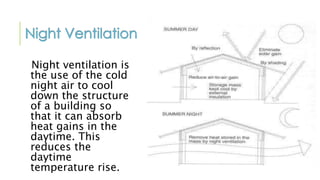
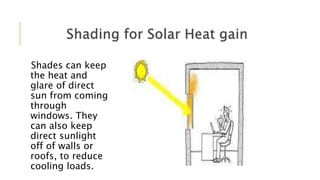
This document discusses passive solar design and passive cooling techniques. It describes how passive solar design uses windows, walls and floors to collect, store and distribute solar heat in winter and reject it in summer. The key elements are proper window placement and size, thermal insulation, thermal mass and shading. Passive cooling techniques like natural ventilation can provide indoor comfort with zero energy use through strategies like stack ventilation, cross ventilation and night ventilation.