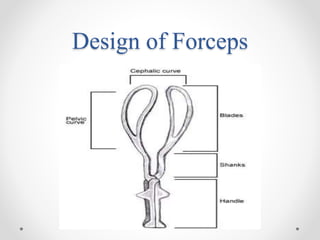
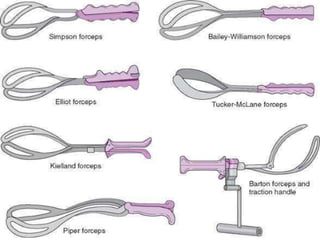
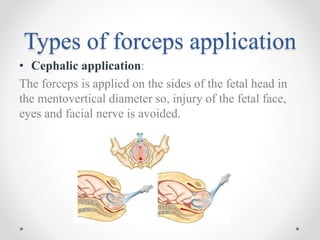
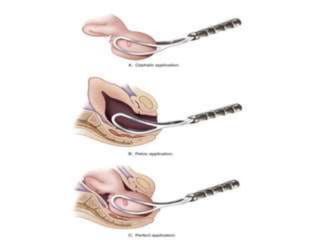
This document outlines the indications, application, and management of forceps delivery, a procedure used to assist in the extraction of the fetal head during childbirth. It discusses the types of forceps, pre-requisites for their application, potential complications for both the mother and fetus, and contraindications for use. Key factors for successful forceps delivery include favorable maternal positioning, adequate pelvic outlet, and the presence of uterine contractions.