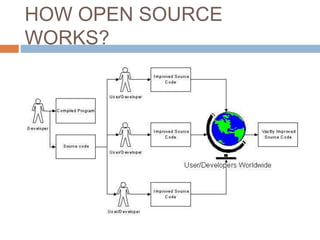
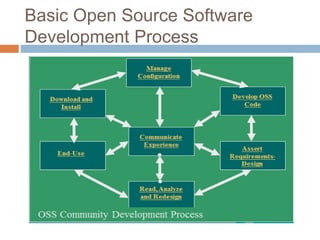
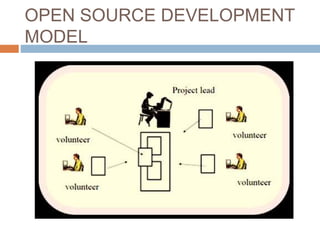
Open source software development refers to software with source code that is made available to the public with a license that allows users and developers to study, change, and improve the design of the software. The document outlines the history and rise of open source development, comparing it to the traditional closed source model. It describes how open source works through a community-based development process and lists some key advantages like customizability and lower costs compared to proprietary software. Examples of popular open source applications, operating systems, and programming languages are provided.