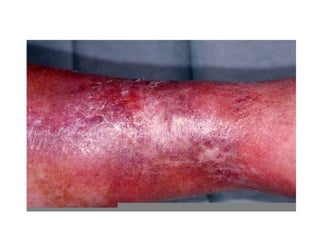
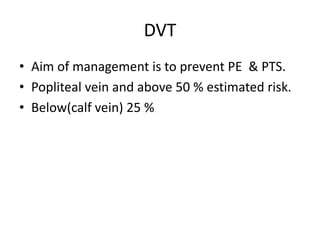
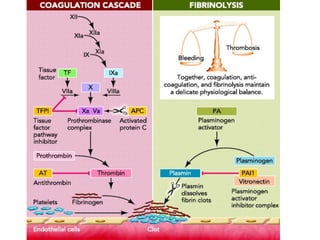
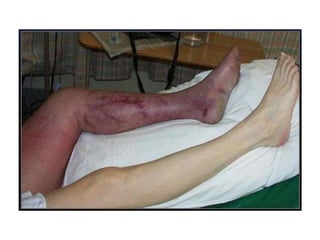
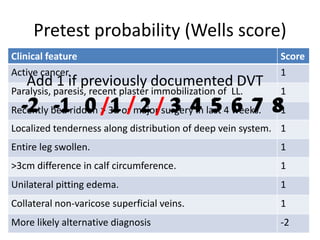
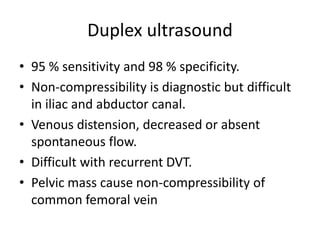
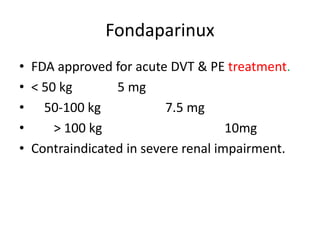
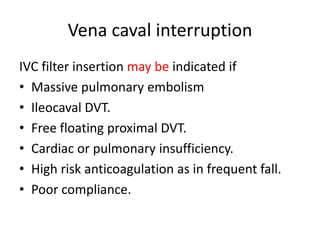
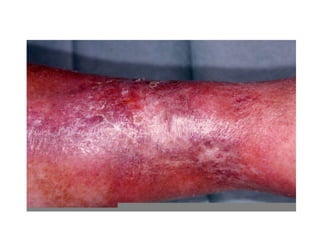
This document discusses deep vein thrombosis (DVT), its causes, diagnosis, and treatment. DVT is a clinical entity that can be lethal or recurrent. It occurs in both hospitalized and non-hospitalized patients and can lead to long-term complications like pulmonary hypertension or post-thrombotic syndrome. DVT is diagnosed using tools like ultrasound, MRI, CT scans, or venography. Treatment involves anticoagulation to prevent pulmonary embolism and further complications. The duration of anticoagulation treatment depends on individual risk factors for recurrence.