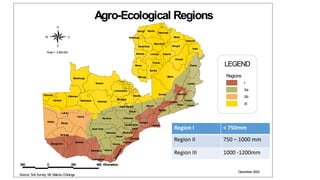
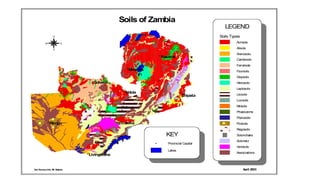
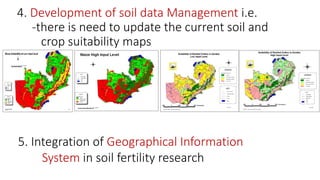
The document outlines the management of soils in Zambia, highlighting the challenges of soil erosion, degradation, and soil acidity, which affects agricultural productivity. It emphasizes the importance of agriculture as a major employment source and provides recommended priorities for sustainable soil management practices. Key priorities include enhancing soil fertility, developing site-specific fertilizer recommendations, and promoting irrigation and diversified agricultural production among small-scale farmers.