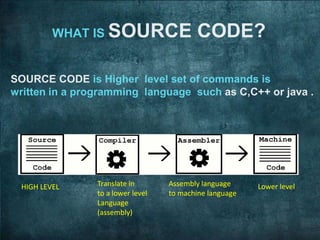
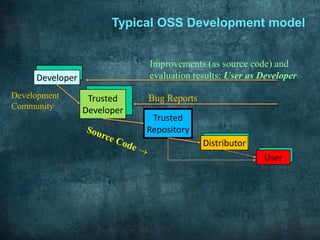
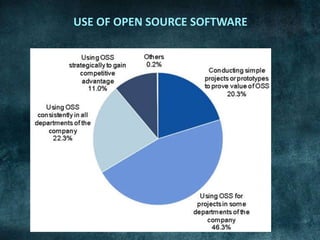
The document discusses a seminar on open source and free software. It defines open source software as software distributed with its source code. It provides a brief history of open source software including the development of UNIX, the founding of the Free Software Foundation, and the release of Linux. It also discusses the key freedoms of free and open source software including the freedom to use, modify, and distribute the software. Examples of widely used open source software are also provided.