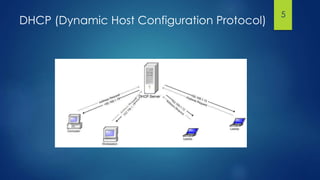
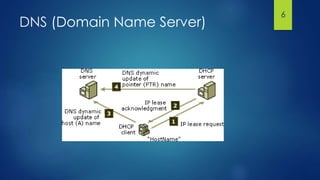
Zero Configuration Networking (Zeroconf) is a set of technologies that allow devices to automatically configure network settings and discover services without requiring any centralized servers. It uses IPv4 link-local addressing, Multicast DNS for name resolution, and DNS Service Discovery to find and list services on the network. Popular implementations of Zeroconf include Apple Bonjour, Avahi, and Mono.Zeroconf.