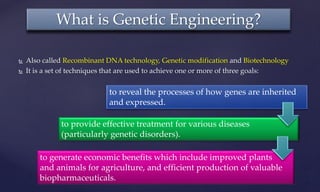
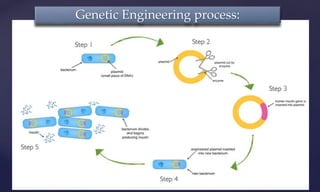
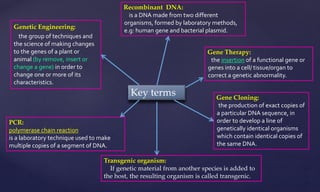
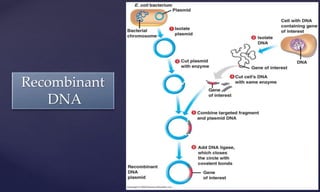
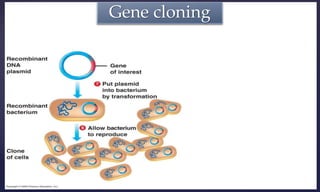
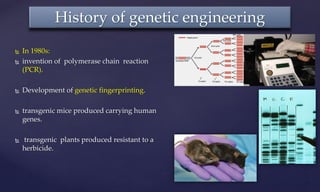
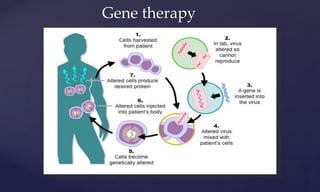
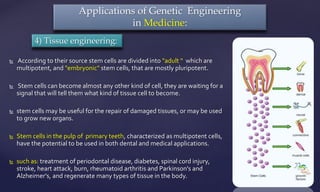
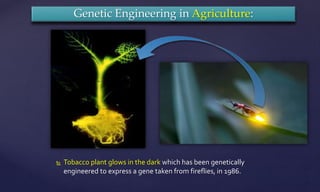
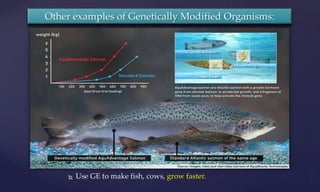
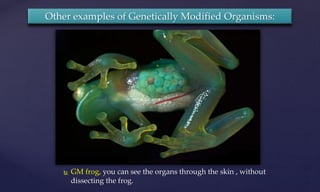
Genetic engineering is the process of manipulating genes to introduce desirable traits. It can be used to produce insulin and vaccines, treat genetic disorders through gene therapy or somatic cell gene therapy, and engineer plants and animals. Some applications include producing human growth hormone to treat dwarfism, making human albumin and anti-hemophilic factors, and developing GM crops with traits like pest resistance. However, critics argue that genetic engineering poses environmental and ethical risks by interfering with nature and potentially having irreversible effects.