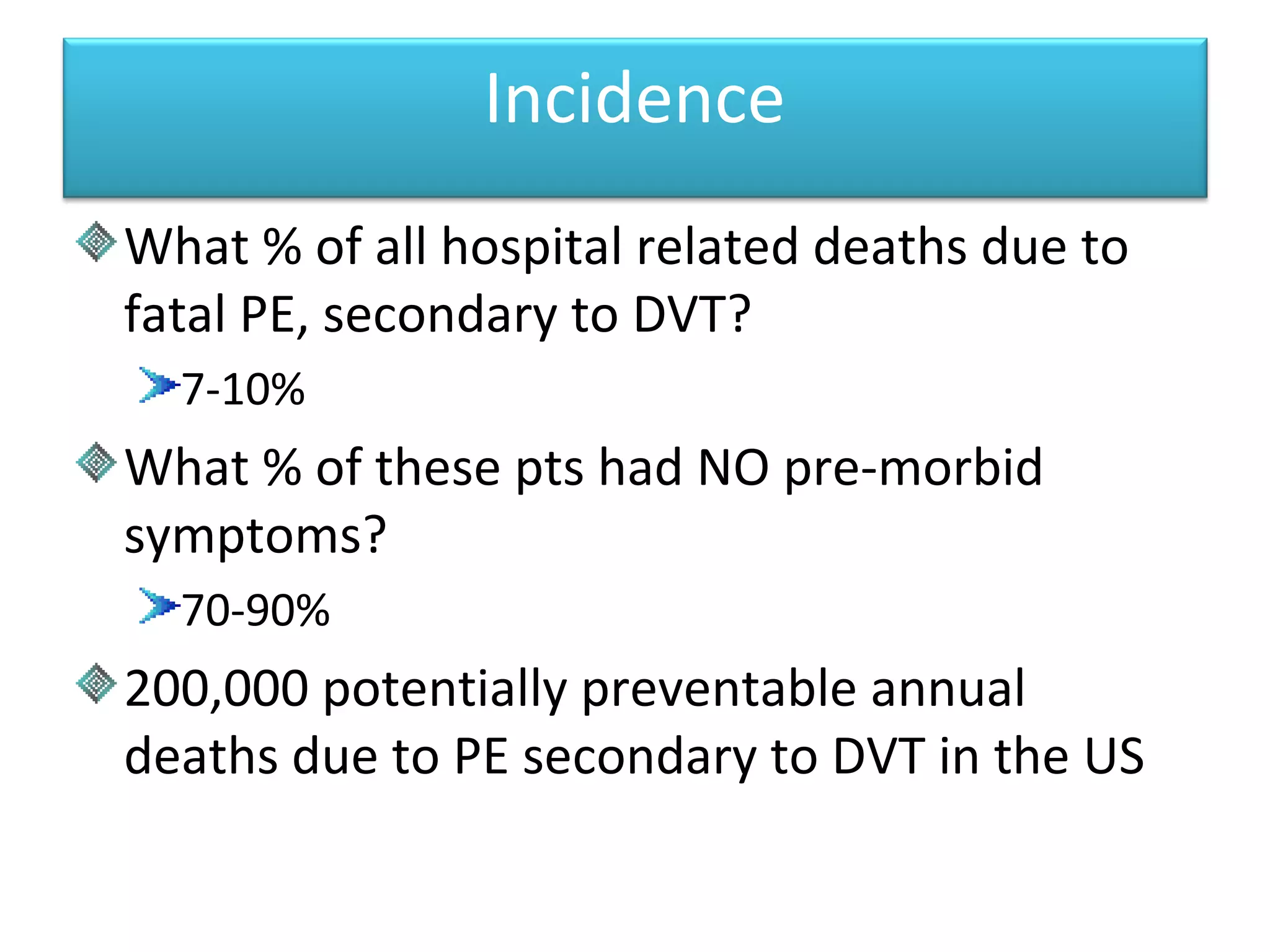
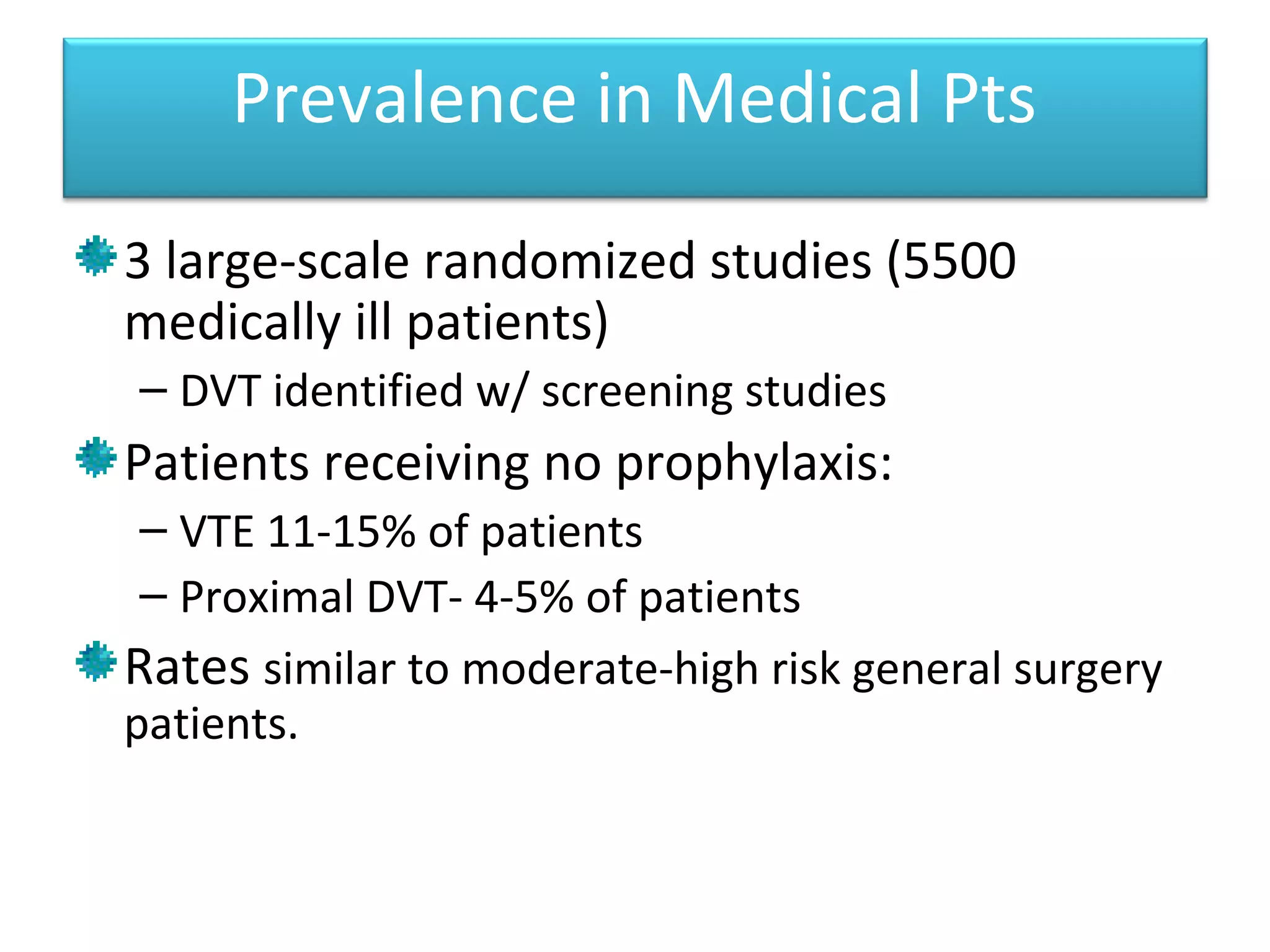
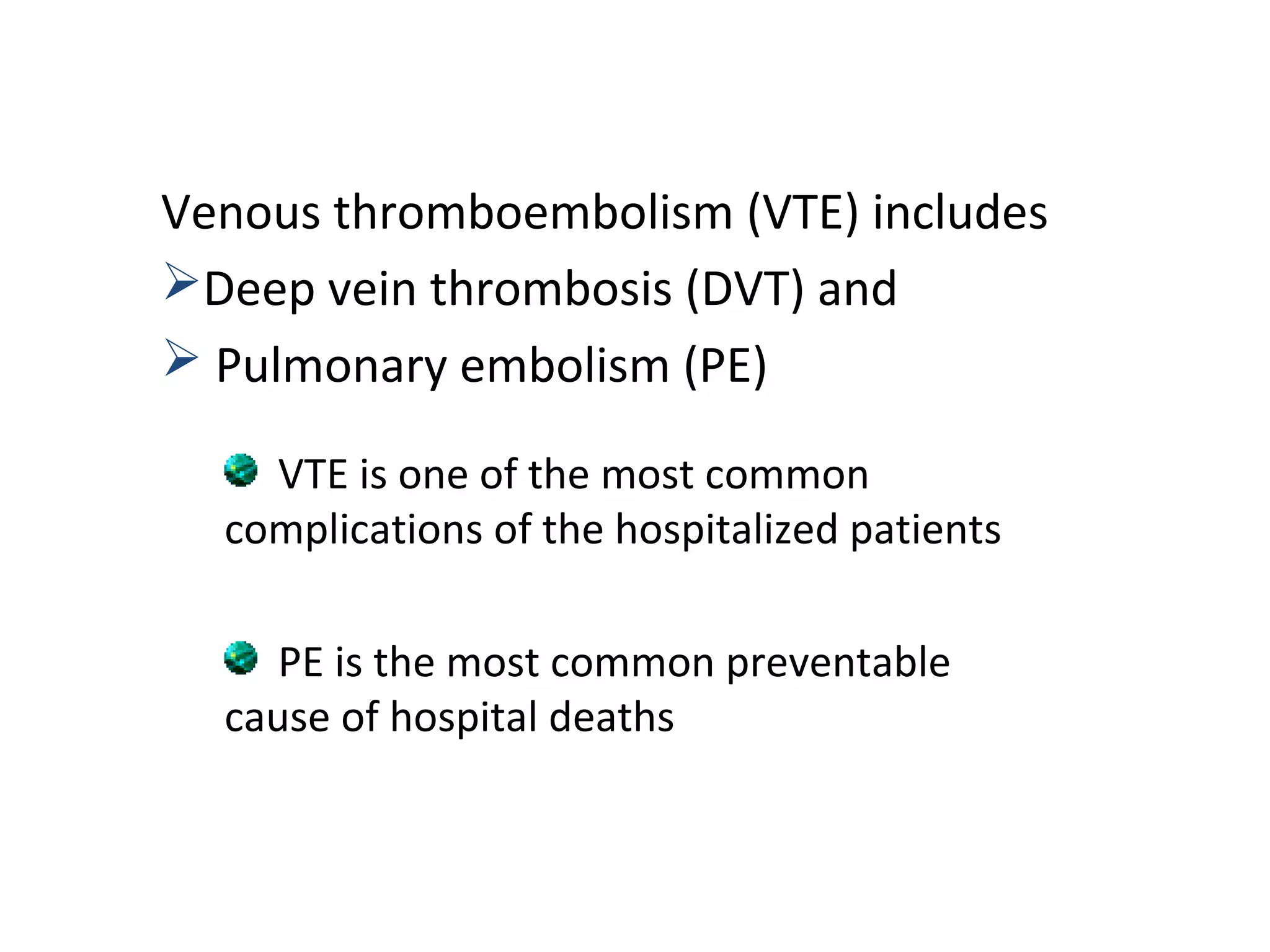
