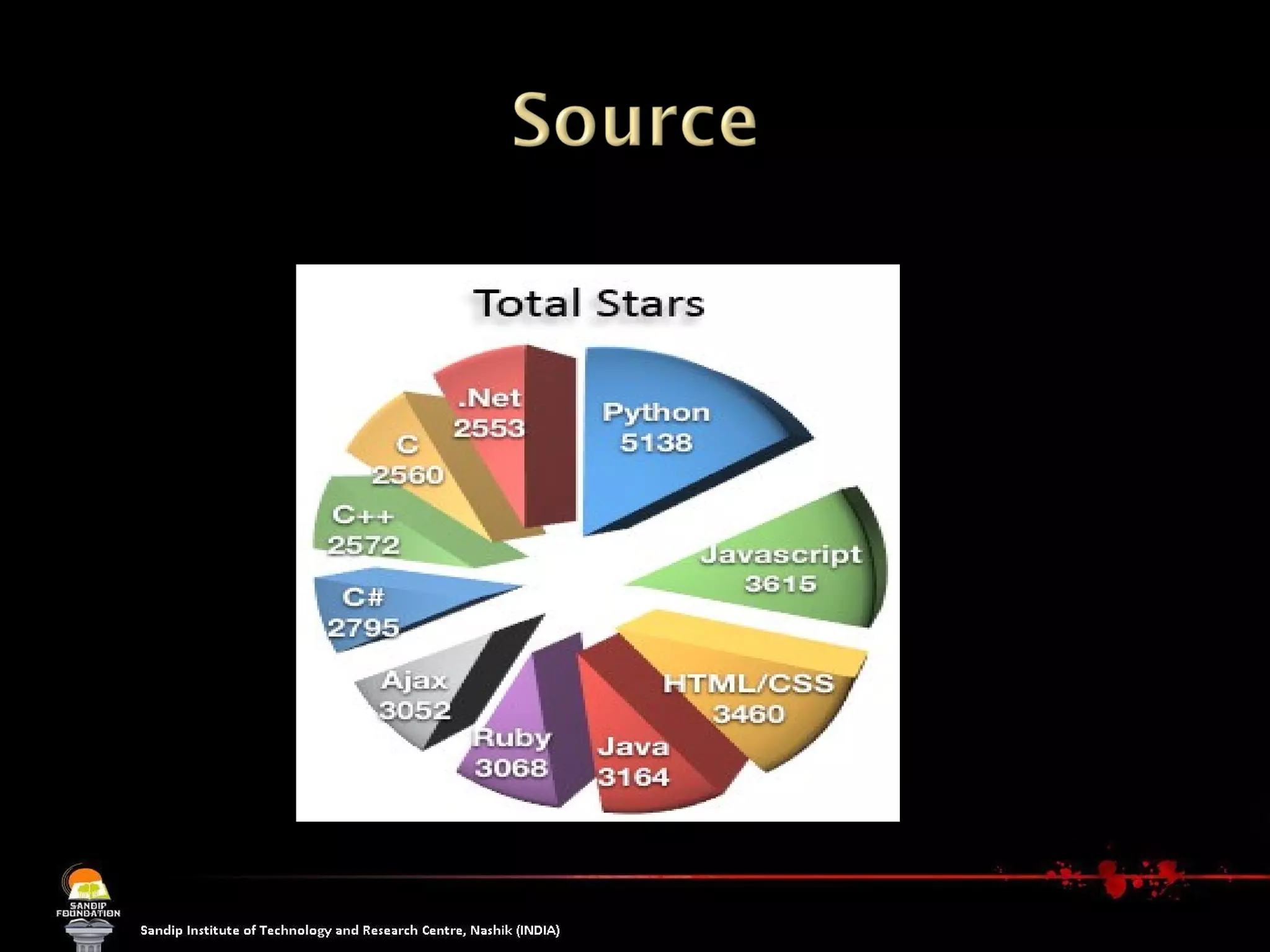
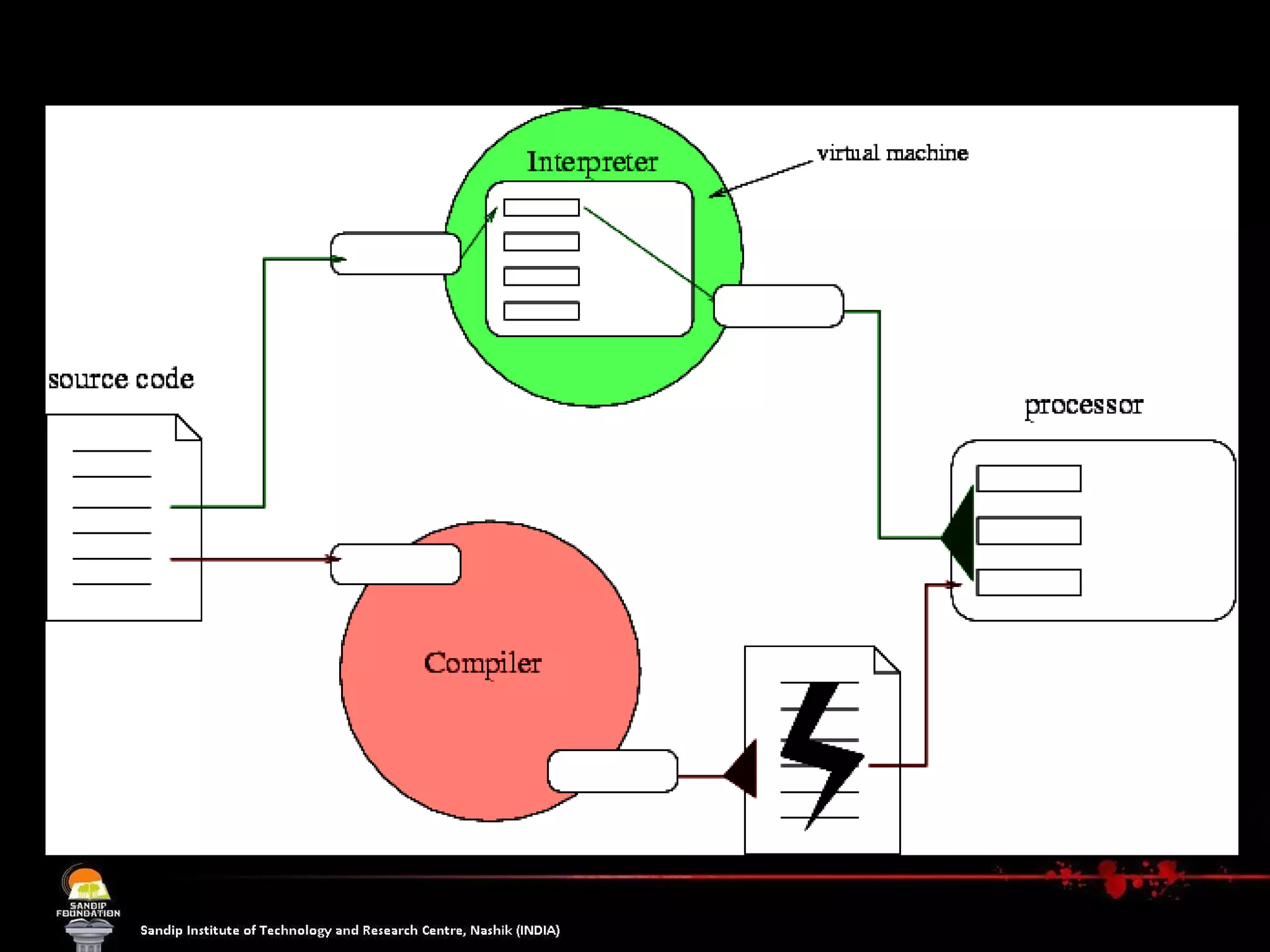
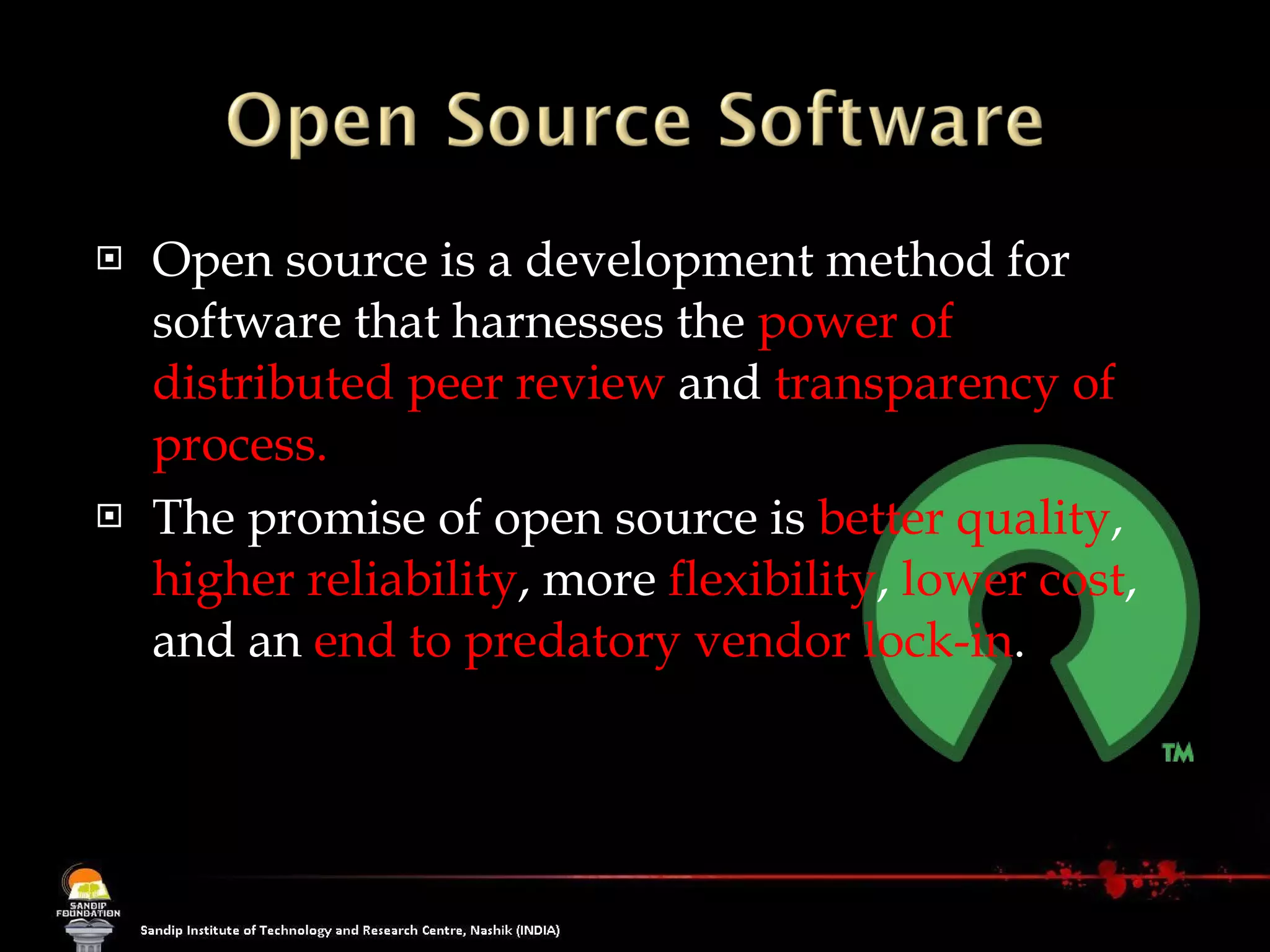
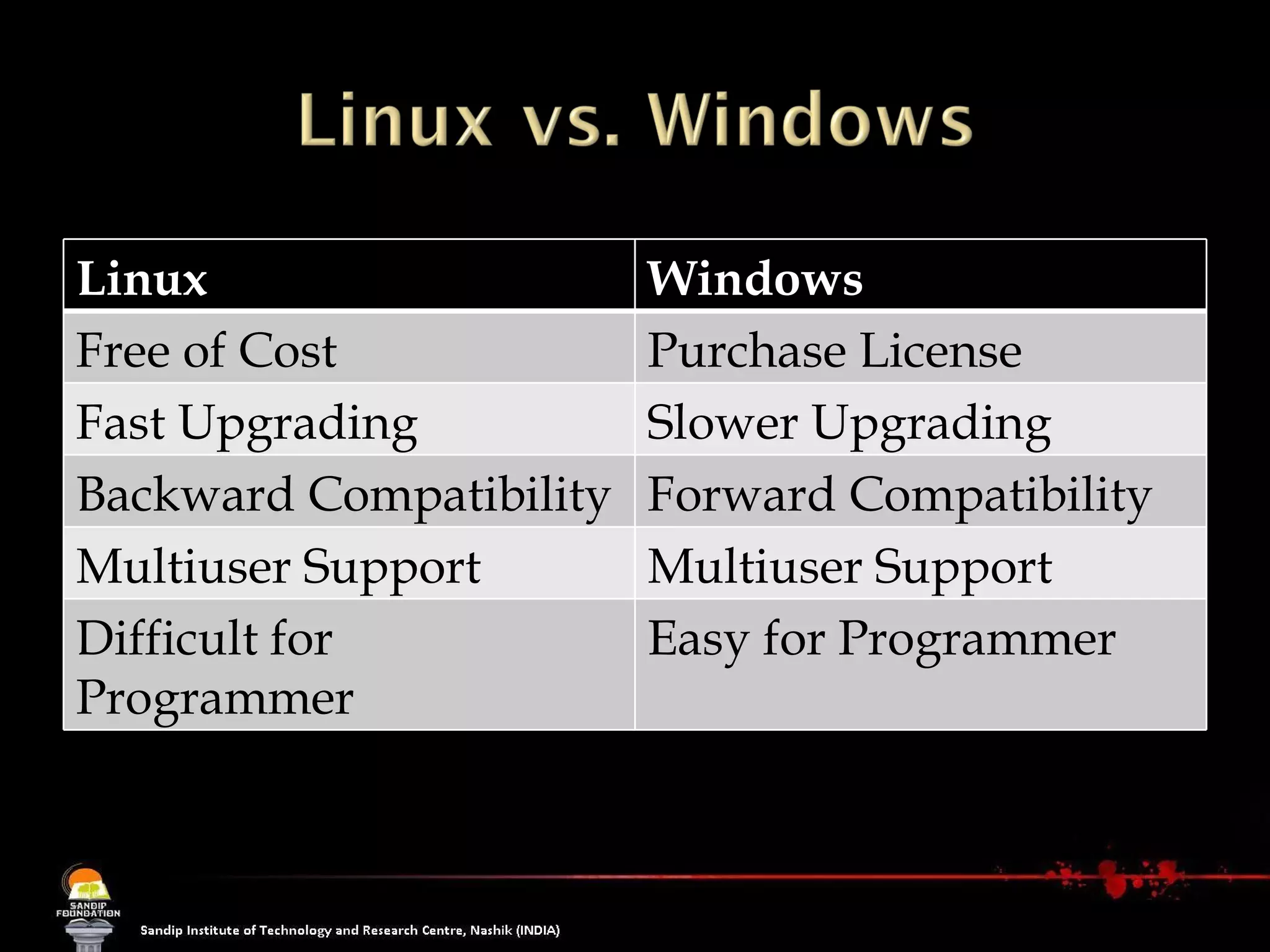
The document explains the concept of software, focusing on open source software, which allows users access to the source code for modification and distribution. It outlines the benefits of open source, such as better quality and flexibility, and differentiates between open source and free software, emphasizing that 'free' refers to freedom, not cost. Additionally, it lists prominent open source software examples and discusses the licensing aspects that define open source software.