This document provides an overview of big data, including:
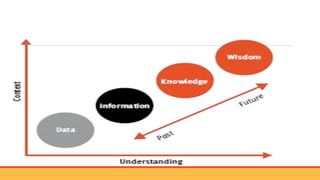
- Defining big data as large datasets that can reveal patterns when analyzed computationally.
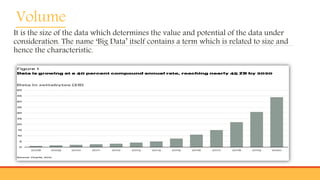
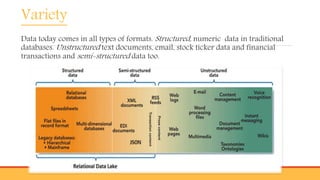
- Describing the 3 Vs of big data - volume, velocity, and variety. It discusses how big data comes from many sources and is characterized by its large size and fast generation.
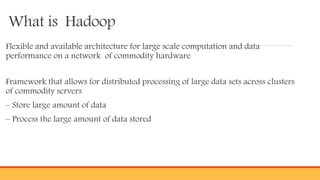
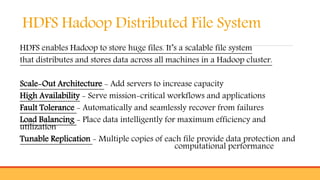
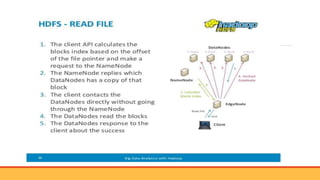
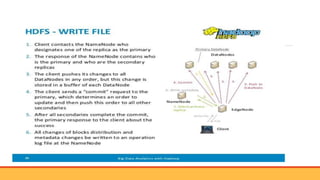
- Introducing Hadoop as an open-source software framework for distributed storage and processing of big data across clusters of commodity servers. Key Hadoop components HDFS and MapReduce are outlined.