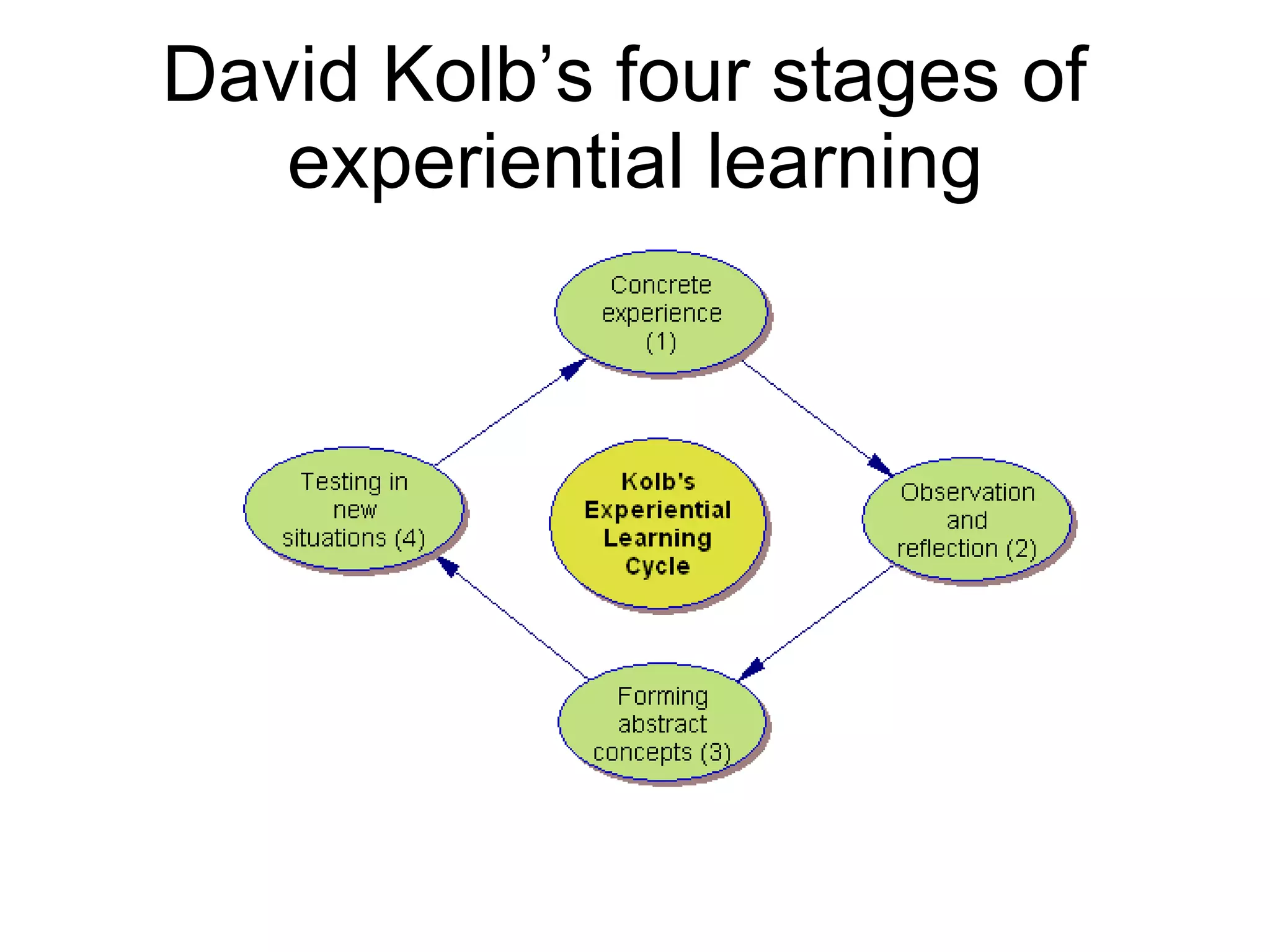
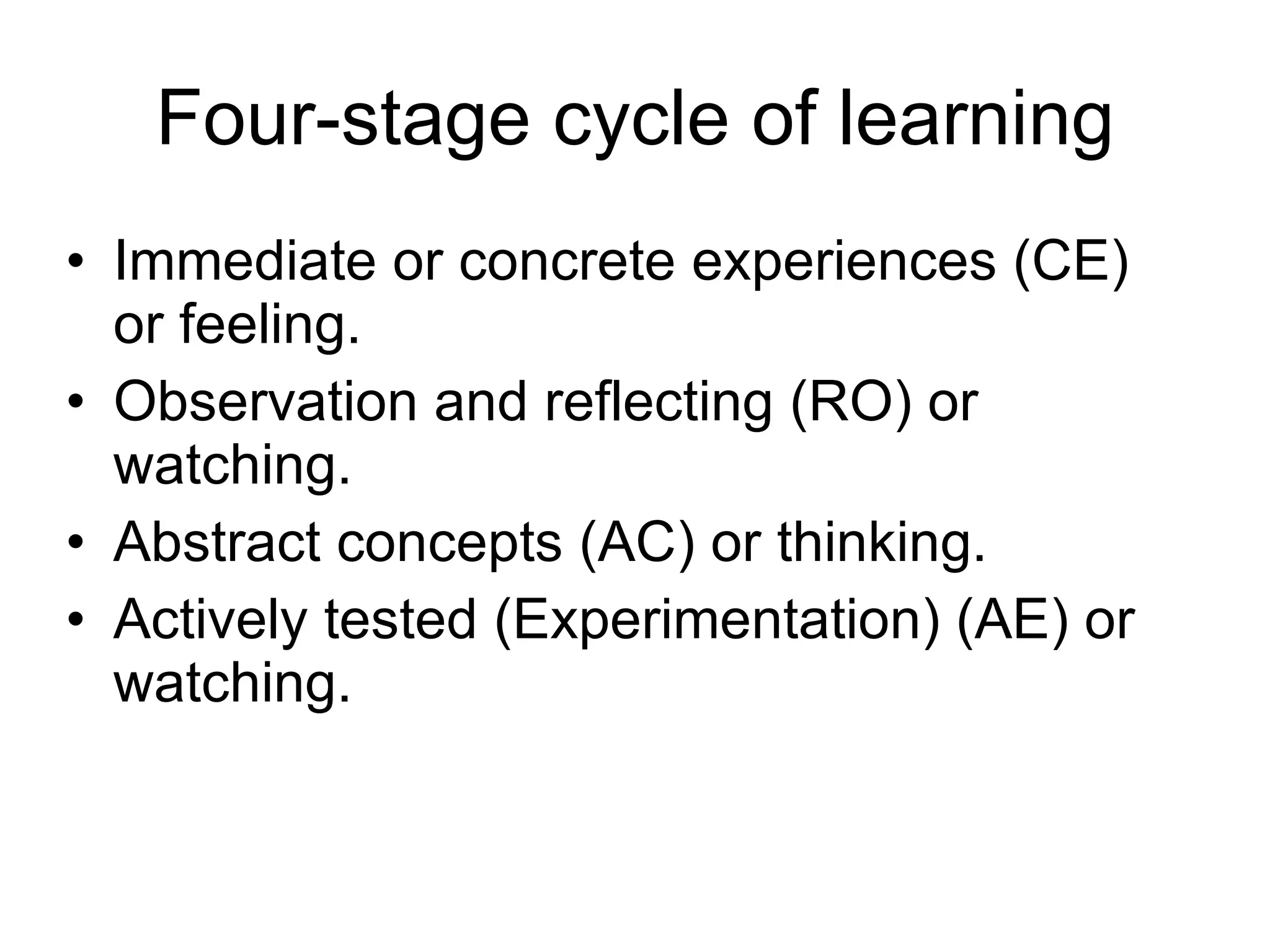
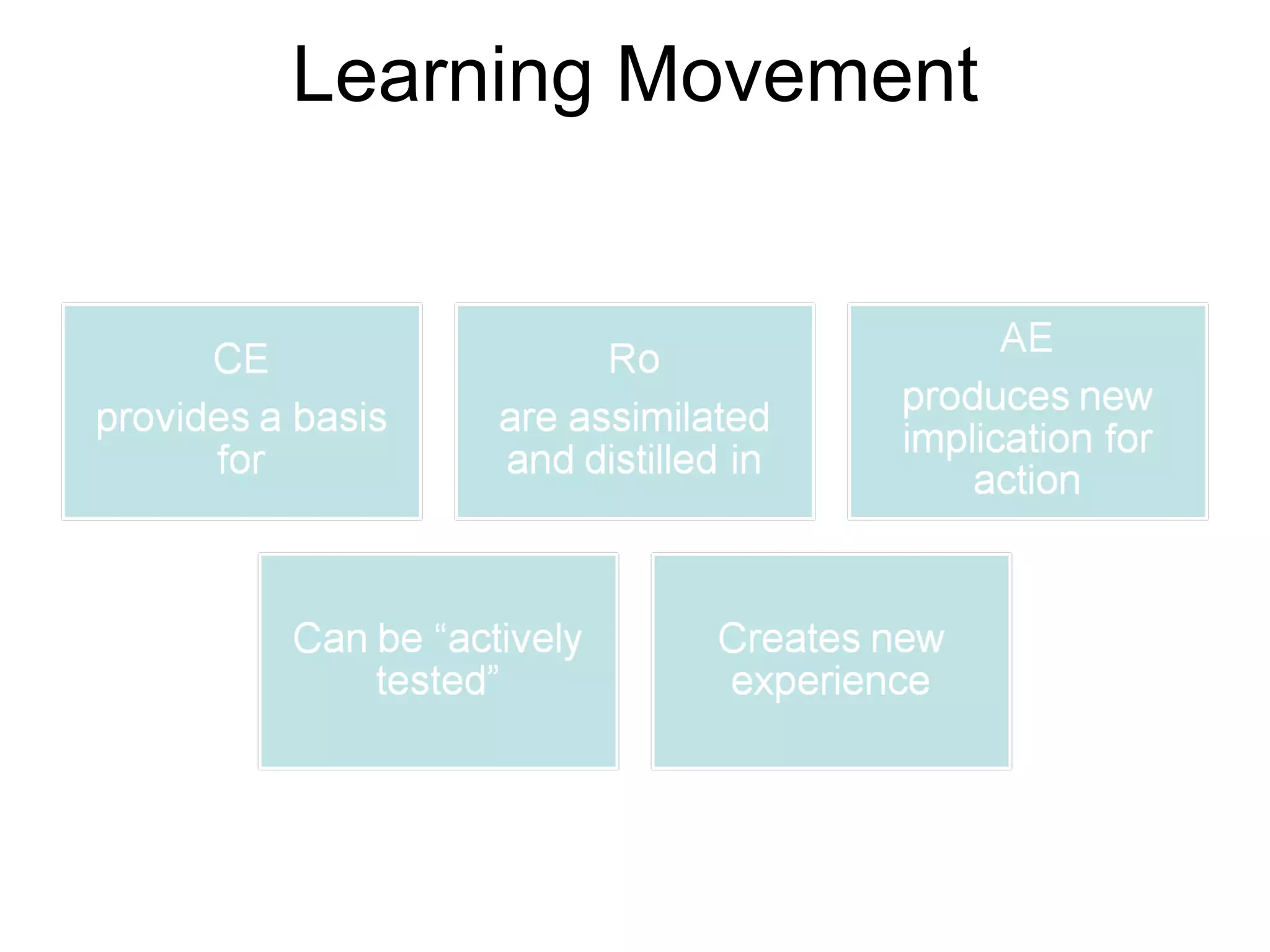
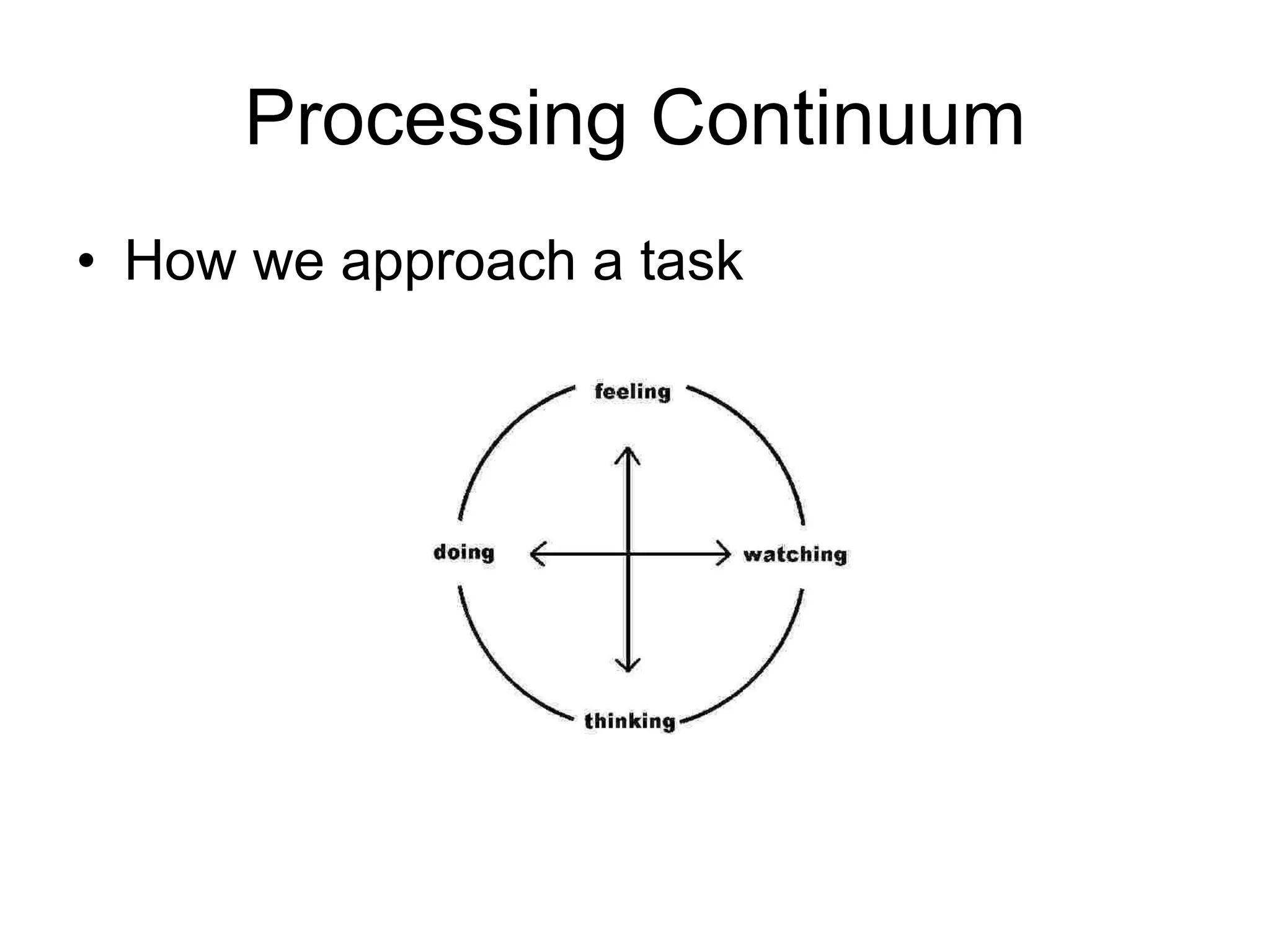
