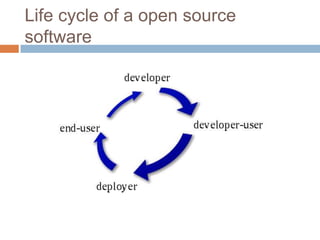
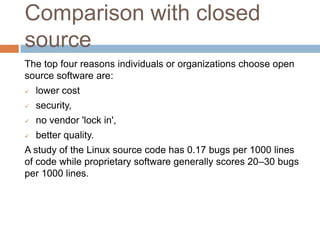
Open source software refers to computer programs where the source code is made available to the public with an open source license that allows users to study, change, and improve the design of the software. Open source software is typically developed collaboratively by a community of programmers who improve upon the code and share their changes. It is often funded through universities, personal projects, consulting work, proprietary add-ons, or donations. Some benefits of open source software include lower costs, greater security, avoidance of vendor lock-in, and higher quality code. Widely used examples include the Apache HTTP Server, Mozilla Firefox, Linux, Android, MySQL, Java Development Kit, Eclipse, and content management systems like Wikipedia.