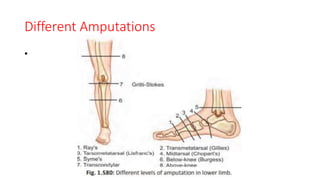
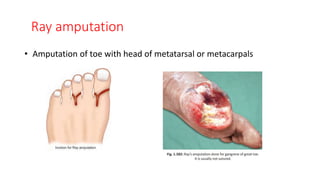
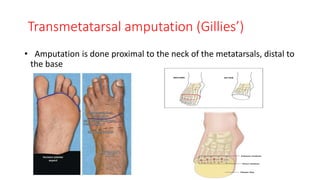
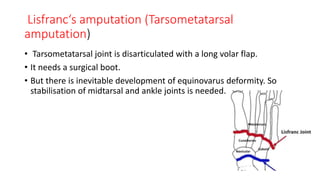
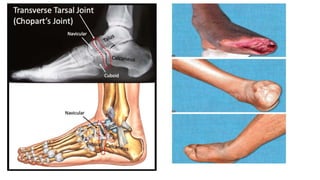
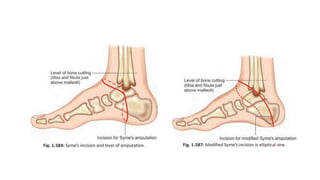
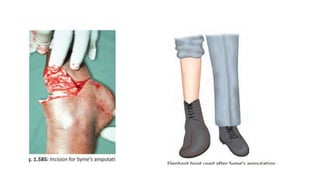
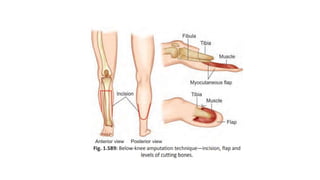
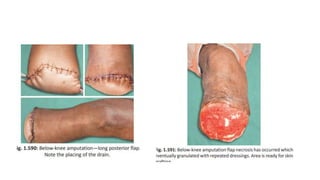
The document discusses various indications and principles for amputations, including medical conditions that necessitate the procedure, types of flaps, and ideal requirements for stumps. It details evaluation methods for patients needing amputation, surgical techniques, and different types of amputations, such as below-knee and above-knee. Additionally, it outlines the postoperative care, complications, and rehabilitation necessary for successful recovery and prosthetic use.