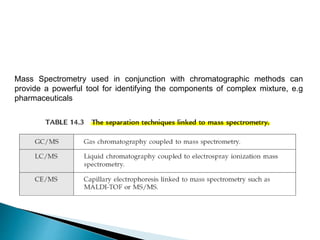
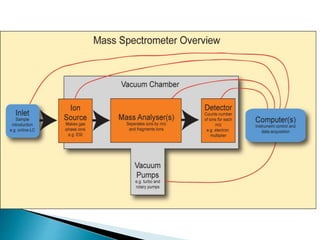
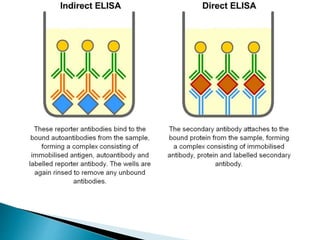
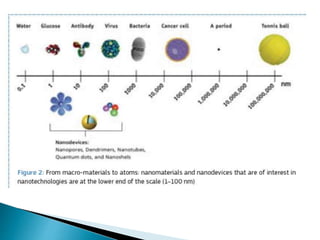
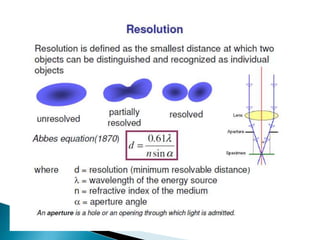
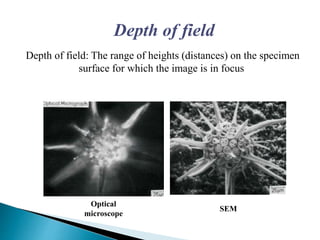
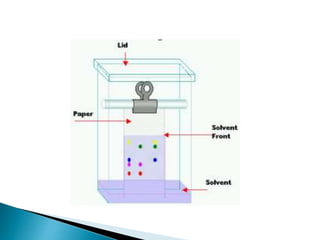
Gas chromatography (GC) separates volatile compounds using an inert gas as the mobile phase. The sample is injected into a heated port to volatilize it. The gas mobile phase carries the volatilized sample through a heated column coated with a stationary phase that interacts with analytes. Components are separated based on differences in volatility and affinity for the stationary phase, then detected and recorded. GC is useful for separating volatile, non-polar compounds.






![o Water softening: Removal of Ca2+, Mg2+ & other multivalent ions
causing hardness of water by filtration through a layer of strong cation
resin.
o Water demineralization: Removal of cations & anions dissolved in
water. Usually carried by the two step technique in which two columns of
strongly acid cation exchanger in [H+] form & strongly basic anion
exchanger in [OH-] form are used in sequence.
o Neutralization: Cationic exchanger in [H+] can be used to neutralize
alkali hydroxide & anionic exchanger in [OH+] form to neutralize the
acidity.
o Separation of electrolytes from non-electrolytes.
o Separation of carbohydrates & their derivatives:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/techniquesandlaborotoryequipments-160428223750/85/Advanced-techniques-and-laborotory-equipments-for-biologists-22-320.jpg)