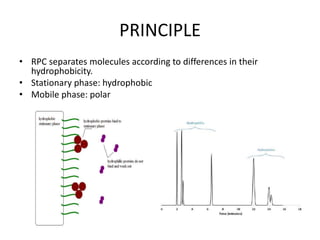
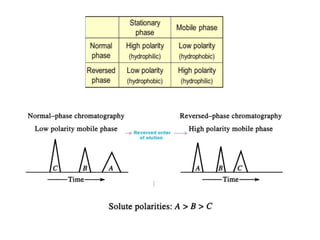
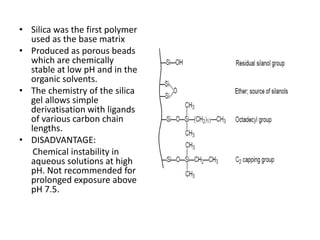
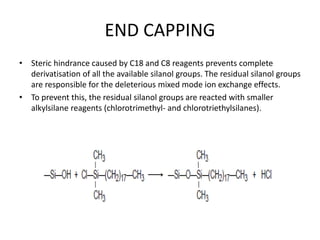
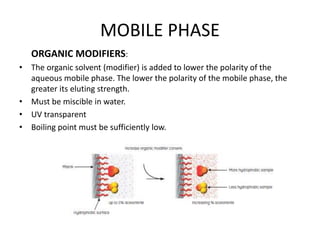
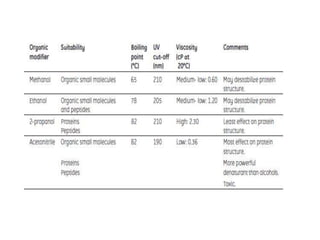
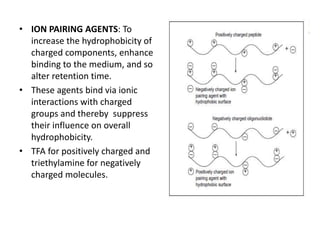
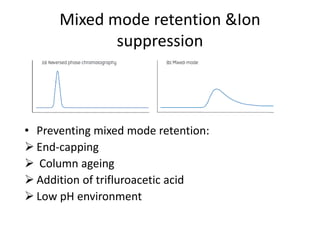
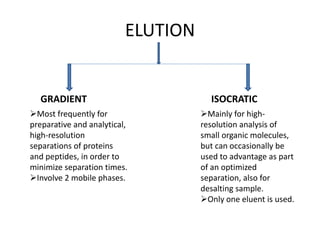
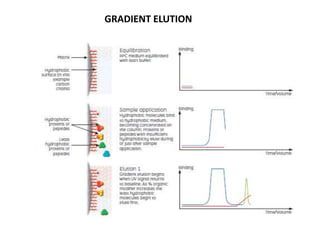
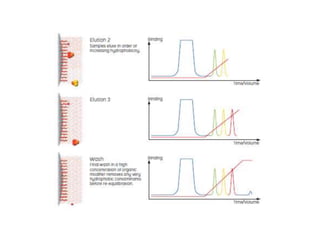
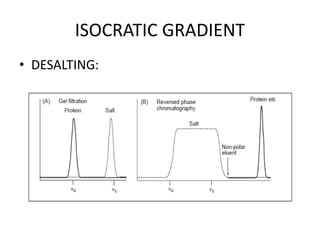
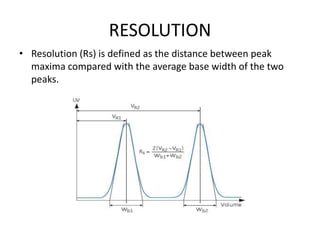
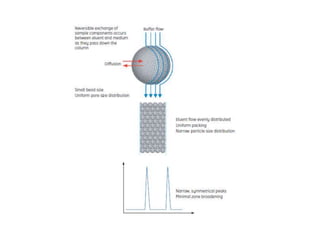
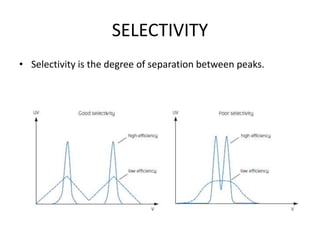
This document discusses reversed phase chromatography (RPC). RPC separates molecules based on differences in hydrophobicity using a hydrophobic stationary phase and polar mobile phase. Common stationary phases include silica or polystyrene beads chemically bonded to hydrophobic ligands like C18 chains. Mobile phase modifiers and ion pairing agents are used to control selectivity. RPC is useful for high resolution separation and analysis of proteins, peptides, and nucleic acids.