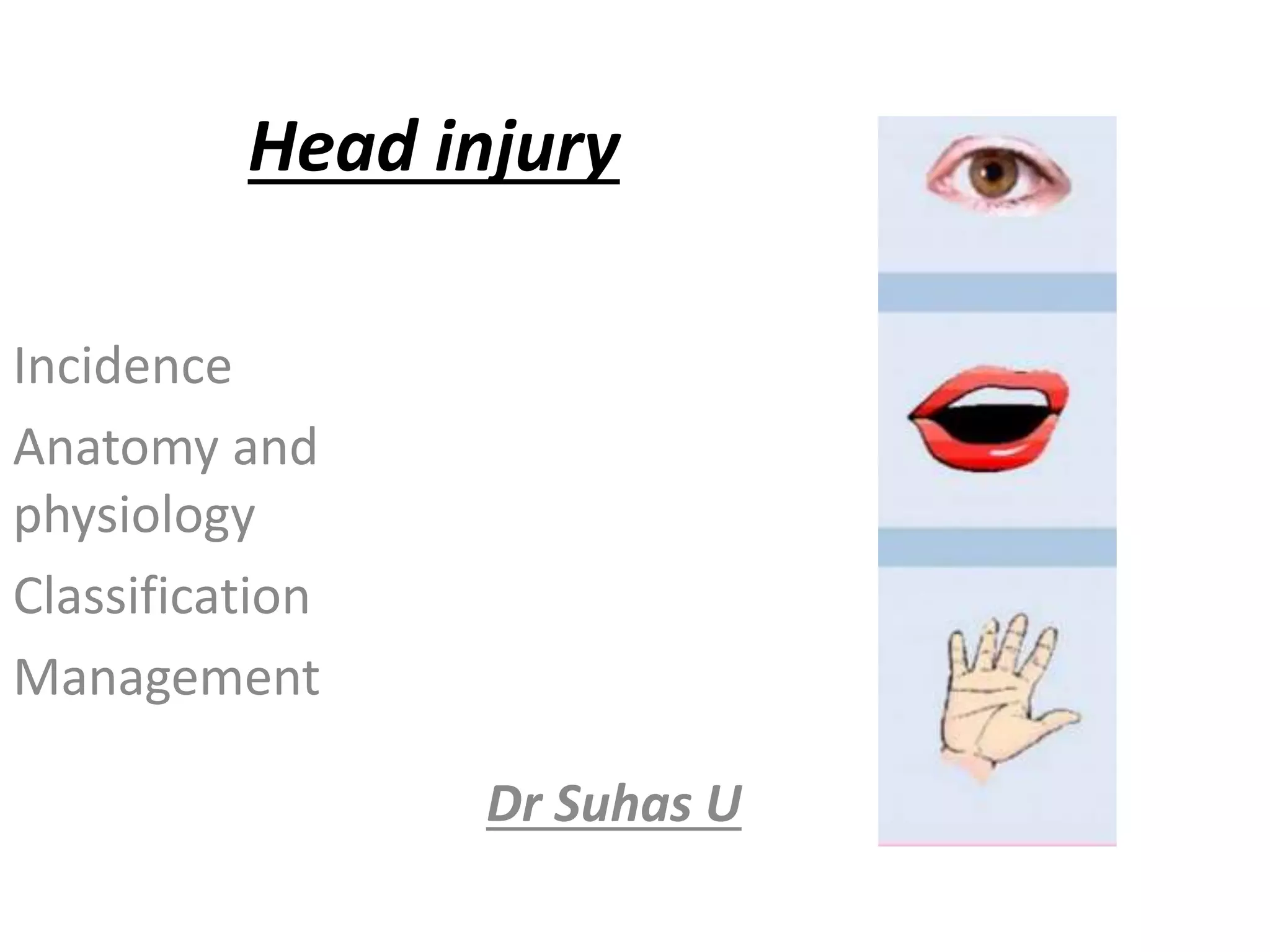
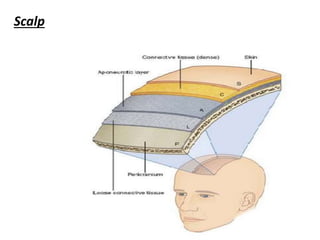
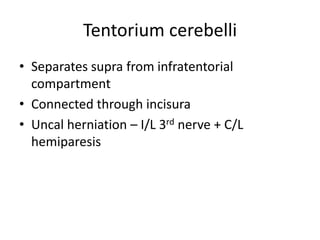
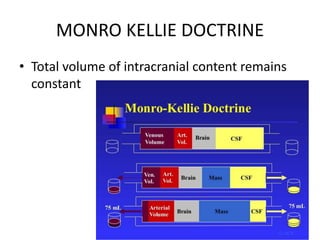
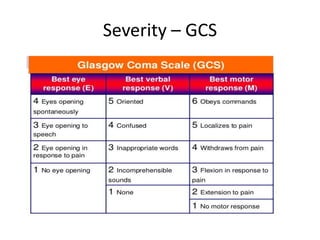
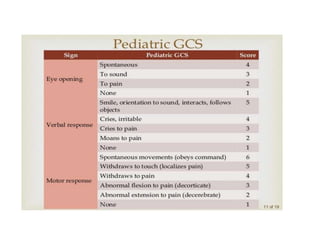
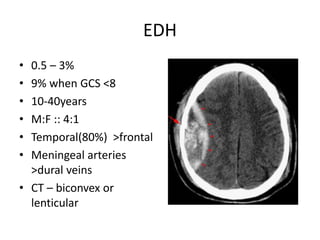
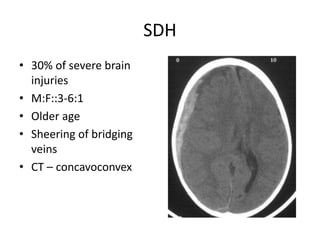
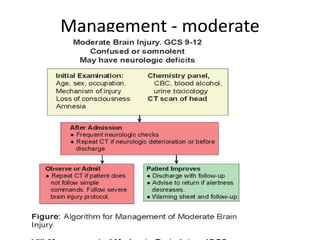
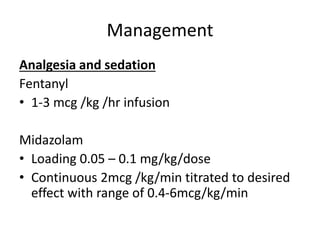
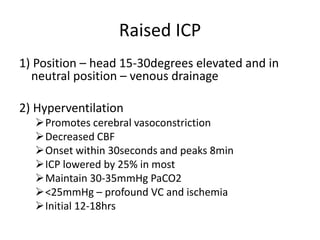
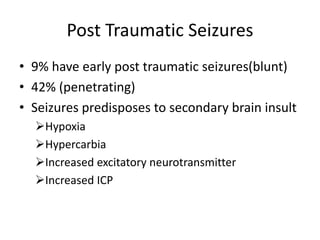
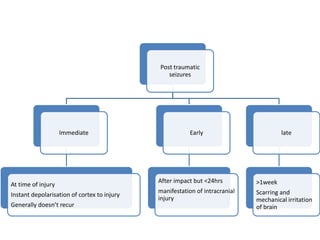
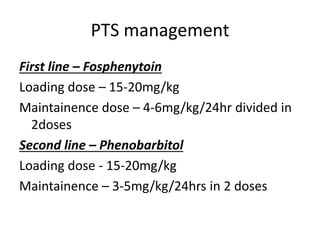
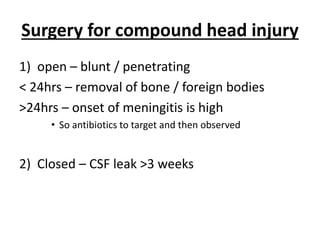
Head injury is a leading cause of death and disability worldwide. It can be classified based on mechanism, severity, and morphology of injuries. Management involves stabilizing the patient, treating increased intracranial pressure through ventilation, osmotherapy, or surgery to remove mass lesions. The goal is to prevent secondary brain injury while allowing for recovery from primary damage.