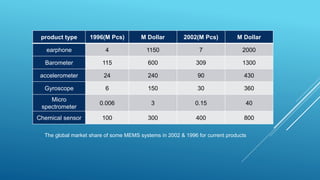
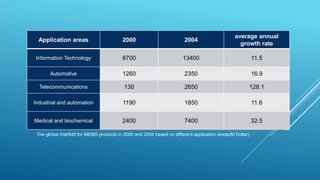
MEMS (Micro Electro Mechanical Systems) are tiny engineering systems that combine electrical and mechanical functions at a micrometer scale, made from materials like silicon and polymers. They have diverse applications in medicine, automotive, communications, and defense, with uses ranging from implanted sensors to automotive safety features. The technology promises significant advancements and market growth, driven by the need for miniaturization and efficiency across various industries.