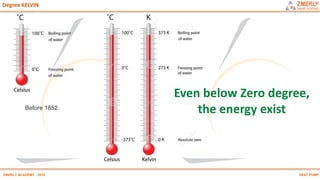
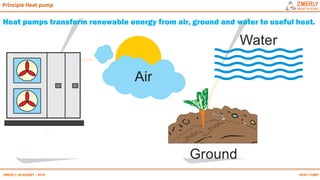
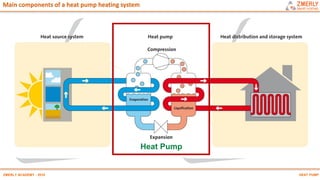
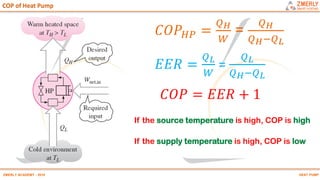
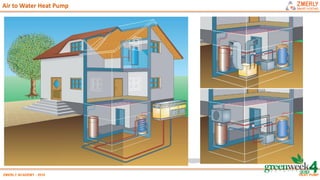
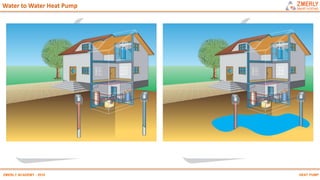
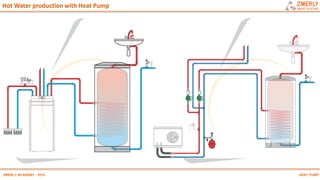
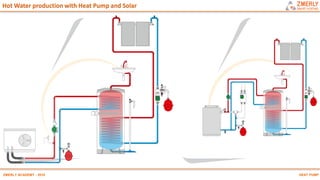
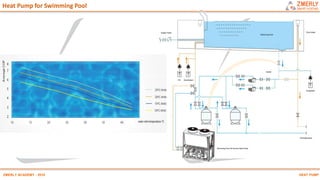
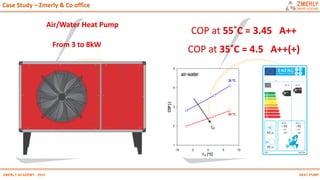
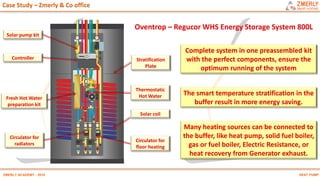
Heat pumps have existed since the 1850s and work by transferring heat from outdoor or underground sources into buildings for heating. They have four main components: an outdoor heat exchanger, compressor, indoor heat exchanger, and expansion device. Common heat sources are air, water, or ground. Heat pumps can provide space heating, cooling, and water heating. They are more efficient than resistance heating because they take advantage of renewable heat sources and can achieve coefficients of performance (COPs) of 3-6.