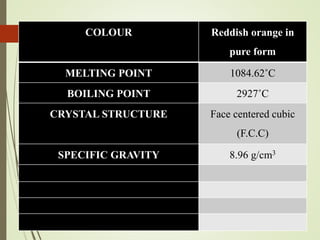
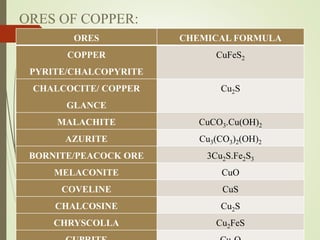
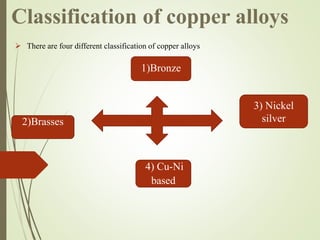
This document discusses copper and copper alloys, including their properties, extraction, production, uses, and applications. It covers the classification of copper alloys into categories like brasses, bronzes, and cupronickels. The key extraction process described is pyrometallurgy to extract copper from sulfide ores via concentration, roasting, smelting, and bessemerization. Finally, the major applications of copper and its alloys are in electrical systems, construction, transport, medicine, kitchens, and common items like coins.