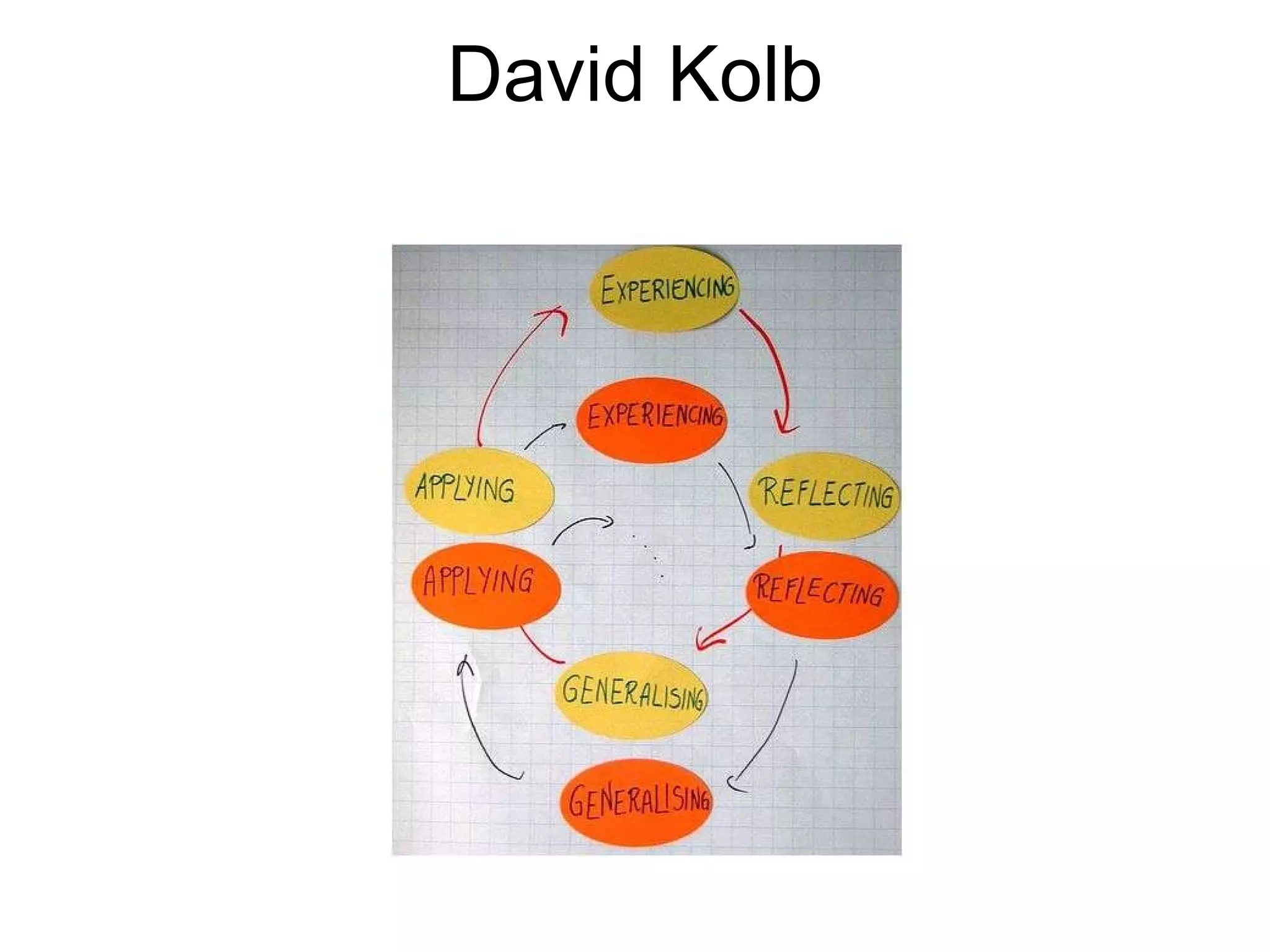
The document discusses experiential learning theory. It defines experiential learning as learning through hands-on experience rather than passive learning. David Kolb's model of experiential learning involves four stages: concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation. Kolb also identified four learning styles: diverging, assimilating, converging, and accommodating. Experiential learning has benefits like increased motivation and the ability to acquire durable knowledge through self-initiated learning.