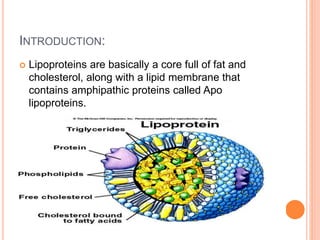
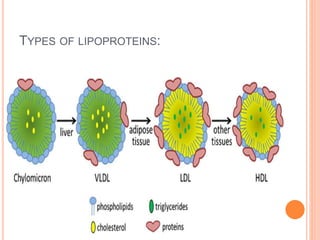
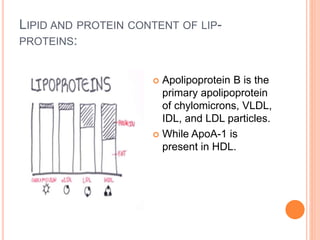
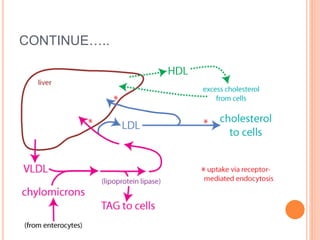
Lipoproteins are particles that contain a core of cholesterol and triglycerides surrounded by a membrane containing apolipoproteins. There are several main types of lipoproteins: chylomicrons and VLDL deliver triglycerides to cells, LDL delivers cholesterol to cells, and HDL transports excess cholesterol from cells back to the liver. The primary apolipoproteins are apoB in chylomicrons, VLDL, IDL, and LDL, and apoA1 in HDL.