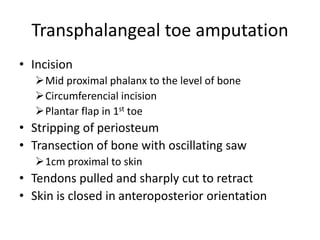
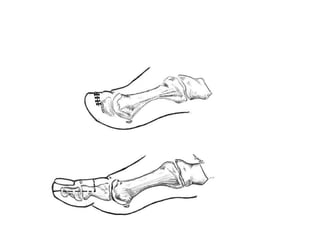
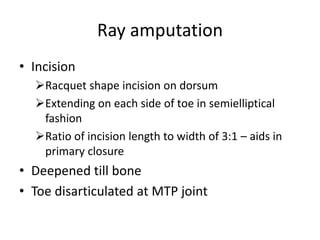
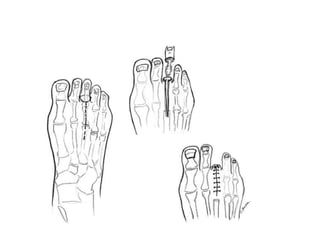
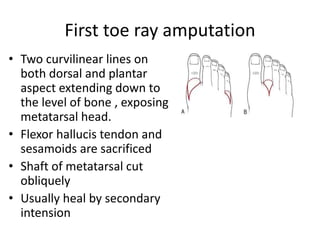
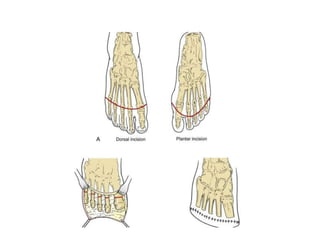
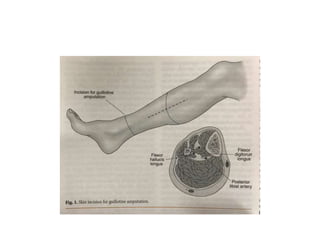
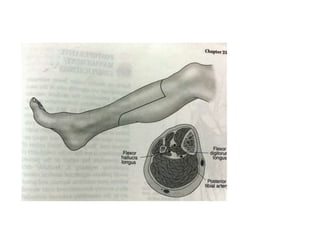
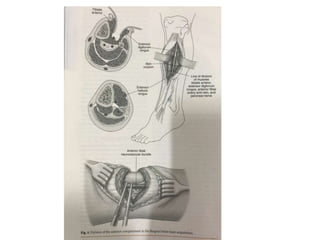
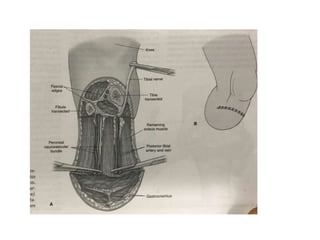
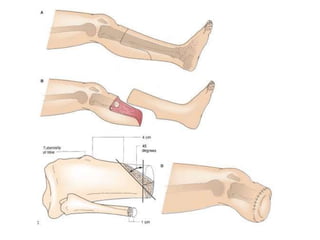
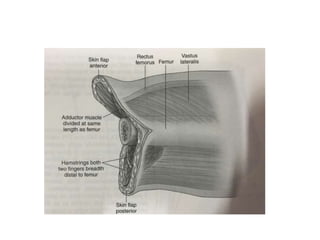
This document discusses different types and procedures for lower limb amputations. It describes minor amputations like transphalangeal toe amputation and transmetatarsal amputation, which aim to preserve foot function. Major amputations include below knee (BKA), above knee, and through knee disarticulation. The Burgess technique is described for BKA, involving a myocutaneous flap from gastrocnemius and soleus muscles. Above knee amputation involves a transverse incision and ligation of the superficial femoral artery and sciatic nerve division. Postoperative management focuses on wound healing and prosthetic fitting.