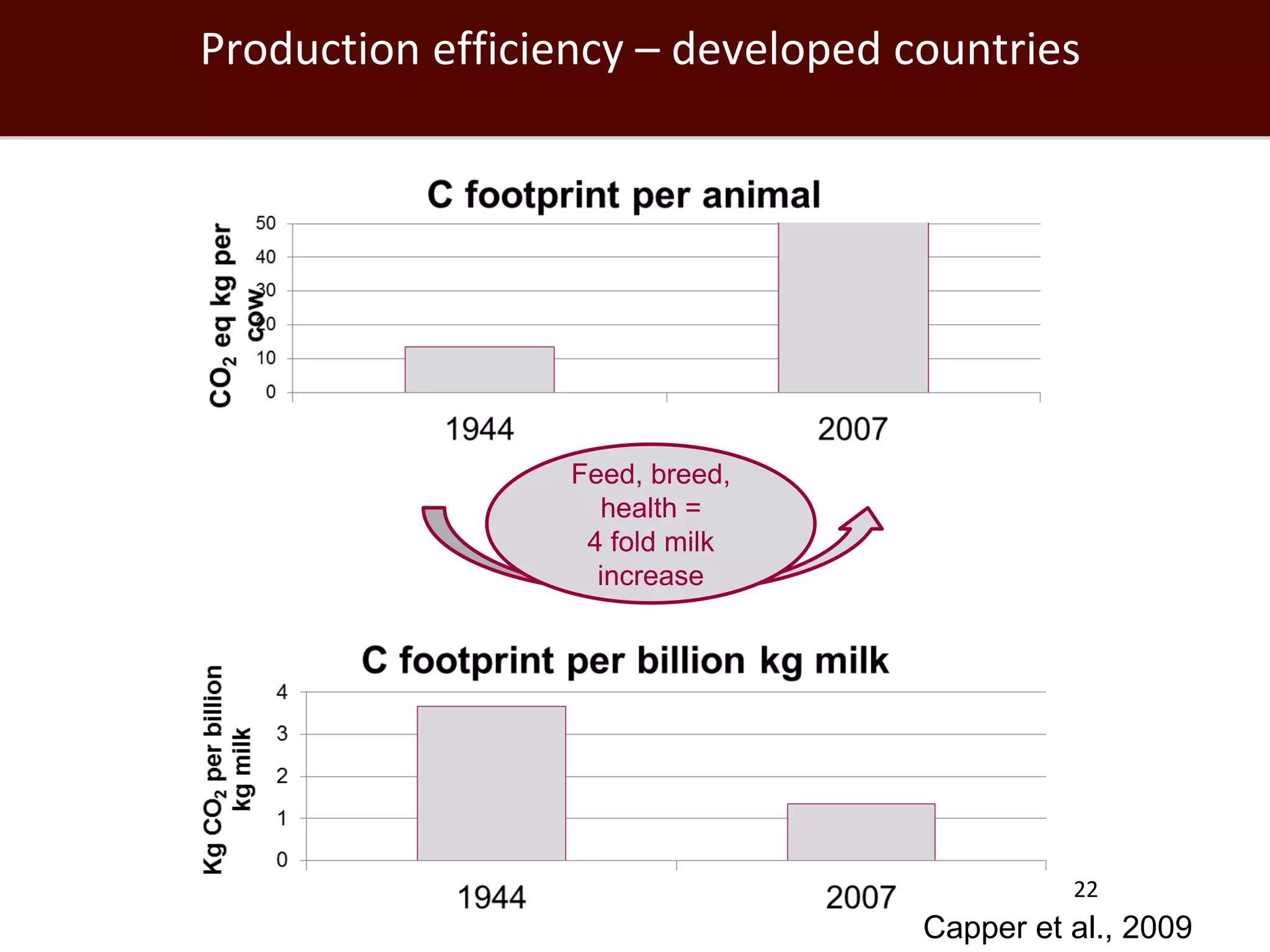
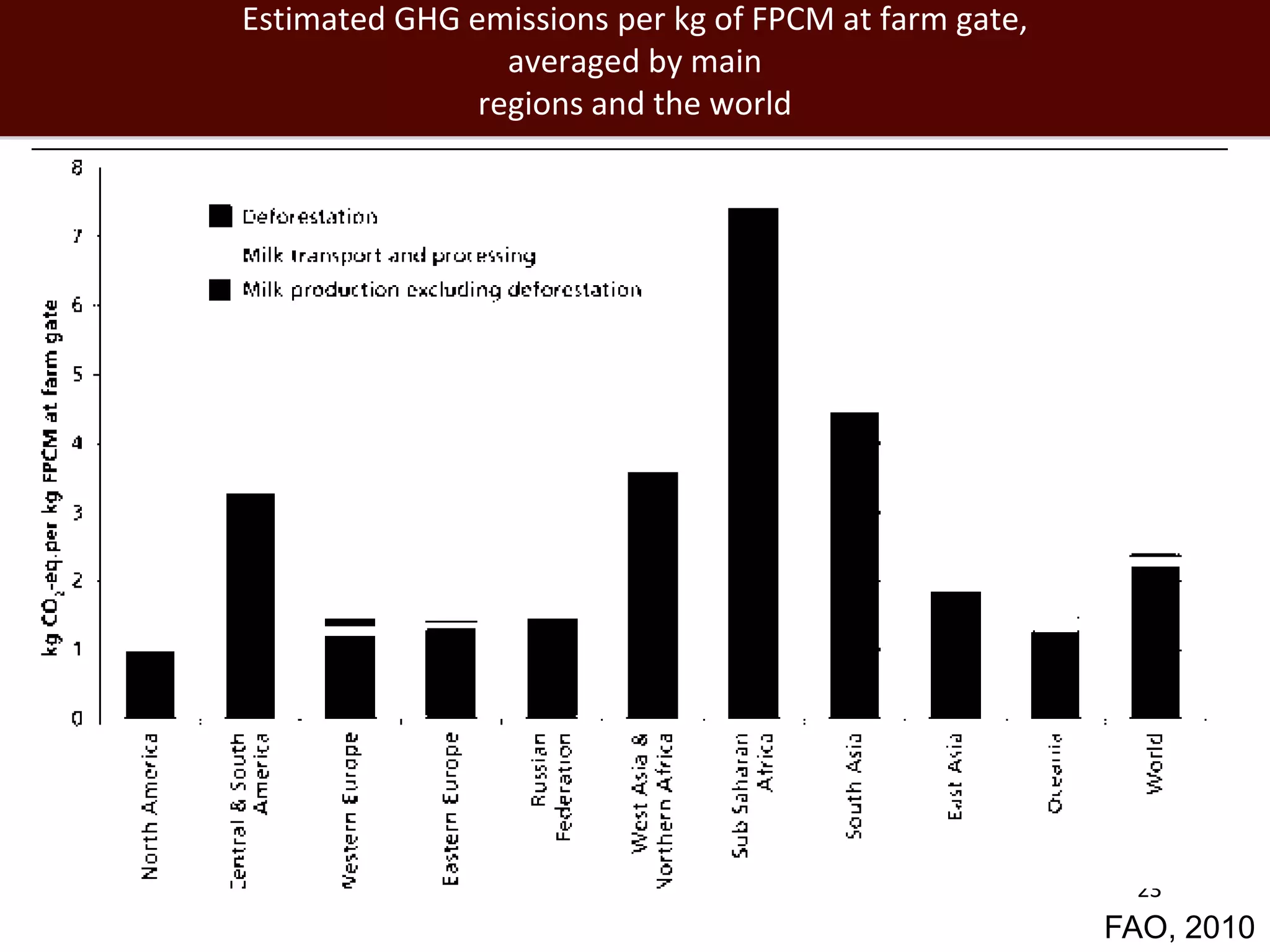
The global livestock sector, comprising 17 billion domestic animals valued at $1.4 trillion, plays a crucial role in food production, economic development, and livelihood security for nearly a billion people. However, it faces challenges such as environmental impact, health risks from zoonoses, and the need for sustainable growth amidst rising demand due to population growth and urbanization. Research and innovative solutions are needed to enhance productivity while addressing environmental and health concerns, ensuring that livestock systems contribute positively to global development.