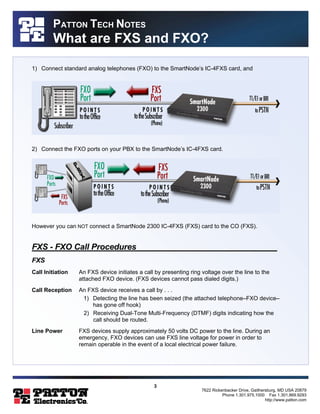
FXS and FXO are interface types used in analog telephony. FXS interfaces provide services like dial tone and battery current to subscriber devices, while FXO interfaces provide on/off hook detection to the telephone network. An FXS port connects to an FXO port for calls to work properly. The document discusses how FXS and FXO ports are used in devices like phones, PBXs, and VoIP gateways to connect analog lines to each other and to the telephone network.