Embed presentation
Download to read offline



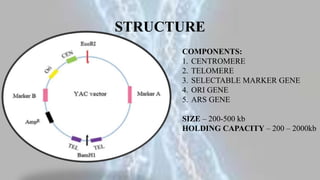
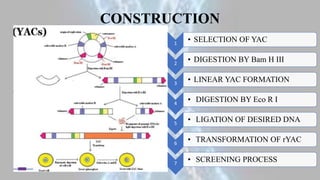


Yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs) are engineered chromosomes derived from yeast DNA that are used to clone and propagate large DNA sequences in yeast cells. YACs contain components like a centromere, telomeres, selectable marker genes, origin of replication genes, and autonomously replicating sequence genes. They can hold between 200-2000kb of DNA and are constructed by selecting a YAC, digesting it with restriction enzymes, ligating the desired DNA, and transforming the resulting recombinant YAC into yeast cells. YACs have advantages like their ability to accommodate large DNA fragments and replicate like natural chromosomes, but also have disadvantages such as instability and lower yields compared to bacterial artificial chromosomes.






