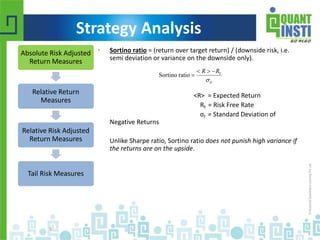
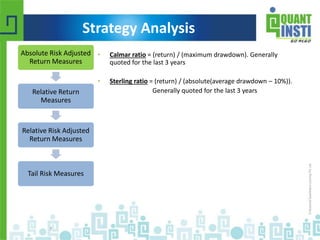
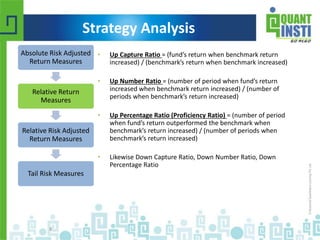
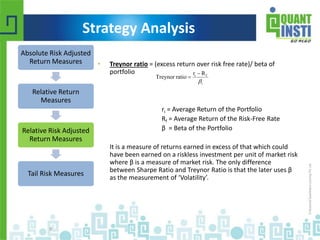
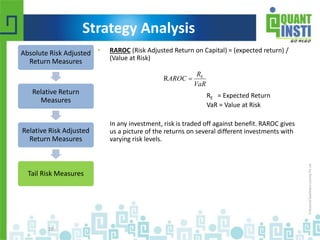
The document discusses various financial performance evaluation metrics, including the Sharpe, Sortino, Calmar, and Treynor ratios, highlighting their formulas, uses, and limitations. It emphasizes the importance of understanding absolute and relative risk-adjusted return measures, along with methods for trade sizing and cautions against certain trading strategies that assume dependencies between trades. The document also introduces Kelly's Criterion for optimal portfolio management focused on long-term capital growth.