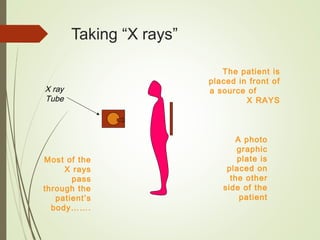
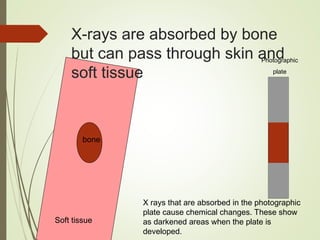
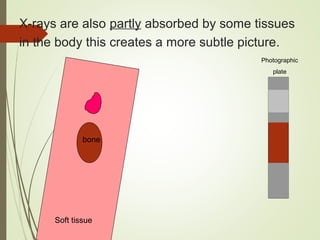
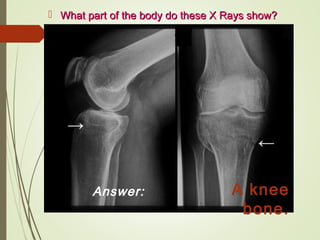
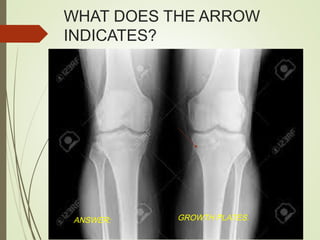
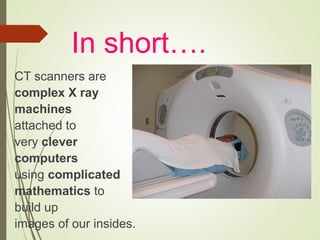
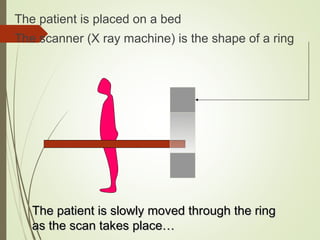
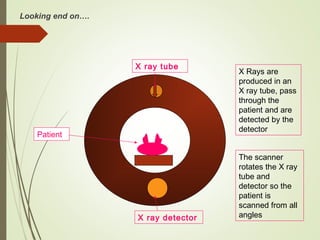
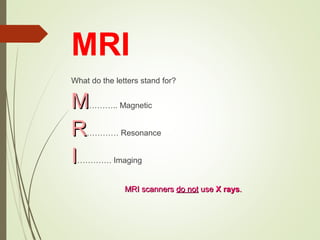
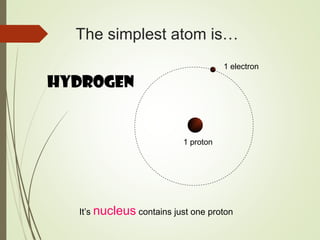
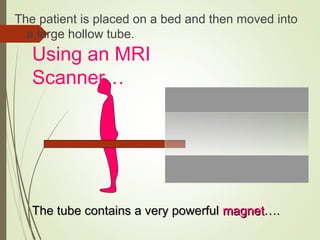
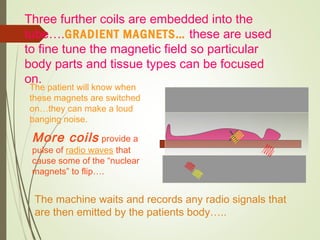
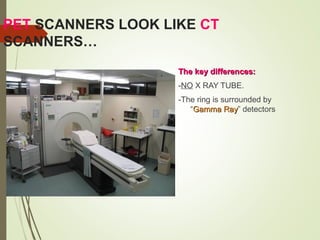
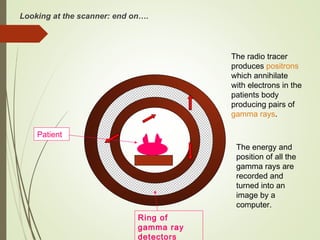
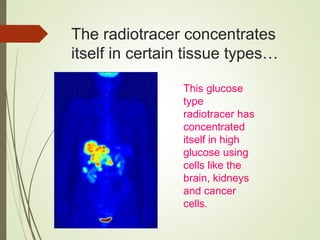
The document discusses various medical imaging techniques, including X-rays, CT scans, MRI, PET scans, and MEG, explaining how each technology works and its applications. It highlights the specific use cases, safety considerations, and limitations of these imaging methods, especially in diagnosing conditions related to the brain, heart, and cancer. The document also touches upon the fundamental physics behind these technologies, such as the role of different particles and magnetic fields in imaging.