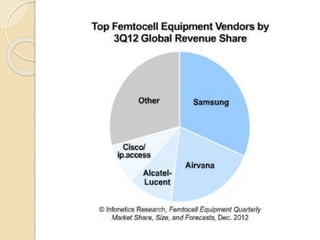
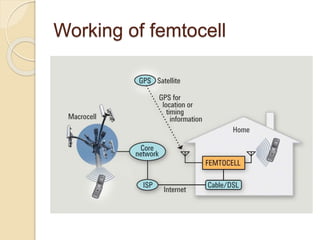
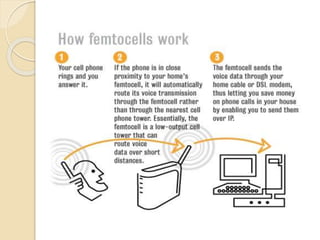
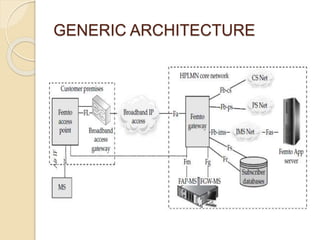
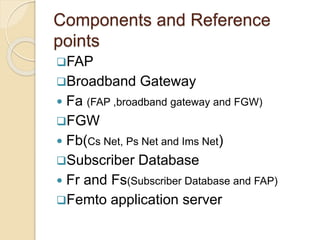
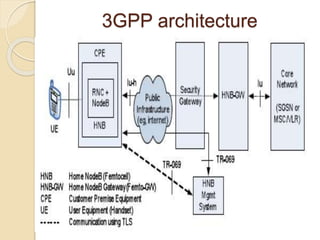
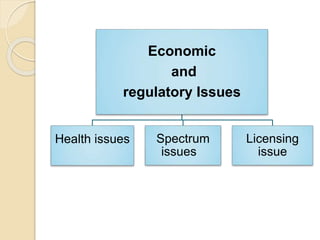
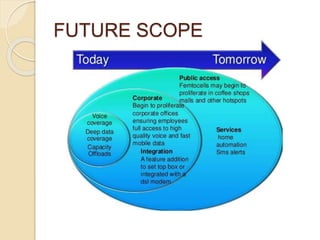
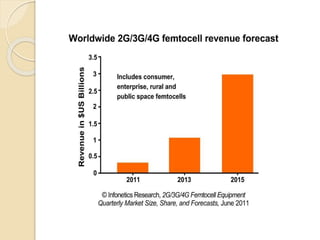
This document discusses femtocells, which are small, low-power cellular base stations that improve indoor wireless coverage and capacity. It outlines problems with existing mobile technologies like low indoor signal strength. Femtocells have a range of 10-50 meters, are installed in homes, and connect to a broadband internet connection. The document describes femtocell components, architecture, benefits for cellular users and networks in terms of improved coverage, capacity and offloading data traffic. It also covers technical and economic challenges and concludes that femtocells can alleviate pressure on macrocell networks and help accelerate existing mobile technologies.