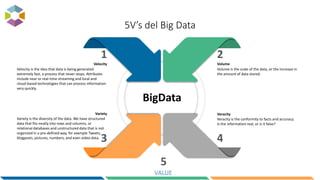
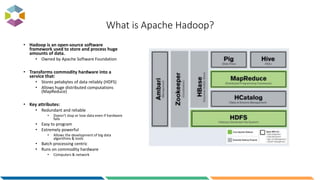
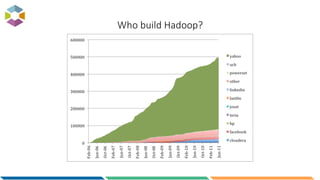
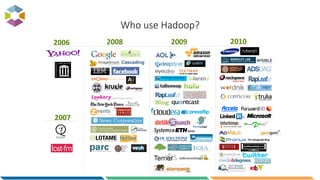
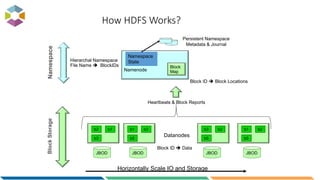
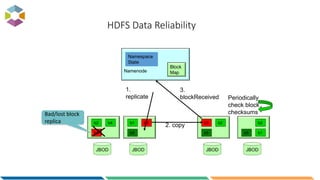
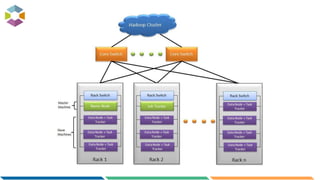
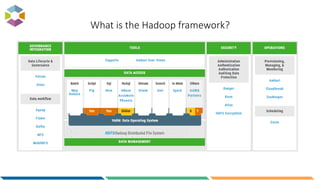
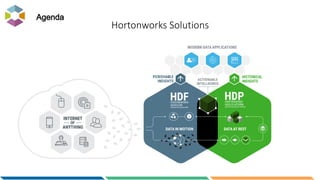
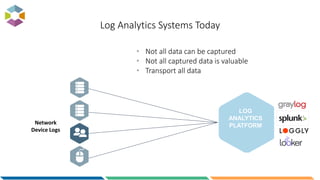
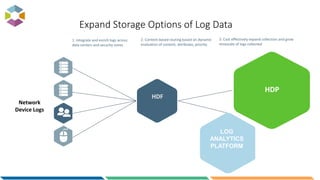
The document provides an overview of big data, defining it as large, dynamic, and varied data requiring innovative technologies for processing and analysis. Key aspects include the 5 V's of big data: variety, velocity, veracity, volume, and value, along with an introduction to Hadoop as a key technology for big data storage and processing. It also discusses the importance of log analytics and the role of Hadoop distributions like Hortonworks in managing and analyzing vast data sets.