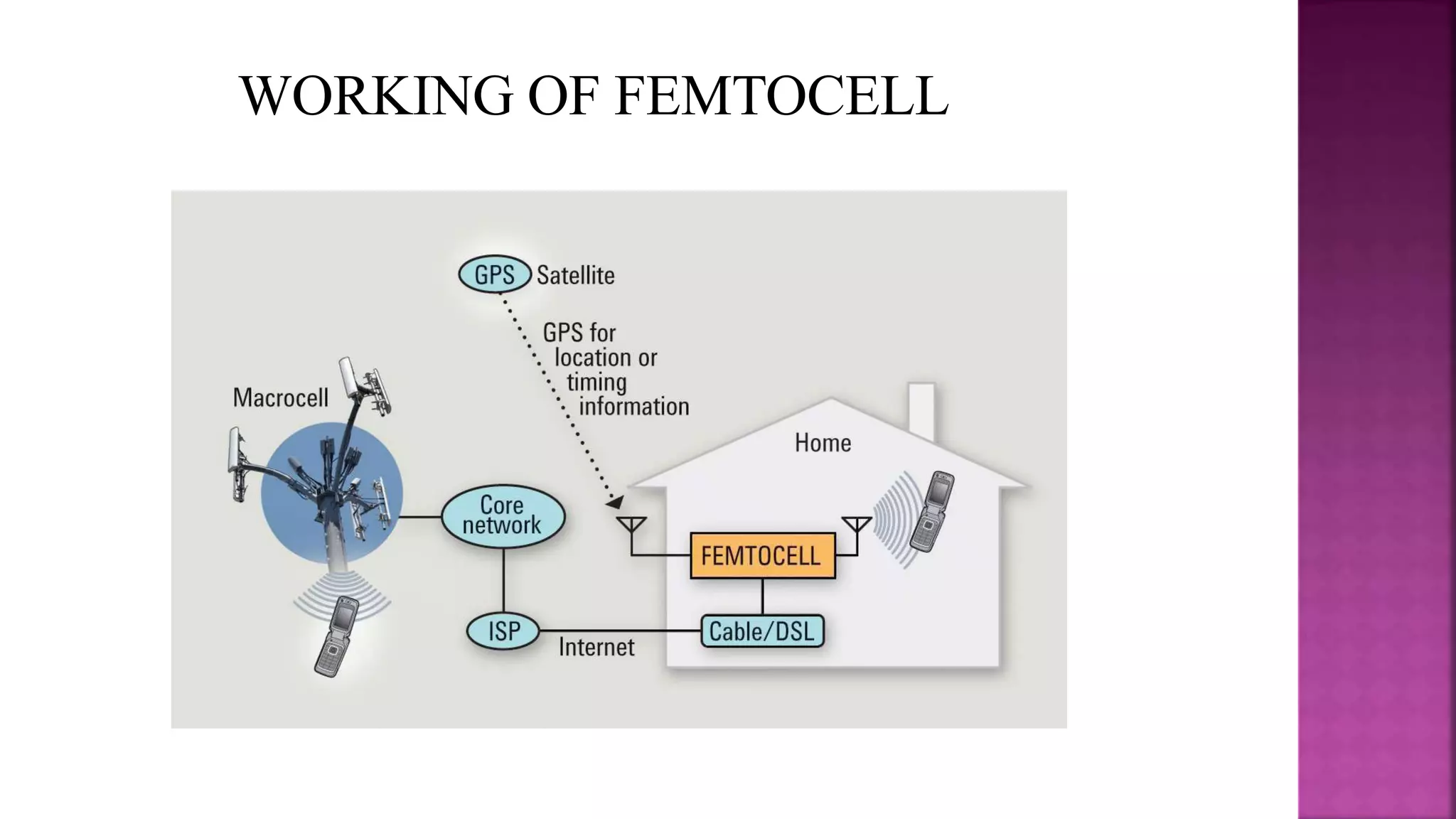
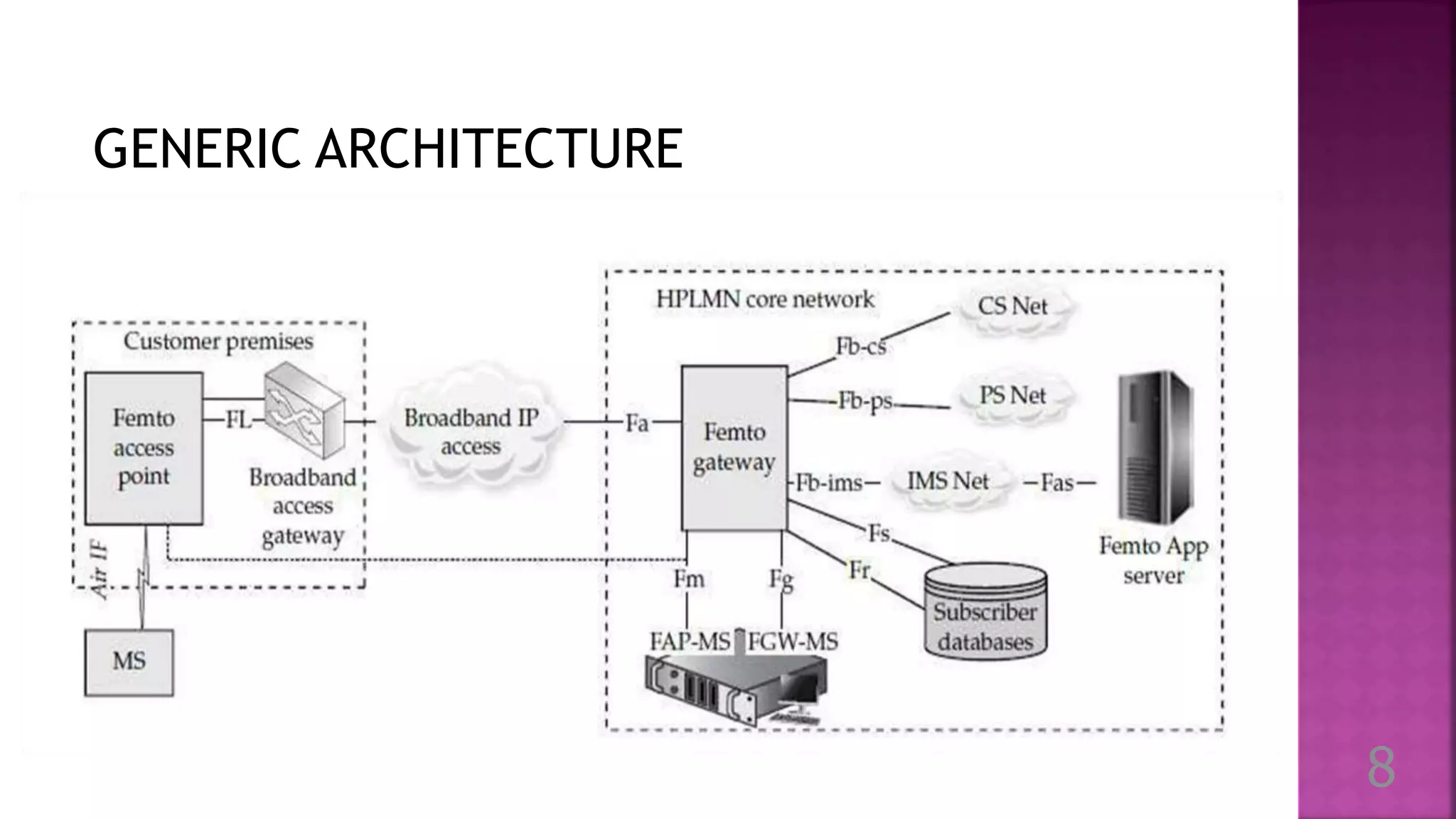
Femtocells are small cellular base stations that connect to a service provider's network via broadband to improve indoor cellular coverage. They allow service providers to extend network coverage inside homes and businesses without expensive cellular towers. Femtocells route mobile phone traffic through the IP network to decrease costs for service providers. They typically support 2-5 mobile phones in residential settings. Femtocells were first conceptualized in 2002 and gained momentum in 2004 as companies investigated their potential. The Femto Forum was established in 2007 to promote femtocell adoption. Femtocells provide benefits like improved coverage and capacity for network providers as well as enhanced service, rates, and satisfaction for subscribers.