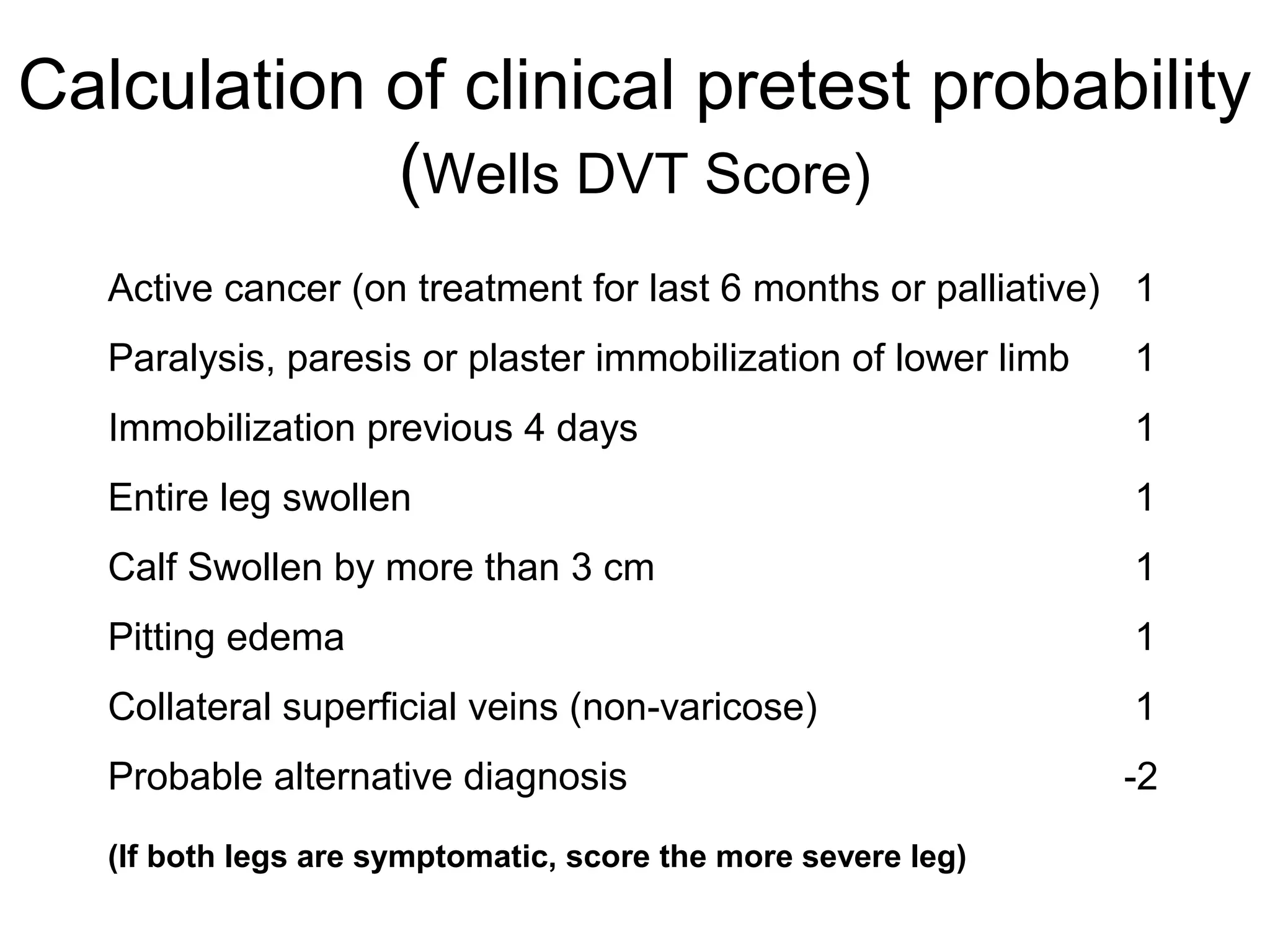
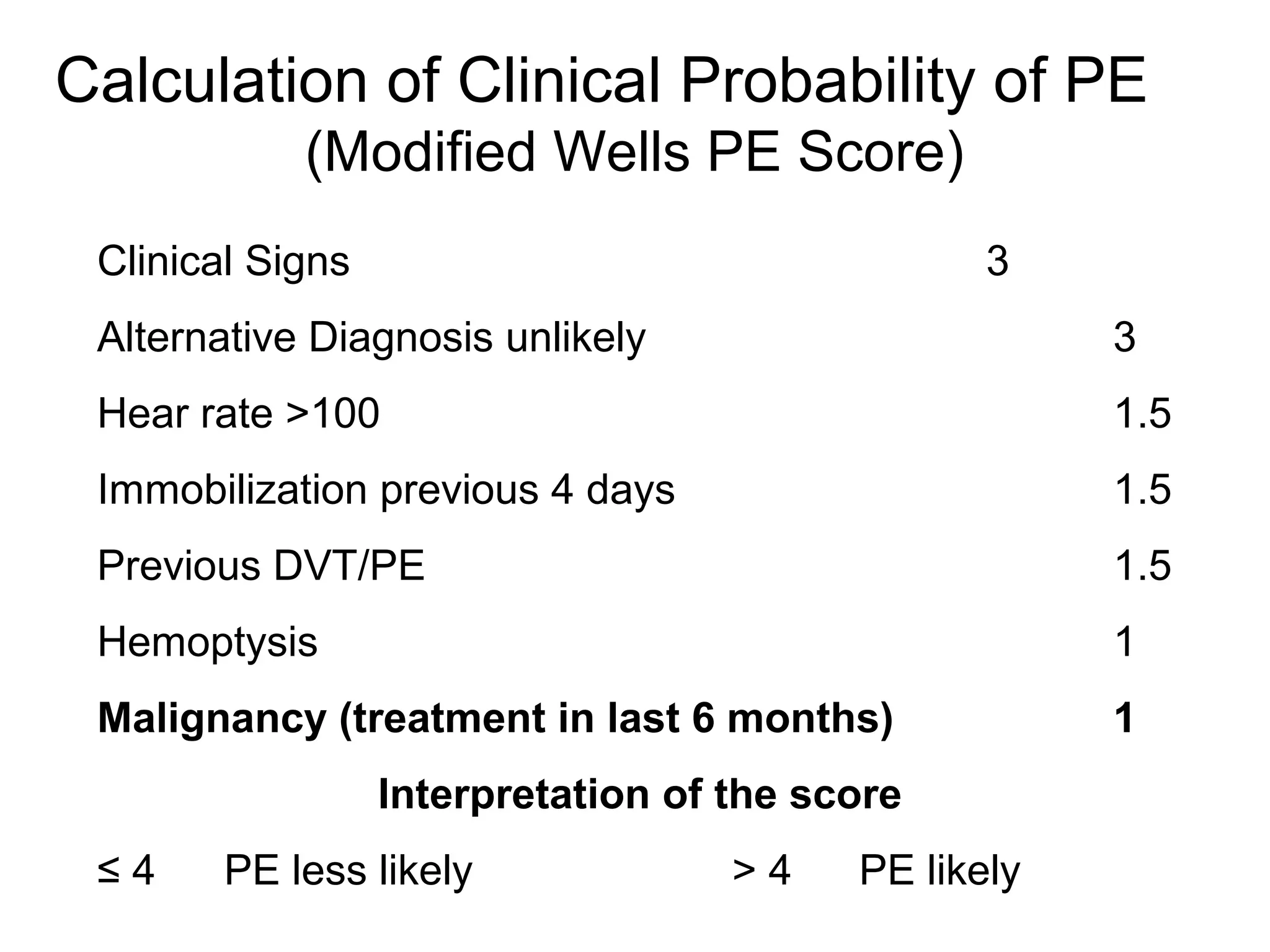
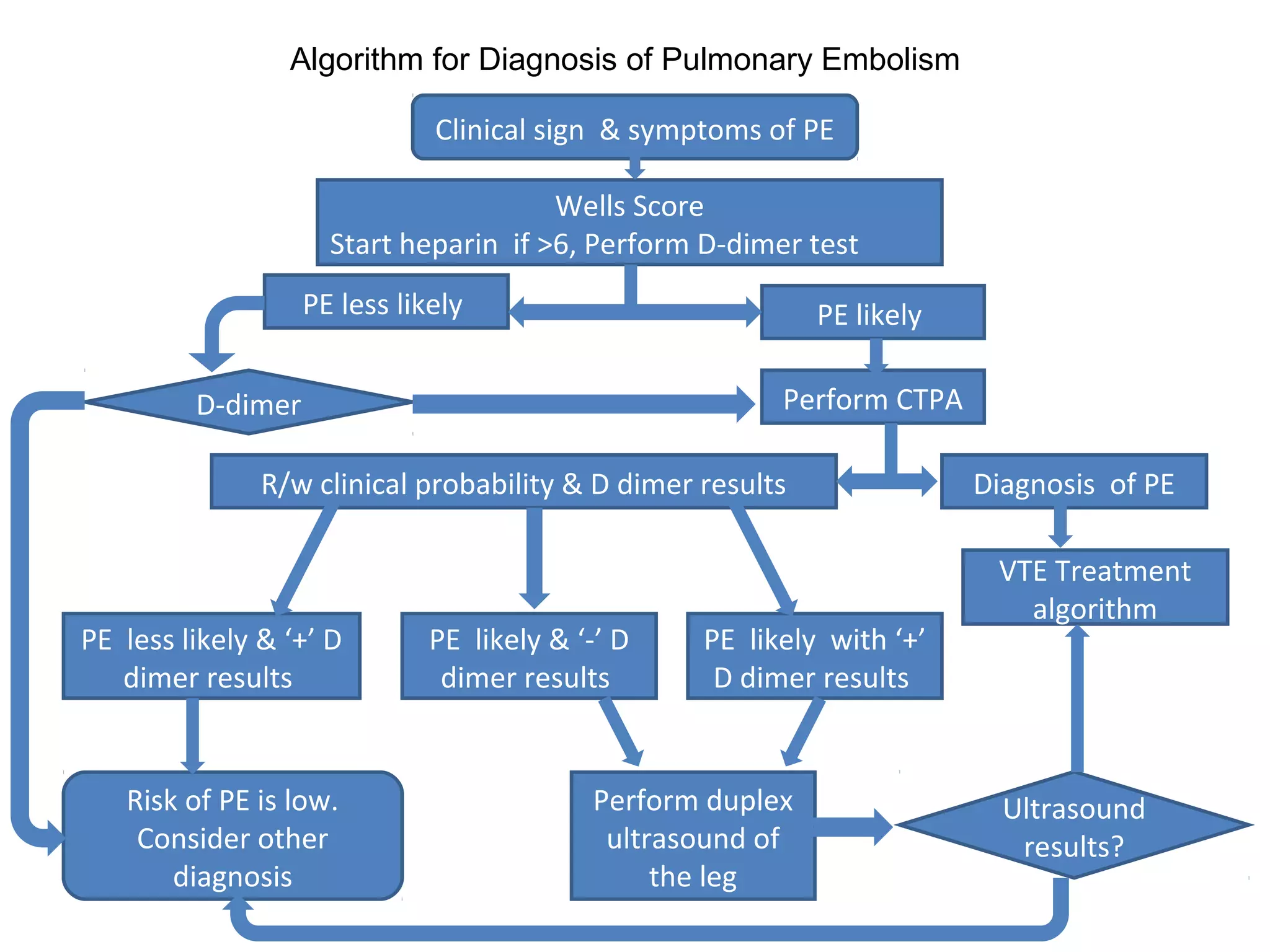
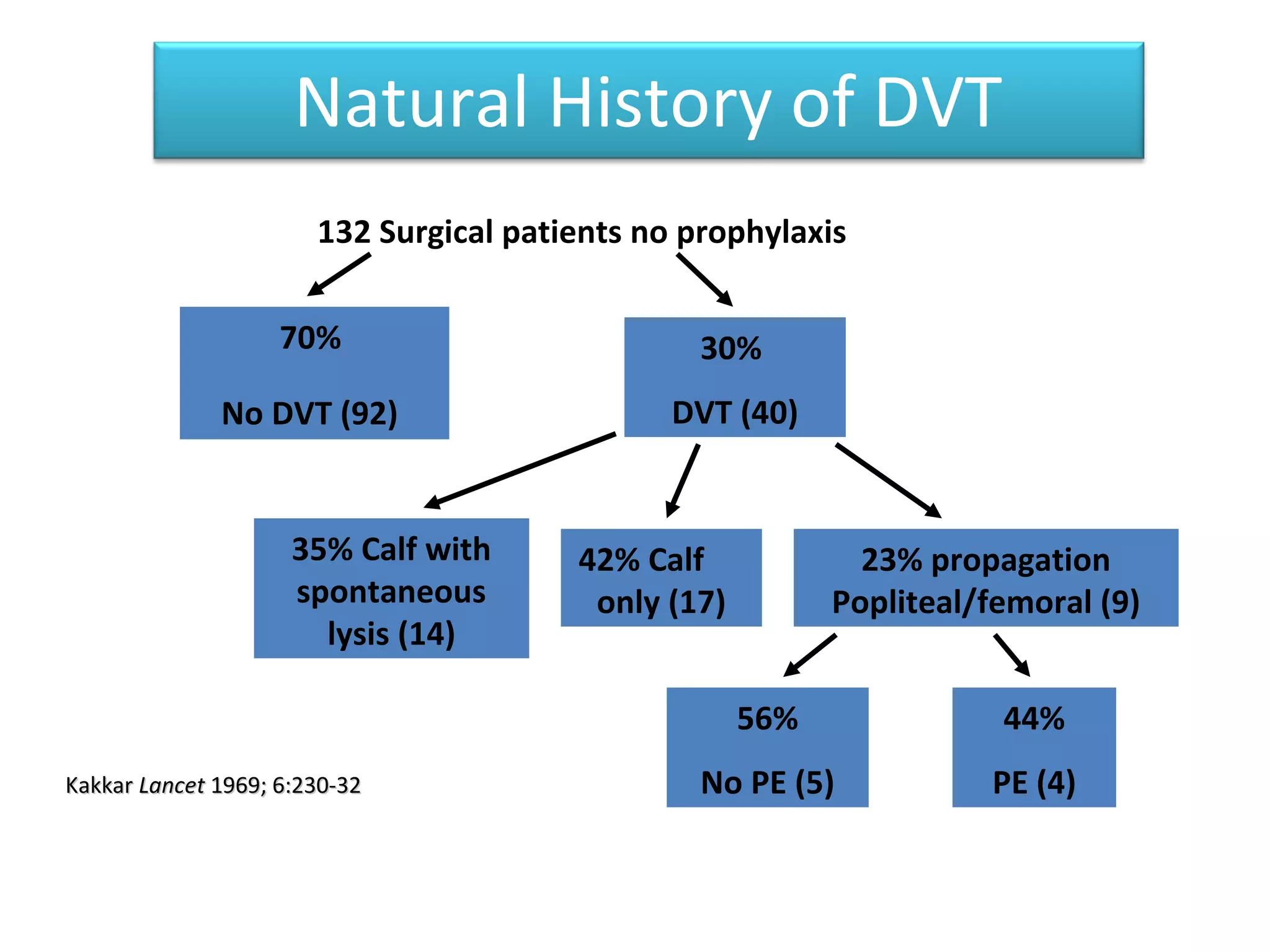
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a common and potentially fatal condition. It can lead to pulmonary embolism (PE), which is a leading cause of preventable hospital death. While DVT often has no symptoms, it puts patients at risk for long-term complications. Standard diagnostic tests include ultrasound, CT scans, and D-dimer tests. Risk factors include surgery, trauma, immobility, and cancer. Prophylaxis with blood thinners, compression devices, and stockings can significantly reduce the risk of DVT, especially in high-risk hospitalized patients. Early diagnosis and treatment are important to prevent fatal PE and long-term issues.