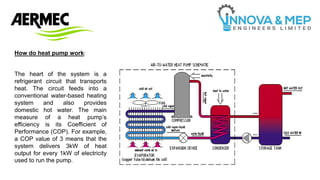
A heat pump is a device that transfers heat from one place to another using a refrigerant and compressor. It extracts heat from outside sources and uses it to heat water or indoor spaces. Heat pumps can be 3-4 times more energy efficient than electric heaters or furnaces. They are widely used for heating, cooling, and hot water in buildings like hospitals, hotels, and industrial facilities. Heat pumps work by circulating refrigerant through a circuit that transports heat and feeds into a water-based heating system. Their efficiency is measured by their coefficient of performance, with higher COP values indicating more efficient heat transfer. Heat pumps provide advantages like significant energy savings, long lifespan, safety, environmental friendliness, and easy installation and maintenance.