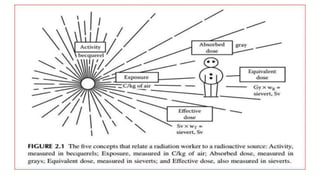
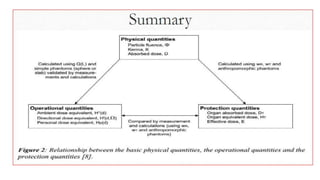
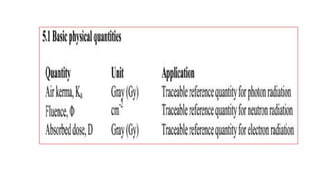
This document discusses various radiation quantities and units used in medical physics. It defines units like becquerel (Bq), gray (Gy), sievert (Sv), and rem (Roentgen equivalent man) used to measure activity, absorbed dose, equivalent dose, and effective dose. It also discusses concepts like half-life, decay constant, kerma, exposure, and dose conversion factors. International organizations like ICRP and ICRU provide recommendations on radiation quantities, units, and safety limits.